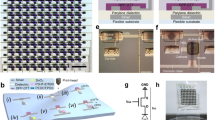
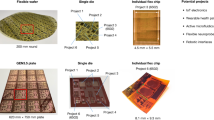
Abstract
At present, flexible displays are an important focus of research1,2,3. Further development of large, flexible displays requires a cost-effective manufacturing process for the active-matrix backplane, which contains one transistor per pixel. One way to further reduce costs is to integrate (part of) the display drive circuitry, such as row shift registers, directly on the display substrate. Here, we demonstrate flexible active-matrix monochrome electrophoretic displays based on solution-processed organic transistors on 25-μm-thick polyimide substrates. The displays can be bent to a radius of 1 cm without significant loss in performance. Using the same process flow we prepared row shift registers. With 1,888 transistors, these are the largest organic integrated circuits reported to date. More importantly, the operating frequency of 5 kHz is sufficiently high to allow integration with the display operating at video speed. This work therefore represents a major step towards 'system-on-plastic'.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Young, N.D. et al. Thin film transistor and diode addressed AMLCDs on polymer substrates. J. SID 5/3, 275–281 (1997).
Gustafsson, G. et al. Flexible light-emitting diodes made from soluble conducting polymers. Nature 357, 477–479 (1992).
Chen, Y. et al. Flexible active-matrix electronic ink display. Nature 423, 136 (2003).
Voss, D. Cheap and cheerful circuits. Nature 407, 442–444 (2000).
Brown, A.R., Pomp, A. Hart, C.M. & De Leeuw, D.M. Logic gates made from polymer transistors and their use in ring oscillators. Science 270, 972–974 (1995).
Kane, M.G. et al. Analog and digital circuits using organic thin-film transistors on polyester substrates. IEEE Electr. Dev. Lett. 21, 534–536 (2000).
Crone, B. et al. Large-scale complementary integrated circuits based on organic transistors. Nature 403, 521–523 (2000).
Drury, C.J., Mutsaers, C.M.J., Hart, C.M., Matters M. & De Leeuw D.M. Low-cost all-polymer integrated circuits. Appl. Phys. Lett. 73, 108–110 (1998).
Gelinck, G.H., Geuns, T.C.T. & De Leeuw, D.M. High-performance all-polymer integrated circuits. Appl. Phys. Lett. 77, 1487–1489 (2000).
Touwslager, F.J., Willard, N.P. & De Leeuw, D.M. I-line lithography of poly-(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) electrodes and application in all-polymer integrated circuits. Appl. Phys. Lett. 81, 4556–4558 (2002).
Sirringhaus, H., Tessler, N. & Friend, R.H. Integrated optoelectronic devices based on conjugated polymers. Science 280, 1741–1744 (1998).
Dodabalapur, A. et al. Organic smart pixels. Appl. Phys. Lett. 73, 142–144 (1998).
Rogers, J.A. et al. Paper-like electronic displays: Large-area rubber-stamped plastic sheets of electronics and microencapsulated electrophoretic inks. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 98, 4835–4840 (2001).
Mach, P., Rodriquez, S.J., Nortrup, R., Wiltzius, P. & Rogers, J.A. Monolithically integrated flexible display of polymer-dispersed liquid crystal driven by rubber-stamped organic thin-film transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 78, 3592–3594 (2001).
Kane, M.G. et al. AMLCDs using organic thin-film transistors on polyester substrates. SID Digest 57–59 (2001).
Dimitrakopoulos, C.D. & Malenfant, P.R.L. Organic thin film transistors for large area electronics. Adv. Mater. 14, 99–117 (2002).
Huitema, H.E.A. et al. Plastic transistors in active-matrix displays. Nature 414, 599 (2001).
Sirringhaus H. et al. Active matrix displays made with printed polymer thin film transistors. SID Digest 1084–1086 (2003).
Huitema, H.E.A. et al. Plastic transistors used as pixel switches in AMLCD. J. SID 10/3, 195–202 (2002).
Brown, A.R., Jarrett, C.P., De Leeuw, D.M. & Matters, M. Field-effect transistors made from solution-processed organic semiconductors. Synth. Met. 88, 37–55 (1997).
Meijer, E.J. et al. Switch-on voltage in disordered organic field-effect transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 3838–3840 (2002).
Zilker, S.J., Detcheverry, C., Cantatore, E. & De Leeuw, D.M. Bias stress in organic thin-film transistors and logic gates. Appl. Phys. Lett. 79, 1124–1126 (2001).
Knipp, D., Street, R.A., Völkel, A. & Ho, J. Pentacene thin film transistors on inorganic dielectrics: Morphology, structural properties and electronic transport. J. Appl. Phys. 93, 347–355 (2003).
Salleo, A. & Street, R.A. Light induced bias stress reversal in polyfluorene thin-film transistors. J. Appl. Phys. 94, 471–479 (2003).
Qiu, Y. et al. H2O effect on the stability of organic thin-film field-effect transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 1644–1646 (2003).
Comiskey, B., Albert, J.D., Yoshizawa, H. & Jacobsen, J. An electrophoretic ink for all-printed reflective electronic displays. Nature 394, 253–255 (1998).
Fix, W. et al. in Proc. 23rd European Solid-State Device Research Conference (eds Baccarani, G., Gnani, E. & Rudan, M.) 527–529 (Univ. Bologna, Firenze, Italy, 2002).
Klauk, H., Halik, M., Zschieschang, U., Schmid, G. & Radlik, W. Polymer gate dielectric pentacene TFTs and circuits on flexible substrates. IEDM Technical Digest 557–560 (2002).
Herwig, P.T. & Müllen, K. A soluble pentacene precursor: synthesis, solid-state conversion into pentacene and application in a field-effect transistor. Adv. Mater. 11, 480–483 (1999).
Kymissis, I., Dimtrakopolous, C.D. & Purushothaman, S. Patterning pentacene organic thin film transistors. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 20, 956–959 (2002).
Acknowledgements
We thank E ink Corporation, Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA for supplying electrophoretic (E ink) frontpanel laminates.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gelinck, G., Huitema, H., van Veenendaal, E. et al. Flexible active-matrix displays and shift registers based on solution-processed organic transistors. Nature Mater 3, 106–110 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1061
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1061
This article is cited by
-
Forming free bipolar resistive switching in SiOx-based flexible MIM devices
Bulletin of Materials Science (2024)
-
Research progress of filled-type high-thermal-conductivity flexible polyimide composites: a review
Journal of Materials Science (2023)
-
A printed proximity-sensing surface based on organic pyroelectric sensors and organic thin-film transistor electronics
Nature Electronics (2022)
-
Topological design of strain sensing nanocomposites
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Advances in flexible organic field-effect transistors and their applications for flexible electronics
npj Flexible Electronics (2022)