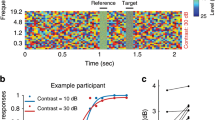
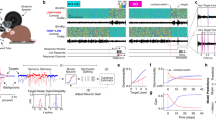
Abstract
Some neurons in auditory cortex respond to recent stimulus history by adapting their response functions to track stimulus statistics directly, as might be expected. In contrast, some neurons respond to loud sounds by adjusting their response functions away from high intensities and consequently remain sensitive to softer sounds. In marmoset monkey auditory cortex, the latter type of adaptation appears to exist only in neurons tuned to stimulus intensity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Galambos, R. & Davis, H. J. Neurophysiol. 6, 39–57 (1943).
Kiang, N.Y.S., Watanabe, T., Thomas, E.C. & Clark, L.F. Discharge Patterns of Single Fibers in the Cat's Auditory Nerve (The MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts, 1965).
Rose, J.E., Galambos, R. & Hughes, J.R. Bull. Johns Hopkins Hosp. 104, 211–251 (1959).
Rose, J.E., Greenwood, D.D., Goldberg, J.M. & Hind, J.E. J. Neurophysiol. 26, 295–320 (1963).
Galambos, R., Rose, J.E., Bromiley, R.B. & Hughes, J.R. J. Neurophysiol. 15, 359–380 (1952).
Erulkar, S.D., Rose, J.E. & Davies, P.W. Bull. Johns Hopkins Hosp. 99, 55–86 (1956).
Pfingst, B.E. & O'Connor, T.A. J. Neurophysiol. 45, 16–34 (1981).
Sadagopan, S. & Wang, X. J. Neurosci. 28, 3415–3426 (2008).
Kvale, M.N. & Schreiner, C.E. J. Neurophysiol. 91, 604–612 (2004).
Dean, I., Harper, N.S. & McAlpine, D. Nat. Neurosci. 8, 1684–1689 (2005).
Wehr, M. & Zador, A.M. Nature 426, 442–446 (2003).
Tan, A.Y., Atencio, C.A., Polley, D.B., Merzenich, M.M. & Schreiner, C.E. Neuroscience 146, 449–462 (2007).
Phillips, D.P. & Hall, S.E. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 88, 1403–1411 (1990).
Langner, G. Hear. Res. 60, 115–142 (1992).
Davis, K.A., Ramachandran, R. & May, B.J. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 4, 148–163 (2003).
Acknowledgements
We thank K. Kocher for assistance with animal training and D. Oakley for assistance with software programming. This work was supported by the McDonnell Center for Higher Brain Function, the Wallace H. Coulter Foundation and US National Institutes of Health grant DC008880.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D.L.B conceived of the experiment, D.L.B. and P.V.W. designed the experiment, P.V.W. collected and analyzed the data and D.L.B. wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1 and 2 and Supplementary Methods (PDF 163 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Watkins, P., Barbour, D. Specialized neuronal adaptation for preserving input sensitivity. Nat Neurosci 11, 1259–1261 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2201
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2201
This article is cited by
-
Adaptive mechanisms facilitate robust performance in noise and in reverberation in an auditory categorization model
Communications Biology (2023)
-
Noise exposure levels predict blood levels of the inner ear protein prestin
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Neural Responses and Perceptual Sensitivity to Sound Depend on Sound-Level Statistics
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Adaptation of the human auditory cortex to changing background noise
Nature Communications (2019)
-
Adaptation in the auditory system of a beluga whale: effect of adapting sound parameters
Journal of Comparative Physiology A (2019)