Volume 5
-
No. 12 December 2003
Defects in centromere cohesion result in lagging chromosomes (seen as three DNA bodies). The image shows immunofluorescence microscopy of fission yeast cells mutant for the Sphase regulator Hsk1 (Cdc7) and that contain lagging chromosomes. Staining of mitotic spindles (red) and DNA (blue) is shown.
-
No. 11 November 2003
Stbm7-6 mutant embryo exhibits defects in plasma membrane formation, as visualized by Dlg staining (green). Staining of nuclei and centrosomes (shown in red and blue, respectively) reveal that both nuclei and centrosomes are also lost in these cells.
-
No. 10 October 2003
A confocal image of a pupal retina from Drosophila melanogaster that is mosaic for wild-type (blue) and hippo mutant cells. Hippo mutant cells show excessive inter-ommatidial cells (see excess cone and pigment cells visualized by Discs-large expression, shown in green), a phenotype characteristic of mutants of the Hpo/Sav/Wts pathway. Photoreceptor nuclei are shown in orange.
-
No. 9 September 2003
A scanning electron micrograph of the keratin filament network of human pancreatic cells after sphingosylphosphorylcholine treatment, showing a marked perinuclear reorganisation of keratin filaments accompanied by rarefication of the filaments in the cytoplasm. Cover design: James McQuat
-
No. 8 August 2003
Electron micrographs of synaptosomes treated with the Cdk5 inhibitor roscovitine, which leads to depletion of synaptic vesicles and the formation of numerous plasma membrane invaginations. Cover design: Karen Moore
-
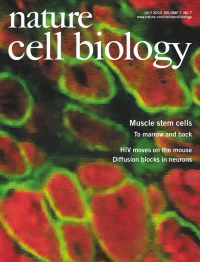
No. 7 July 2003
Muscle cells differentiate into haematopoietic lineages but retain myogenic potential. In the image, donor-derived bone-marrow cells differentiate into myofibres after injection into muscle. Dystrophin is shown in green and myosin heavy chain is shown in red. Cover design: Lawrence Keogh
-
No. 6 June 2003
Drosophila melanogaster Rheb, a small GTPase that functions in the insulin/TOR pathway, promotes cell growth. The image shows fat-body (adipose) tissue from a Drosophila larva in which Rheb was overexpressed in the cells that are marked green with green fluorescent protein (GFP). Blue indicates DNA, and dark areas within the cells are lipid vesicles. This tissue was taken from a larva that had been starved of dietary protein for three days before analysis, a treatment that normally blocks the growth of fat-body cells. Cells over-expressing Rheb continue to grow despite the starvation regime. Cover design: James McQuat
-
No. 5 May 2003
Cross-section through the developing murine Organ of Corti (at E18.5). p27kip1 expression is shown in the supporting cells (red), whereas the hair cells are stained for myosin VIIa (green). Cover design: Karen Moore
-
No. 4 April 2003
Epithelial MDCK cells grown in a collagen gel form three-dimensional cysts, lined by a monolayer of polarized epithelial cells. Single confocal sections of the crosssection of these epithelial cell cysts are shown. In most cells, the typical apicobasal polarization of epithelial cells is retained, with the Golgi (shown in green) located just beneath the apical surface and above the nucleus (blue). Actin is shown in red. Cover design: James McQuat
Focus
-
No. 3 March 2003
GFP-tagged Nbs1 dynamically interacts with DNA double strand breaks inflicted by laser microirradiation of a spatially restricted subnuclear volume (yellow stripe; left). In an undamaged cell, GFPNbs1 is distributed throughout the nucleus (right). The image captures live human cells 30 min after laser treatment. Cover design: Lawrence Keogh
-
No. 2 February 2003
Soluble Fas ligand triggers neurite outgrowth from mouse dorsal root ganglia explants. The explant shown was fixed after one week and stained for neuron-specific tubulin III antibodies.
-
No. 1 January 2003
The Drosophila melanogaster HOAP protein is specifically localized at all mitotic telomeres and is required for telomere capping. The metaphase spread shown is from a female cell. Both chromosomes and HOAP telomeric signals have been pseudo-coloured. Cover design: James McQuat