Abstract
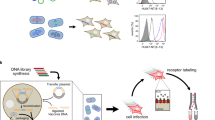
We have developed a widely applicable functional genomics strategy based on alphavirus expression vectors. The technology allows for rapid identification of genes encoding a functional activity such as binding of a defined ligand. Complementary DNA (cDNA) libraries were expressed in mammalian cells following infection with recombinant Sindbis virus (SIN replicon particles), a member of the Alphavirus genus. Virus-infected cells that specifically bound a ligand of choice were isolated using fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS). Replication-competent, infective SIN replicon particles harboring the corresponding cDNA were amplified in a next step. Within one round of selection, viral clones encoding proteins recognized by monoclonal antibodies or Fc-fusion molecules could be isolated and sequenced. Moreover, using the same viral libraries, a plaque-lift assay was established that allowed the identification of secreted, intracellular, and membrane proteins.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boutros, M. & Perrimon, N. Drosophila genome takes flight. Nat. Cell Biol. 2, E53–E54 (2000).
Seed, B. & Aruffo, A. Molecular cloning of the CD2 antigen, the T-cell erythrocyte receptor, by a rapid immunoselection procedure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84, 3365–3369 (1987).
Aruffo, A. & Seed, B. Molecular cloning of a CD28 cDNA by a high-efficiency COS cell expression system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84, 8573–8577 (1987).
Aruffo, A. & Seed, B. Molecular cloning of two CD7 (T-cell leukemia antigen) cDNAs by a COS cell expression system. EMBO J. 6, 3313–3316 (1987).
Kitamura, T. et al. Efficient screening of retroviral cDNA expression libraries. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 9146–9150 (1995).
Seed, B. Developments in expression cloning. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 6, 567–573 (1995).
Lever, A.M. Lentiviral vectors: progress and potential. Curr. Opin. Mol. Ther. 2, 488–496 (2000).
Granziero, L., Nelboeck, P., Bedoucha, M., Lanzavecchia, A. & Reid, H.H. Baculovirus cDNA libraries for expression cloning of genes encoding cell-surface antigens. J. Immunol. Meth. 25, 131–139 (1997).
He, T.C. et al. A simplified system for generating recombinant adenoviruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 2509–2514 (1998).
Xiong, C. et al. Sindbis virus: an efficient, broad host range vector for gene expression in animal cells. Science 243, 1188–1191 (1989).
Strauss, J.H. & Strauss, E.G. The Alphaviruses: gene expression, replication, and evolution. Microbiol. Rev. 58, 491–562 (1994).
Lundstrom, K. Alphaviruses as tools in neurobiology and gene therapy. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. Res. 19, 673–686 (1999).
Xiong, C. et al. Sindbis virus: an efficient, broad host range vector for gene expression in animal cells. Science 243, 1188–1191 (1989).
Gardner, J.P. et al. Infection of human dendritic cells by a Sindbis virus replicon vector is determined by a single amino acid substitution in the E2 glycoprotein. J. Virol. 74, 11849–11857 (2000).
Datwyler, D.A., Eppenberger, H.M., Koller, D., Bailey, J.E. & Magyar, J.P. Efficient gene delivery into adult cardiomyocytes by recombinant Sindbis virus. J. Mol. Med. 77, 859–864 (1999).
Frolov, I. & Schlesinger, S. Translation of Sindbis virus mRNA: effects of sequences downstream of the initiating codon. J. Virol. 68, 8111–8117 (1994).
Hahn, C.S., Hahn, Y.S., Braciale, T.J. & Rice, C.M. Infectious Sindbis virus transient expression vectors for studying antigen processing and presentation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 2679–2683 (1992).
Frolov, I. et al. Alphavirus-based expression vectors: strategies and applications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 11371–11377 (1996).
Bredenbeek, P.J., Frolov, I., Rice, C.M. & Schlesinger, S. Sindbis virus expression vectors: packaging of RNA replicons by using defective helper RNAs. J. Virol. 67, 6439–6446 (1993).
Johnston, R.E., Wan, K. & Bose, H.R. Homologous interference induced by Sindbis virus. J. Virol. 14, 1076–1082 (1974).
Wong, B.Y., Chen, H., Chung, S.W. & Wong, P.M. High-efficiency identification of genes by functional analysis from a retroviral cDNA expression library. J. Virol. 68, 5523–5531 (1994).
Munro, S. & Maniatis, T. Expression cloning of the murine interferon gamma receptor cDNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86, 9248–9252 (1989).
Onishi, M. et al. Applications of retrovirus-mediated expression cloning. Exp. Hematol. 24, 324–329 (1996).
Frolov, I. et al. Selection of RNA replicons capable of persistent noncytopathic replication in mammalian cells. J. Virol. 73, 3845–3865 (1999).
Simonsen, H. & Lodish, H.F. Cloning by function: expression cloning in mammalian cells. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 15, 437–441 (1994).
Kishimoto, T., Akira, S. & Taga, T. Interleukin-6 and its receptor: a paradigm for cytokines. Science 258, 593–597 (1992).
Weiss, B.G. & Schlesinger, S. Recombination between Sindbis virus RNAs. J. Virol. 65, 4017–4025 (1991).
Traunecker, A., Oliveri, F. & Karjalainen, K. Myeloma based expression system for production of large mammalian proteins. TIBTECH 9, 109–113 (1991).
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Gary Jennings and Mark Dyer for carefully reading the manuscript and Prof. Sondra Schlesinger for many helpful discussions and for providing the plasmids pSinRep5 and pDH-EB. This article is dedicated to the memory of Prof. James E. Bailey, who passed away during the preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koller, D., Ruedl, C., Loetscher, M. et al. A high-throughput alphavirus-based expression cloning system for mammalian cells. Nat Biotechnol 19, 851–855 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0901-851
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0901-851
This article is cited by
-
mAbs from mammalian cells
Science-Business eXchange (2008)
-
Viruses as gene delivery vectors: Application to gene function, target validation, and assay development
Cancer Gene Therapy (2002)
-
Genetic selection and the lure of SIN
Nature Biotechnology (2001)