Abstract
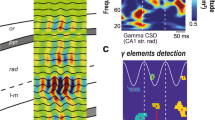
Gamma oscillations are thought to transiently link distributed cell assemblies that are processing related information1,2, a function that is probably important for network processes such as perception1,2,3, attentional selection4 and memory5,6. This ‘binding’ mechanism requires that spatially distributed cells fire together with millisecond range precision7,8; however, it is not clear how such coordinated timing is achieved given that the frequency of gamma oscillations varies substantially across space and time, from ∼25 to almost 150 Hz1,9,10,11,12,13. Here we show that gamma oscillations in the CA1 area of the hippocampus split into distinct fast and slow frequency components that differentially couple CA1 to inputs from the medial entorhinal cortex, an area that provides information about the animal’s current position14,15,16,17, and CA3, a hippocampal subfield essential for storage of such information14,18,19. Fast gamma oscillations in CA1 were synchronized with fast gamma in medial entorhinal cortex, and slow gamma oscillations in CA1 were coherent with slow gamma in CA3. Significant proportions of cells in medial entorhinal cortex and CA3 were phase-locked to fast and slow CA1 gamma waves, respectively. The two types of gamma occurred at different phases of the CA1 theta rhythm and mostly on different theta cycles. These results point to routeing of information as a possible function of gamma frequency variations in the brain and provide a mechanism for temporal segregation of potentially interfering information from different sources.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gray, C. M., Konig, P., Engel, A. K. & Singer, W. Oscillatory responses in cat visual cortex exhibit inter-columnar synchronization which reflects global stimulus properties. Nature 338, 334–337 (1989)
Fries, P., Nikolic, D. & Singer, W. The gamma cycle. Trends Neurosci. 30, 309–316 (2007)
Freeman, W. J. Spatial properties of an EEG event in the olfactory bulb and cortex. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 44, 586–605 (1978)
Fries, P., Reynolds, J. H., Rorie, A. E. & Desimone, R. Modulation of oscillatory neuronal synchronization by selective visual attention. Science 291, 1560–1563 (2001)
Lisman, J. E. & Idiart, M. A. Storage of 7 +/- 2 short-term memories in oscillatory subcycles. Science 267, 1512–1515 (1995)
Montgomery, S. M. & Buzsaki, G. Gamma oscillations dynamically couple hippocampal CA3 and CA1 regions during memory task performance. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 104, 14495–14500 (2007)
von der Malsburg, C. in Models of Neural Networks II (eds van Hemmen, J. L. & Hordemann, G. J.) 95–119 (Springer, 1994)
Engel, A. K., Fries, P. & Singer, W. Dynamic predictions: oscillations and synchrony in top-down processing. Nature Rev. Neurosci. 2, 704–716 (2001)
Bragin, A. et al. Gamma (40–100 Hz) oscillation in the hippocampus of the behaving rat. J. Neurosci. 15, 47–60 (1995)
Csicsvari, J., Jamieson, B., Wise, K. D. & Buzsaki, G. Mechanisms of gamma oscillations in the hippocampus of the behaving rat. Neuron 37, 311–322 (2003)
Kay, L. M. Two species of gamma oscillations in the olfactory bulb: dependence on behavioral state and synaptic interactions. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2, 31–44 (2003)
Canolty, R. T. et al. High gamma power is phase-locked to theta oscillations in human neocortex. Science 313, 1626–1628 (2006)
Sirota, A. et al. Entrainment of neocortical neurons and gamma oscillations by the hippocampal theta rhythm. Neuron 60, 683–697 (2008)
Brun, V. H. et al. Place cells and place recognition maintained by direct entorhinal-hippocampal circuitry. Science 296, 2243–2246 (2002)
Fyhn, M., Molden, S., Witter, M. P., Moser, E. I. & Moser, M. B. Spatial representation in the entorhinal cortex. Science 305, 1258–1264 (2004)
Hafting, T., Fyhn, M., Molden, S., Moser, M. B. & Moser, E. I. Microstructure of a spatial map in the entorhinal cortex. Nature 436, 801–806 (2005)
Brun, V. H. et al. Impaired spatial representation in CA1 after lesion of direct input from entorhinal cortex. Neuron 57, 290–302 (2008)
Sutherland, R. J., Whishaw, I. Q. & Kolb, B. A behavioural analysis of spatial localization following electrolytic, kainite- or colchicines-induced damage to the hippocampal formation in the rat. Behav. Brain Res. 7, 133–153 (1983)
Steffenach, H. A., Sloviter, R. S., Moser, E. I. & Moser, M. B. Impaired retention of spatial memory after transaction of longitudinally oriented axons of hippocampal CA3 pyramidal cells. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 99, 3194–3198 (2002)
Squire, L. R., Stark, C. E. & Clark, R. E. The medial temporal lobe. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 27, 279–306 (2004)
Charpak, S., Pare, D. & Llinas, R. The entorhinal cortex entrains fast CA1 hippocampal oscillations in the anaesthetized guinea-pig: role of the monosynaptic component of the perforant path. Eur. J. Neurosci. 7, 1548–1557 (1995)
Chrobak, J. J. & Buzsaki, G. Gamma oscillations in the entorhinal cortex of the freely behaving rat. J. Neurosci. 18, 388–398 (1998)
Senior, T. J., Huxter, J. R., Allen, K., O’Neill, J. & Csicsvari, J. Gamma oscillatory firing reveals distinct populations of pyramidal cells in the CA1 region of the hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 28, 2274–2286 (2008)
Womelsdorf, T. et al. Modulation of neuronal interactions through neuronal synchronization. Science 316, 1609–1612 (2007)
Martin, S. J., Grimwood, P. D. & Morris, R. G. Synaptic plasticity and memory: an evaluation of the hypothesis. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 23, 649–711 (2000)
Blum, K. I. & Abbott, L. F. A model of spatial map formation in the hippocampus of the rat. Neural Comput. 8, 85–93 (1996)
Mehta, M. R., Barnes, C. A. & McNaughton, B. L. Experience-dependent, asymmetric expansion of hippocampal place fields. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 94, 8918–8921 (1997)
Hasselmo, M. E., Bodelon, C. & Wyble, B. P. A proposed function for hippocampal theta rhythm: separate phases of encoding and retrieval enhance reversal of prior learning. Neural Comput. 14, 793–817 (2002)
Huerta, P. T. & Lisman, J. E. Bidirectional synaptic plasticity induced by a single burst during cholinergic theta oscillation in CA1 in vitro . Neuron 15, 1053–1063 (1995)
Jutras, M. J., Fries, P. & Buffalo, E. A. Gamma-band synchronization in the macaque hippocampus and memory formation. J. Neurosci. 29, 12521–12531 (2009)
Acknowledgements
We thank A. M. Amundsgaard, K. Haugen, K. Jenssen, E. Sjulstad, R. Skjerpeng and H. Waade for technical assistance, M. P. Witter for assistance with recording site localization, E. J. Henriksen and K. Jezek for donating rats for supplementary analyses, C. A. Barnes for helpful comments on the manuscript and G. Buzsáki and a number of other colleagues for helpful discussions. This work was supported by the Kavli Foundation and a Centre of Excellence grant from the Norwegian Research Council.
Author Contributions L.L.C., O.J., M.-B.M. and E.I.M. planned experiments and analyses, L.L.C., T.D., M.F., T.H. and T.B. collected data, L.L.C., T.D. and O.J. wrote analysis programs, L.L.C. and T.D. analysed data, and L.L.C. and E.I.M. wrote the paper, in collaboration with M.-B.M. All authors discussed the results.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
This file contains Supplementary Figures 1-18 with Legends, Supplementary Tables 1-3, Supplementary Methods and Supplementary References. (PDF 2307 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Colgin, L., Denninger, T., Fyhn, M. et al. Frequency of gamma oscillations routes flow of information in the hippocampus. Nature 462, 353–357 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08573
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08573
This article is cited by
-
Silencing CA1 pyramidal cells output reveals the role of feedback inhibition in hippocampal oscillations
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Intracellular magnesium optimizes transmission efficiency and plasticity of hippocampal synapses by reconfiguring their connectivity
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Gamma oscillatory complexity conveys behavioral information in hippocampal networks
Nature Communications (2024)
-
A perspective on neuroethology: what the past teaches us about the future of neuroethology
Journal of Comparative Physiology A (2024)
-
Reduced Reward Processing in Schizophrenia: A Comprehensive EEG Event-Related Oscillation Study
Brain Topography (2024)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.