Abstract
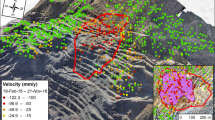
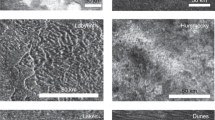
Cassini's Titan Radar Mapper imaged the surface of Saturn's moon Titan on its February 2005 fly-by (denoted T3), collecting high-resolution synthetic-aperture radar and larger-scale radiometry and scatterometry data. These data provide the first definitive identification of impact craters on the surface of Titan, networks of fluvial channels and surficial dark streaks that may be longitudinal dunes. Here we describe this great diversity of landforms. We conclude that much of the surface thus far imaged by radar of the haze-shrouded Titan is very young, with persistent geologic activity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Elachi, C. et al. Cassini Titan Radar Mapper. Proc. IEEE 79, 867–880 (1991)
Elachi, C. et al. RADAR: The Cassini Titan Radar Mapper. Space Sci. Rev. 117, 71–110 (2005)
Elachi, C. et al. Cassini radar views the surface of Titan. Science 308, 970–974 (2005)
Sotin, C. et al. Release of volatiles from a possible cryovolcano from near-infrared imaging of Titan. Nature 435, 786–789 (2005)
Mitri, G., Lunine, J., Showman, A. & Lopes, R. Resurfacing of Titan by ammonia-water cryomagma. Icarus (submitted)
Porco, C. et al. Imaging of Titan from the Cassini spacecraft. Nature 434, 159–168 (2005)
Schenk, P. Central pit and dome craters: Exposing the interiors of Ganymede and Callisto. J. Geophys. Res. 98, 7475–7498 (1993)
Kirk, R. et al. & the Cassini Radar Team. RADAR reveals Titan topography. Proc. 36th Annu. Lunar Planet. Sci. XXXVI abstr. 2227 (2005).
Melosh, H. Impact Cratering: A Geologic Process 87–111 (Oxford Univ., Oxford, 1989)
Lorenz, R. Impacts and cratering on Titan: A pre-Cassini view. Planet. Space Sci. 45, 1009–1019 (1997)
Wood, C., Lopes, R., Stofan, E., Paganelli, F. & Elachi, C. Impact craters on Titan? Cassini RADAR view. Proc. 36th Annu. Lunar Planet. Sci. XXXVI abstr. 1117 (2005).
Tomasko, M. G. et al. Rain, winds and haze during the Huygens probe's descent to Titan's surface. Nature 438, 765–778 (2005)
Kargel, J., Croft, S., Lunine, J. & Lewis, J. Rheological properties of ammonia-water liquids and crystal-liquid slurries: Planetological applications. Icarus 89, 93–112 (1991)
Blom, R. & Elachi, C. Spaceborne and airborne imaging radar observations of sand dunes. J. Geophys. Res. 86 (B4), 3061–3073 (1981)
Fahnestock, M., Scambos, T., Shuman, C., Arthern, R., Winebrenner, D. & Kwok, R. Snow megadunes fields on the East Antarctica Plateau: Extreme atmosphere-ice interaction. Geophys. Res. Lett. 27(22), 3719–3722 (2000)
Lorenz, R., Lunine, J., Grier, J. & Fisher, M. Prediction of aeolian features on planets: Application to Titan paleoclimatology. J. Geophys. Res. 100, 26377–26386 (1995)
Tokano, T. & Neubauer, F. Tidal winds on Titan caused by Saturn. Icarus 158, 499–515 (2002)
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge those who designed, developed, and operate the Cassini/Huygens mission. Cassini is a joint endeavour of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Italian Space Agency (ASI) and is managed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, under a contract with NASA. Author Contributions C.E. is the RADAR Team Leader. All authors contributed equally to this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Reprints and permissions information is available at npg.nature.com/reprintsandpermissions. The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Image
This file contains the Cassini Radar SAR T3 swath, acquired during the February 15, 2005 Cassini flyby. Each pixel represents 600 x 600 m of the surface. The image is centered at 21 degrees N Latitude by 69 degrees W Longitude. Pixel brightness is not directly convertible to surface radar cross section due to JPEG compression. The map projection is an oblique cylindrical projection with the equator of the projection along Cassini's ground track and the prime meridian passing through the point of closest approach. The long dimension of the image is roughly East-West with both ends of the swath bowing down toward Titan's equator. (JPG 4259 kb)
Because of the nature of this projection and the quantization of the data, we do not recommend use of these data for quantitative analysis, whether in terms of brightness, distance or pixel location. For such uses please use the full-resolution data from the NASA Planetary Data System at http://starbrite.jpl.nasa.gov/pds/index.jsp.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elachi, C., Wall, S., Janssen, M. et al. Titan Radar Mapper observations from Cassini's T3 fly-by. Nature 441, 709–713 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04786
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04786
This article is cited by
-
Planetary polar explorer – the case for a next-generation remote sensing mission to low Mars orbit
Experimental Astronomy (2022)
-
Characteristics of Icy Surfaces
Space Science Reviews (2010)
-
The identification of liquid ethane in Titan’s Ontario Lacus
Nature (2008)
-
Astrophysics in 2006
Space Science Reviews (2007)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.