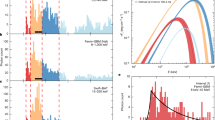
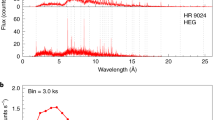
Abstract
Recent measurements of stellar orbits1,2,3 provide compelling evidence that the compact radio source Sagittarius A* (refs 4, 5) at the Galactic Centre is a 3.6-million-solar-mass black hole. Sgr A* is remarkably faint in all wavebands other than the radio region6,7, however, which challenges current theories of matter accretion and radiation surrounding black holes8. The black hole's rotation rate is not known, and therefore neither is the structure of space-time around it. Here we report high-resolution infrared observations of Sgr A* that reveal ‘quiescent’ emission and several flares. The infrared emission originates from within a few milliarcseconds of the black hole, and traces very energetic electrons or moderately hot gas within the innermost accretion region. Two flares exhibit a 17-minute quasi-periodic variability. If the periodicity arises from relativistic modulation of orbiting gas, the emission must come from just outside the event horizon, and the black hole must be rotating at about half of the maximum possible rate.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schödel, R. et al. A star in a 15.2 year orbit around the supermassive black hole at the centre of the Milky Way. Nature 419, 694–696 (2002)
Ghez, A. M. et al. The first measurement of spectral lines in a short-period star bound to the Galaxy's central black hole: A paradox of youth. Astrophys. J. 586, L127–L131 (2003)
Eisenhauer, F. et al. A geometric determination of the distance to the Galactic Center. Astrophys. J. Lett. (in the press); preprint at 〈http://arXiv.org/astro-ph/0306220〉 (2003)
Doeleman, S. S. et al. Structure of SgrA* at 86 GHz using VLBI closure quantities. Astron. J. 121, 2610–2617 (2001)
Backer, D. C. & Sramek, R. A. Proper motion of the compact, nonthermal radio source in the Galactic Center, SgrA*. Astrophys. J. 524, 805–815 (1999)
Baganoff, F. K. et al. Chandra X-ray spectroscopic imaging of SgrA* and the central parsec of the Galaxy. Astrophys. J. 591, 891–915 (2003)
Hornstein, S. D. et al. Limits on the short-term variability of SgrA* in the near-IR. Astrophys. J. 577, L9–L13 (2002)
Melia, F. & Falcke, H. The supermassive black hole at the Galactic Center. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 39, 309–352 (2001)
Lenzen, R., Hofmann, R., Bizenberger, P. & Tusche, A. CONICA: The high-resolution near-infrared camera for the ESO VLT. Proc. SPIE 3354 (IR Astronomical Instrumentation), 606–614 (1998)
Rousset, G. et al. Design of the Nasmyth adaptive optics system (NAOS) of the VLT. Proc. SPIE 3353 (Adaptive Optics Technology), 508–516 (1998)
Benlloch, S., Wilms, J., Edelson, R., Raqoob, T. & Staubert, T. Quasi-periodic oscillation in Seyfert galaxies: Significance levels. The case of Mrk 766. Astrophys. J. 562, L121–L124 (2001)
Ghez, A. M. et al. Variable infrared emission from the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way. Astrophys. J. Lett. (submitted); preprint at 〈http://arXiv.org/astro-ph/0309076〉 (2003)
Baganoff, F. K. Multi-wavelength monitoring of SgrA* during Chandra observations of multiple X-ray flares. High Energy Astrophysics Division (HEAD) AAS Abstr. 3.02, 35 (2003)
Alexander, T. & Sternberg, A. Near-IR microlensing of stars by the supermassive black hole in the Galactic Center. Astrophys. J. 520, 137–148 (1999)
Yuan, F., Markoff, S. & Falcke, H. A jet-ADAF model for SgrA*. Astron. Astrophys. 854, 854–863 (2002)
Liu, S. & Melia, F. New constraints on the nature of the radio emission in SgrA*. Astrophys. J. 561, L77–L80 (2001)
Yuan, F., Quataert, E. & Narayan, R. Nonthermal electrons in radiatively inefficient flow models of SgrA*. Astrophys. J. (submitted); preprint at 〈http://arXiv.org/astro-ph/0304125〉 (2003)
Markoff, S., Falcke, H., Yuan, F. & Biermann, P. L. The nature of the 10ksec X-ray flare in SgrA*. Astron. Astrophys. 379, L13–L16 (2001)
Baganoff, F. K. et al. Rapid X-ray flaring from the direction of the supermassive black hole at the Galactic Centre. Nature 413, 45–48 (2001)
Porquet, D. et al. XMM-Newton observation of the brightest X-ray flare detected so far from SgrA*. Astron. Astrophys. 407, L17–L20 (2003)
Zhao, J.-H. et al. Variability of SgrA*: Flares at 1 mm. Astrophys. J. 586, L29–L32 (2003)
Miyazaki, A., Tstsumi, T. & Tsuboi, M. Flares of SgrA* at short submm wavelengths. Astron. Nachr. 324, 3–9 (2003)
Nayakshin, S., Cuadra, J. & Sunyaev, R. X-ray flares from SgrA*: Star-disk interactions? Astron. Astrophys. (in the press); preprint at 〈http://arXiv.org/astro-ph/0304126〉 (2003)
Hollywood, J. M. & Melia, F. General relativistic effects on the infrared spectrum of thin accretion disks in active galactic nuclei: Application to SgrA*. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 112, 423–455 (1997)
Bardeen, J. M., Press, W. M. & Teukolsky, S. A. Rotating black holes: Locally non-rotating frames, energy extraction and scalar synchrotron radiation. Astrophys. J. 178, 347–369 (1972)
Melia, F., Bromley, C., Liu, S. & Walker, C. K. Measuring the black hole spin in SgrA*. Astrophys. J. 554, L37–L40 (2001)
De Villiers, J.-P., Hawley, J. F. & Krolik, J. H. Magnetically driven accretion flows in the Kerr metric I: Models and overall structure. Astrophys. J. (submitted); preprint at 〈http://arXiv.org/astro-ph/0307260〉 (2003)
Nowak, M. A., Wagoner, R. V., Begelman, M. C. & Lehr, D. E. The 67 Hz feature in the black hole candidate GRS1915 + 105 as a possible diskoseismic mode. Astrophys. J. 477, L91–L94 (1997)
Bardeen, J. M. & Pettersen, J. A. The Lense-Thirring effect and accretion disks around Kerr black holes. Astrophys. J. 105, L65–L67 (1975)
Acknowledgements
This Letter is based on observations at the VLT of the European Observatory (ESO) in Chile. We thank the teams who developed and constructed the near-infrared camera CONICA and the AO system NAOS, and especially their principal investigators, R. Lenzen, R. Hofmann and G. Rousset. We thank H. Falcke and S. Markoff for access to their database of the SgrA* SED, as well as discussions of emission processes. We are grateful to D. Porquet and P. Predehl for discussions of their XMM data, S. Nayakshin, M. Rees, R. Sunyaev and especially E. Quataert for discussions of accretion disk physics, and A. Sternberg for suggestions on the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Genzel, R., Schödel, R., Ott, T. et al. Near-infrared flares from accreting gas around the supermassive black hole at the Galactic Centre. Nature 425, 934–937 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02065
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02065
This article is cited by
-
Black holes up close
Nature (2023)
-
High-resolution imaging for advances in astronomy
Journal of Optics (2021)
-
Testing general relativity with the Event Horizon Telescope
General Relativity and Gravitation (2019)
-
The Milky Way’s Supermassive Black Hole: How Good a Case Is It?
Foundations of Physics (2017)
-
Detection of Gravitational Wave Emission by Supermassive Black Hole Binaries Through Tidal Disruption Flares
Scientific Reports (2016)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.