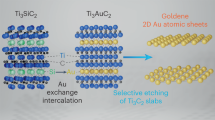
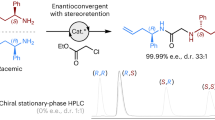
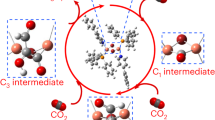
Abstract
Many biomolecules are chiral—they can exist in one of two enantiomeric forms that only differ in that their structures are mirror images of each other. Because only one enantiomer tends to be physiologically active while the other is inactive or even toxic, drug compounds are increasingly produced in an enantiomerically pure form1 using solution-phase homogeneous catalysts and enzymes. Chiral surfaces offer the possibility of developing heterogeneous enantioselective catalysts that can more readily be separated from the products and reused. In addition, such surfaces might serve as electrochemical sensors for chiral molecules. To date, chiral surfaces have been obtained by adsorbing chiral molecules2,3,4,5,6 or slicing single crystals so that they exhibit high-index faces7,8,9,10,11,12,13, and some of these surfaces act as enantioselective heterogeneous catalysts5,6,10. Here we show that chiral surfaces can also be produced through electrodeposition, a relatively simple solution-based process that resembles biomineralization14,15,16,17 in that organic molecules adsorbed on surfaces have profound effects on the morphology of the inorganic deposits18,19,20. When electrodepositing a copper oxide film on an achiral gold surface in the presence of tartrate ion in the deposition solution, the chirality of the ion determines the chirality of the deposited film, which in turn determines the film's enantiospecificity during subsequent electrochemical oxidation reactions.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stinson, S. C. Chiral pharmaceuticals. Chem. Eng. News 79, 79–97 (2001)
Lorenzo, M. O., Baddeley, C. J., Muryn, C. & Raval, R. Extended surface chirality from supramolecular assemblies of adsorbed chiral molecules. Nature 404, 376–379 (2000)
Humblot, V., Haq, S., Muryn, C., Hofer, W. A. & Raval, R. From local adsorption stresses to chiral surfaces: (R,R)-tartaric acid on Ni(110). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 503–510 (2002)
Kühnle, A., Linderoth, T. R., Hammer, B. & Besenbacher, F. Chiral recognition in dimerization of adsorbed cysteine observed by scanning tunnelling microscopy. Nature 415, 891–893 (2002)
Izumi, Y. in Advances in Catalysis Vol. 32, 215–271 (Academic, New York, 1983)
LeBlond, C., Wang, J., Liu, J., Andrews, A. T. & Sun, Y.-K. Highly enantioselective heterogeneously catalyzed hydrogenation of α-ketoesters under mild conditions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 121, 4920–4921 (1999)
McFadden, C. F., Cremer, P. S. & Gellman, A. J. Adsorption of chiral alcohols on “chiral” metal surfaces. Langmuir 12, 2483–2487 (1996)
Horvath, J. D. & Gellman, A. J. Enantiospecific desorption of R- and S-propylene oxide from a chiral Cu(643) surface. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123, 7953–7954 (2001)
Horvath, J. D. & Gellman, A. J. Enantiospecific desorption of chiral compounds from chiral Cu(643) and achiral Cu(111) surfaces. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 2384–2392 (2002)
Ahmadi, A., Attard, G., Feliu, J. & Rodes, A. Surface reactivity at “chiral” platinum surfaces. Langmuir 15, 2420–2424 (1999)
Attard, G. A. et al. Temperature effects in the enantiomeric electro-oxidation of D- and L-glucose on Pt{643}S. J. Phys. Chem. B 103, 1381–1385 (1999)
Attard, G. A. Electrochemical studies of enantioselectivity of chiral metal surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. B 105, 3158–3167 (2001)
Sholl, D. S., Asthagiri, A. & Power, T. D. Naturally chiral metal surfaces as enantiospecific adsorbents. J. Phys. Chem. B 105, 4771–4782 (2001)
Orme, C. A. et al. Formation of chiral morphologies through selective binding of amino acids to calcite surface steps. Nature 411, 775–779 (2001)
Addadi, L. & Weiner, S. Crystals, asymmetry and life. Nature 411, 753–755 (2001)
Teng, H. H., Dove, P. M., Orme, C. A. & De Yoreo, J. J. Thermodynamics of calcite growth: baseline for understanding biomineral formation. Science 282, 724–727 (1998)
Cody, A. M. & Cody, R. D. Chiral habit modifications of gypsum from epitaxial-like adsorption of stereospecific growth inhibitors. J. Cryst. Growth 113, 508–519 (1991)
Paunovic, M. & Schlesinger, M. Fundamentals of Electrochemical Deposition 167–186 (Wiley-Interscience, New York, 1998)
Josell, D., Wheeler, D., Huber, W. H. & Moffat, T. P. Superconformal electrodeposition in submicron features. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 016102 (2001)
Vazhev, V. V. & Mardashev, Yu. S. A “memory” effect in formic and oxalic acid oxidation at gold electrodes. Sov. Electrochem. 16, 1445–1447 (1980)
Switzer, J. A., Shumsky, M. G. & Bohannan, E. W. Electrodeposited ceramic single crystals. Science 284, 293–296 (1999)
Bohannan, E. W., Shumsky, M. G. & Switzer, J. A. Epitaxial electrodeposition of copper(I) oxide on single-crystal Au(100). Chem. Mater. 11, 2289–2291 (1999)
Sorenson, T. A., Morton, S. A., Waddill, G. D. & Switzer, J. A. Epitaxial electrodeposition of Fe3O4 thin films on the low-index planes of gold. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 7604–7609 (2002)
Switzer, J. A., Kothari, H. M. & Bohannan, E. W. Thermodynamic to kinetic transition in epitaxial electrodeposition. J. Phys. Chem. B 106, 4027–4031 (2002)
Switzer, J. A., Liu, R., Bohannan, E. W. & Ernst, F. Epitaxial electrodeposition of a crystalline metal oxide onto single-crystalline silicon. J. Phys. Chem. B 106, 12369–12372 (2002)
Poizot, P., Hung, C.-J., Nikiforov, M. P., Bohannan, E. W. & Switzer, J. A. An electrochemical method for CuO thin film deposition from aqueous solution. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 6, C21–C25 (2003)
Catana, A., Locquet, J.-P., Paik, S. M. & Schuller, I. K. Local epitaxial growth of copper monoxide films on magnesium oxide. Phys. Rev. B 46, 15477–15483 (1992)
Missavage, R. J., Belford, R. L. & Paul, I. C. Crystal and molecular structure of tetrasodium dicopper(ii)-dl-tartrate decahydrate. J. Coord. Chem. 2, 145–157 (1972)
Hazen, R. M., Filley, T. R. & Goodfriend, G. A. Selective adsorption of L- and D-amino acids on calcite: Implications for biochemical homochirality. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 98, 5487–5490 (2001)
Xie, Y. & Huber, C. O. Electrocatalysis and amperometric detection using an electrode made of copper oxide and carbon paste. Anal. Chem. 63, 1714–1719 (1991)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation and the University of Missouri Research Board.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Switzer, J., Kothari, H., Poizot, P. et al. Enantiospecific electrodeposition of a chiral catalyst. Nature 425, 490–493 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01990
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01990
This article is cited by
-
Heteroepitaxial growth of Au@Pd core–shell nanocrystals with intrinsic chiral surfaces for enantiomeric recognition
Rare Metals (2024)
-
Synchronous quantitative analysis of chiral mesostructured inorganic crystals by 3D electron diffraction tomography
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Chiral nanoporous networks featuring various chiral vertices from an achiral molecule on Ag(100)
Nano Research (2022)
-
Nanoengineered chiral Pt-Ir alloys for high-performance enantioselective electrosynthesis
Nature Communications (2021)
-
Pharmacokinetic Properties of S-oxiracetam After Single and Multiple Intravenous Infusions in Healthy Volunteers
European Journal of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics (2021)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.