Abstract
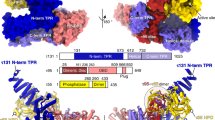
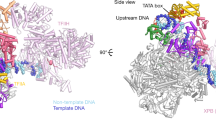
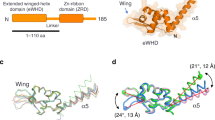
Transcription factor IIIB (TFIIIB), consisting of the TATA-binding protein (TBP), TFIIB-related factor (Brf1) and Bdp1, is a central component in basal and regulated transcription by RNA polymerase III1,2,3,4. TFIIIB recruits its polymerase to the promoter and subsequently has an essential role in the formation of the open initiation complex. The amino-terminal half of Brf1 shares a high degree of sequence similarity with the polymerase II general transcription factor TFIIB, but it is the carboxy-terminal half of Brf1 that contributes most of its binding affinity with TBP5,6,7,8. The principal anchoring region is located between residues 435 and 545 of yeast Brf1, comprising its homology domain II. The same region also provides the primary interface for assembling Bdp1 into the TFIIIB complex9. We report here a 2.95 Å resolution crystal structure of the ternary complex containing Brf1 homology domain II, the conserved region of TBP and 19 base pairs of U6 promoter DNA. The structure reveals the core interface for assembly of TFIIIB and demonstrates how the loosely packed Brf1 domain achieves remarkable binding specificity with the convex and lateral surfaces of TBP.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
White, R. J. RNA Polymerase III Transcription (Springer/Landes Bioscience, New York/Georgetown, 1998)
Geiduschek, E. P. & Kassavetis, G. A. The RNA polymerase III transcription apparatus. J. Mol. Biol. 310, 1–26 (2001)
Schramm, L. & Hernandez, N. Recruitment of RNA polymerase III to its target promoters. Genes Dev. 16, 2593–2620 (2002)
Willis, I. M. A universal nomenclature for subunits of the RNA polymerase III transcription initiation factor TFIIIB. Genes Dev. 16, 1337–1338 (2002)
Khoo, B., Brophy, B. & Jackson, S. P. Conserved functional domains of the RNA polymerase III general transcription factor BRF. Genes Dev. 8, 2879–2890 (1994)
Wang, Z. & Roeder, R. G. Structure and function of a human transcription factor TFIIIB subunit that is evolutionarily conserved and contains both TFIIB- and high-mobility-group protein 2-related domains. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 92, 7026–7030 (1995)
Chaussivert, N., Conesa, C., Shaaban, S. & Sentenac, A. Complex interactions between yeast TFIIIB and TFIIIC. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 15353–15358 (1995)
Ruth, J. et al. A suppressor of mutations in the class III transcription system encodes a component of yeast TFIIIB. EMBO J. 15, 1941–1949 (1996)
Kassavetis, G. A., Kumar, A., Ramirez, E. & Geiduschek, E. P. Functional and structural organization of Brf, the TFIIB-related component of the RNA polymerase III transcription initiation complex. Mol. Cell Biol. 18, 5587–5599 (1998)
Patikoglou, G. & Burley, S. K. Eukaryotic transcription factor-DNA complexes. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 26, 289–325 (1997)
Stebbins, C. E. & Galan, J. E. Maintenance of an unfolded polypeptide by a cognate chaperone in bacterial type III secretion. Nature 414, 77–81 (2001)
Huet, J., Conesa, C., Carles, C. & Sentenac, A. A cryptic DNA binding domain at the COOH terminus of TFIIIB70 affects formation, stability, and function of preinitiation complexes. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 18341–18349 (1997)
Chasman, D. I., Flaherty, K. M., Sharp, P. A. & Kornberg, R. D. Crystal structure of yeast TATA-binding protein and model for interaction with DNA. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 90, 8174–8178 (1993)
Juo, Z. S. et al. How proteins recognize the TATA box. J. Mol. Biol. 261, 239–254 (1996)
Rost, B. PHD: predicting 1D protein structure by profile based neural networks. Methods Enzymol. 266, 525–539 (1996)
Radhakrishnan, I. et al. Solution structure of the KIX domain of CBP bound to the transactivation domain of CREB: a model for activator:coactivator interactions. Cell 91, 741–752 (1997)
Andrau, J. C., Sentenac, A. & Werner, M. Mutagenesis of yeast TFIIIB70 reveals C-terminal residues critical for interaction with TBP and C34. J. Mol. Biol. 288, 511–520 (1999)
Colbert, T., Lee, S., Schimmack, G. & Hahn, S. Architecture of protein and DNA contacts within the TFIIIB-DNA complex. Mol. Cell Biol. 18, 1682–1691 (1998)
Shen, Y., Kassavetis, G. A., Bryant, G. O. & Berk, A. J. Polymerase (Pol) III TATA box-binding protein (TBP)-associated factor Brf binds to a surface on TBP also required for activated Pol II transcription. Mol. Cell Biol. 18, 1692–1700 (1998)
Cormack, B. P. & Struhl, K. Regional codon randomization: defining a TATA-binding protein surface required for RNA polymerase III transcription. Science 262, 244–248 (1993)
Tora, L. A unified nomenclature for TATA box binding protein (TBP)-associated factors (TAFs) involved in RNA polymerase II transcription. Genes Dev. 16, 673–675 (2002)
Martel, L. S., Brown, H. J. & Berk, A. J. Evidence that TAF-TATA box-binding protein interactions are required for activated transcription in mammalian cells. Mol. Cell Biol. 22, 2788–2798 (2002)
Tan, S., Hunziker, Y., Sargent, D. F. & Richmond, T. J. Crystal structure of a yeast TFIIA/TBP/DNA complex. Nature 381, 127–151 (1996)
Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. Processing of X-ray diffraction data collected in oscillation mode. Methods Enzymol. 276, 307–326 (1997)
de la Fortelle, E. & Bricogne, G. Maximum-likelihood heavy-atom parameter refinement for multiple isomorphous replacement and multiwavelength anomalous diffraction methods. Methods Enzymol. 276, 472–494 (1997)
Brunger, A. T. et al. Crystallography and NMR system (CNS): A new software system for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D 54, 905–921 (1998)
Winn, M., Isupov, M. & Murshudov, G. N. Use of TLS parameters to model anisotropic displacements in macromolecular refinement. Acta Crystallogr. D 57, 122–133 (2001)
Murshudov, G. N., Vagin, A. A. & Dodson, E. J. Refinement of macromolecular structures by the maximum-likelihood method. Acta Crystallogr. D 53, 240–255 (1997)
Laskowski, R. A., MacArthur, M. W., Moss, D. S. & Thornton, J. M. PROCHECK: a program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J. Appl. Crystallor. 26, 283–291 (1993)
Acknowledgements
Z.S.J. would like to thank T. Steitz for financial support. The authors would like to thank A. Berk, J. Cabral, S. Harrison, N. Hernandez, F. Li, K. Struhl and Y. Xiong for discussions; G. Olack for assistance in mass spectrum analysis; M. Wilson for help with data collection; P. Mann for assistance with protein preparation; Yale CSB core staff for advice on software-related issues; W. Henderickson, C. Ogata (NSLS beamline X4A), M. Becker, L. Berman, R. Sweet (NSLS beamline X25), A. Joachimiak and SBC staff (ANL beamline 19 ID) for help with synchrotron data acquisition; and Z. Otwinowski, W. Minor, I. Minor, C. Vonrhein and G. Murshudov for advice on programs. This work was supported in part by the Howard Hughes Medical Institute and by the National Institutes of Health (E.P.G., P.B.S. and T. Steitz).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Juo, Z., Kassavetis, G., Wang, J. et al. Crystal structure of a transcription factor IIIB core interface ternary complex. Nature 422, 534–539 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01534
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01534
This article is cited by
-
Molecular determinants underlying functional innovations of TBP and their impact on transcription initiation
Nature Communications (2020)
-
Structural basis of RNA polymerase III transcription initiation
Nature (2018)
-
Near-atomic resolution visualization of human transcription promoter opening
Nature (2016)
-
High-resolution structure of TBP with TAF1 reveals anchoring patterns in transcriptional regulation
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (2013)
-
Conformational flexibility of RNA polymerase III during transcriptional elongation
The EMBO Journal (2010)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.