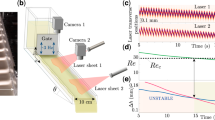
Abstract
Unstable waves have been long studied in fluid shear layers1,2,3. These waves affect transport in the atmosphere and oceans, in addition to slipstream stability behind ships, aeroplanes and heat-transfer devices. Corresponding instabilities in granular flows have not been previously documented4, despite the importance of these flows in geophysical and industrial systems5,6,7. Here we report that breaking waves can form at the interface between two streams of identical grains flowing on an inclined plane downstream of a splitter plate. Changes in either the shear rate or the angle of incline cause such waves to appear abruptly. We analyse a granular flow model that agrees qualitatively with our experimental data; the model suggests that the waves result from competition between shear and extensional strains in the flowing granular bed. We propose a dimensionless shear number that governs the transition between steady and wavy flows.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lamb, H. Hydrodynamics (Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, 1932).
Chandrasekhar, S. Hydrodynamic and Hydromagnetic Stability (Clarendon, Oxford, 1961).
Thorpe, S. A. Experiments on the instability of stratified shear flows: immiscible fluids. J. Fluid Mech. 39, 25–48 (1969).
Goddard, J. D. & Alam, M. Shear-flow and material instabilities in particulate suspensions and granular media. Particulate Sci. Technol. 17, 69–96 (1999).
Denlinger, R. P. & Iverson, R. M. Flow of variably fluidized granular masses across three-dimensional terrain. 2. Numerical predictions and experimental tests. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 553–566 (2001).
Bagnold, R. A. The movement of desert sand. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 157, 594–620 (2001).
Shinbrot, T. & Muzzio, F. J. Nonequilibrium patterns in granular mixing and segregation. Phys. Today 25–30 (March, 2000).
Melosh, H. J. Dynamical weakening of faults by acoustic fluidization. Nature 379, 601–606 (1996).
Scott, D. R. Seismicity and stress rotation in a granular model of the brittle crust. Nature 381, 592–595 (1996).
Liu, A. J. & Nagel, S. R. Nonlinear dynamics—Jamming is not just cool any more. Nature 396, 21–22 (1998).
Pouliquen, O., Delour, J. & Savage, S. B. Fingering in granular flows. Nature 386, 816–817 (1997).
Losert, W., Bocquet, L., Lubensky, T. C. & Gollub, J. P. Particle dynamics in sheared granular matter. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 1428–1431 (2000).
Menon, N. & Durian, D. J. Diffusing-wave spectroscopy of dynamics in a three-dimensional granular flow. Science 275, 1920 (1997).
Howell, D. & Behringer, R. P. Fluctuations in a 2D granular Couette experiment: A critical transition. Phys. Rev. Lett. 82, 5241–5244 (1999).
Mueth, D. M. et al. Signatures of granular microstructure in dense shear flows. Nature 406, 385–389 (2000).
Louge, M. Y. & Keast, S. C. On dense granular flows down flat frictional inclines. Phys. Fluids 13, 1213–1233 (2001).
Forterre, Y. & Pouliquen, O. Longitudinal vortices in granular flows. Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 5886–5889 (2001).
Hanes, D. M. & Walton, O. R. Simulations and physical measurements of glass spheres flowing down a bumpy incline. Powder Technol. 109, 133–144 (2000).
Savage, S. B. & Hutter, K. The motion of a finite mass of granular material down a rough incline. J. Fluid Mech. 199, 177–215 (1989).
Pouliquen, O. & Gutfraind, R. Stress fluctuations and shear zones in quasistatic granular chute flows. Phys. Rev. E 53, 552–561 (1996).
Davies, C. E., Weir, G. & McGavin, P. Behaviour of a dense stream of non-cohesive particles impacting on an inclined plate. Powder Technol. 106, 1–6 (1999).
Lueptow, R. M., Akonur, A. & Shinbrot, T. PIV for granular flows. Exp. Fluids 28, 183–186 (2000).
Kadanoff, L. P. Built upon sand: Theoretical ideas inspired by granular flows. Rev. Mod. Phys. 71, 435–444 (1999).
Johnson, P. C., Nott, P. & Jackson, R. Frictional-collisional equations of motion for particulate flows and their application to chutes. J. Fluid Mech. 210, 501–535 (1990).
Rericha, E. C., Bizon, C., Shattuck, M. D. & Swinney, H. L. Shocks in supersonic sand. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 014302 (2002).
Wang, C.-H., Jackson, R. & Sundaresan, S. Instabilities of fully developed rapid flow of a granular material in a channel. J. Fluid Mech. 342, 179–197 (1997).
Natarajan, V. V. R., Hunt, M. L. & Taylor, E. D. Local measurements of velocity fluctuations and diffusion coefficients for a granular material flow. J. Fluid Mech. 304, 1–25 (1995).
Iverson, R. M. The physics of debris flows. Rev. Geophys. 35, 245–296 (1997).
Aider, J. L., Sommier, N., Raafat, T. & Hulin, J. P. Experimental study of a granular flow in a vertical pipe: a spatiotemporal analysis. Phys. Rev. E 59, 778–786 (1999).
Chan, K. & Rothman, D. H. Coupled length scales in eroding landscapes. Phys. Rev. E 63, 55102–55105 (2001).
Acknowledgements
We thank A. Hasan, J. Leung, E. Liss, K. Mehta and J. Pantina for assistance. This work was supported by the US National Science Foundation, Division of Chemical and Transport Systems, and the American Chemical Society, Petroleum Research Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goldfarb, D., Glasser, B. & Shinbrot, T. Shear instabilities in granular flows. Nature 415, 302–305 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/415302a
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/415302a
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.