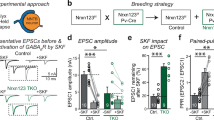
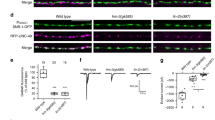
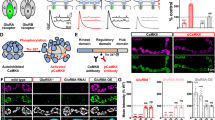
Abstract
Synaptic connections undergo a dynamic process of stabilization or elimination during development, and this process is thought to be critical in memory and learning and in establishing the specificity of synaptic connections1. The type II calcium- and calmodulin-dependent protein kinase (CaMKII) has been proposed to be pivotal in regulating synaptic strength2,3,4 and in maturation of synapses during development5. Here we describe how CaMKII regulates the formation of central glutamatergic synapses in Caenorhabditis elegans. During larval development, the density of ventral nerve cord synapses containing the GLR-1 glutamate receptor is held constant despite marked changes in neurite length. The coupling of synapse number to neurite length requires both CaMKII and voltage-gated calcium channels. CaMKII regulates GLR-1 by at least two distinct mechanisms: regulating transport of GLR-1 from cell bodies to neurites; and regulating the addition or maintenance of GLR-1 to postsynaptic elements.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hebb,D. The Organization of Behavior (Wiley, New York, 1949).
Stevens,C., Tonegawa,S. & Wang,Y. The role of calcium-calmodulin kinase II in three forms of synaptic plasticity. Curr. Biol. 4, 687–693 (1994).
Mayford,M., Wang,J., Kandel,E. & O'Dell,T. CaMKII regulates the frequency-response function of hippocampal synapses for the production of both LTD and LTP. Cell 81, 891–904 (1995).
Lisman,J., Malenka,R. C., Nicoll,R. A. & Malinow,R. Learning mechanisms: the case for CaM-KII. Science 276, 2001–2002 (1997).
Wu,G., Malinow,R. & Cline,H. Maturation of a central glutamatergic synapse. Science 274, 972–976 (1996).
Hart,A., Sims,S. & Kaplan,J. A synaptic code for sensory modalities revealed by analysis of the C. elegans GLR-1 glutamate receptor. Nature 378, 82–85 (1995).
Maricq,A. V., Peckol,E., Driscoll,M. & Bargmann,C. glr-1, a C. elegans glutamate receptor that mediates mechanosensory signalling. Nature 278, 78–81 (1995).
Rongo,C., Whitfield,C. W., Rodal,A., Kim,S. K. & Kaplan,J. M. LIN-10 is a shared component of the polarized protein localization pathways in neurons and epithelia. Cell 94, 751–759 (1998).
White,J. G., Southgate,E., Thomson,J. N. & Brenner,S. The structure of the nervous system of Caenorhabditis elegans. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 314, 1–340 (1986).
Sulston,J. E. & Horvitz,H. R. Abnormal cell lineages in mutants of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev. Biol. 82, 41–55 (1981).
Turrigiano,G. G. Homeostatic plasticity in neuronal networks: the more things change, the more they stay the same. Trends Neurosci. 22, 221–227 (1999).
Riddle,D., Blumenthal,T., Meyer,B. & Priess,J. (eds) C. elegans II (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, 1997).
Rao,A. & Craig,A. M. Activity regulates the synaptic localization of the NMDA receptor in hippocampal neurons. Neuron 19, 801–812 (1997).
O'Brien,R. J. et al. Activity-dependent modulation of synaptic AMPA receptor accumulation. Neuron 21, 1067–1078 (1998).
Reiner,D. J., Newton,E. M., Tian,H. & Thomas,J. H. Diverse behavioural defects caused by mutations in Caenorhabditis elegans unc-43 CaM Kinase II. Nature 402, 199–203 (1999).
Fong,Y. L., Taylor,W. L., Means,A. R. & Soderling,T. R. Studies of the regulatory mechanism of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Mutation of threonine 286 to alanine and aspartate. J. Biol Chem 264, 16759–16763 (1989).
Schafer,W. & Kenyon,C. A calcium-channel homologue required for adaptation to dopamine and serotonin in C. elegans. Nature 375, 73–78 (1995).
Lee,R., Lobel,L., Hengartner,M., Horvitz,H. & Avery,L. Mutations in the alpha1 subunit of an L-type voltage-activated Ca2+ channel cause myotonia in Caenorhabditis elegans. EMBO J. 16, 6066–6076 (1997).
Wu,G. Y. & Cline,H. T. Stabilization of dendritic arbor structure in vivo by CaMKII. Science 279, 222–226 (1998).
Nonet,M., Saifee,O., Zhao,H., Rand,J. & Wei,L. Synaptic transmission deficits in Caenorhabditis elegans synaptobrevin mutants. J. Neurosci. 18, 70–80 (1998).
Carroll,R. C., Lissin,D. V., von Zastrow,M., Nicoll,R. A. & Malenka,R. C. Rapid redistribution of glutamate receptors contributes to long-term depression in hippocampal cultures. Nature Neurosci. 2, 454–460 (1999).
Liao,D., Zhang,X., O'Brien,R., Ehlers,M. D. & Huganir,R. L. Regulation of morphological postsynaptic silent synapses in developing hippocampal neurons. Nature Neurosci. 2, 37–43 (1999).
Shi,S. H. et al. Rapid spine delivery and redistribution of AMPA receptors after synaptic NMDA receptor activation. Science 284, 1811–1816 (1999).
Shen,K. & Meyer,T. Dynamic control of CaMKII translocation and localization in hippocampal neurons by NMDA receptor stimulation. Science 284, 162–166 (1999).
Barria,A., Derkach,V. & Soderling,T. Identification of the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II regulatory phosphorylation site in the alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionate-type glutamate receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 32727–32730 (1997).
Mammen,A. L., Kameyama,K., Roche,K. W. & Huganir,R. L. Phosphorylation of the alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid receptor GluR1 subunit by calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase II. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 32528–32533 (1997).
Kim,J. H. & Huganir,R. L. Organization and regulation of proteins at synapses. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 11, 248–254 (1999).
Acknowledgements
We thank D. Reiner and J. Thomas for sharing unpublished data. In addition, we thank M. Kennedy, H. Schulman, A. Fire, R. Barstead, A. Hart, J. Mendel, C. Mello and V. Maricq for providing plasmids and antibodies, and the C. elegans genome sequencing consortium for providing sequence. Some strains were provided by the C. elegans Genetics Center. We thank T. Serafini, E. Isacoff, G. Garriga and members of the Kaplan lab for comments on the manuscript. This work was supported by grants from the NIH and the Pew Charitable Trust (J.K.) and by a fellowship from Jane Coffin Childs (C.R.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rongo, C., Kaplan, J. CaMKII regulates the density of central glutamatergic synapses in vivo. Nature 402, 195–199 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/46065
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/46065
This article is cited by
-
Investigations of brain-wide functional and structural networks of dopaminergic and CamKIIα-positive neurons in VTA with DREADD-fMRI and neurotropic virus tracing technologies
Journal of Translational Medicine (2023)
-
UNC-43/CaMKII-triggered anterograde signals recruit GABAARs to mediate inhibitory synaptic transmission and plasticity at C. elegans NMJs
Nature Communications (2023)
-
TRPM7 Mediates Neuronal Cell Death Upstream of Calcium/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase II and Calcineurin Mechanism in Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury
Translational Stroke Research (2021)
-
NMDAR-mediated modulation of gap junction circuit regulates olfactory learning in C. elegans
Nature Communications (2020)
-
Stochastic Turing Pattern Formation in a Model with Active and Passive Transport
Bulletin of Mathematical Biology (2020)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.