Abstract
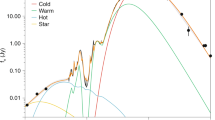
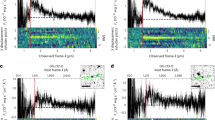
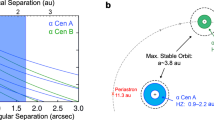
BROWN dwarfs lie in the mass range between the most massive Jupiter-like planets and the least massive stars. They are much less luminous than stars, and so may provide a fraction of the baryonic dark matter in our Galaxy. Only one unambiguous detection of a brown dwarf has been made to date1–6—G1229B, a low-mass companion to the nearby star G1229A. The detection4 of strong methane-band absorption in the spectrum of G1229B, a feature restricted to cool substellar objects5–9, lends weight to the idea7 that differential methane-band imaging (the subtraction of an image taken in the methane band from a continuum-light image taken in the same spectral region) should provide an efficient method for detecting brown dwarfs. Here we demonstrate the potential of this approach by obtaining an image of G1229B with less than two minutes of integration time. This technique promises efficient detection of both isolated brown dwarfs in crowded regions, and brown dwarfs orbiting close to their primary stars.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Geballe, T. R., Kulkarni, S. R., Woodward, C. E. & Sloan, G. C. Astrophys. J. 467, L101–L104 (1996).
Matthews, K., Nakajima, T., Kulkarni, S. R. & Oppenheimer, B. R. Astron. J. (in the press).
Nakajima, T. et al. Nature 378, 463–465 (1995).
Oppenheimer, B. R., Kulkarni, S. R., Matthews, K. & Nakajima, T. Science 270, 1478–1479 (1995).
Allard, R., Hauschildt, P. H., Baraffe, I. & Chabrier, G. Astrophys. J. 465, L123–L127 (1996).
Marley, M. S. et al. Science 272, 1919–1921 (1996).
Smith, W. H. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pacif. 99, 1344–1353 (1987).
Tsuji, T. Annu. Tokyo Astron. Observatory Ser. II 9, 1 (1964).
Tsuji, T., Ohnaka, K., Aoki, W. & Nakajima, T. Astron. Astrophys. 308, 29–32 (1996).
Alcock, C. et al. Astrophys. J. 461, 84–103 (1996).
Flynn, C., Gould, A. & Bahcall, J. N. Astrophys. J. 466, L55–L58 (1996).
Bahcall, J. N., Flynn, C., Gould, A. & Kirhakos, S. Astrophys. J. 435, L51–L54 (1994).
Kuijken, K. & Gilmore, G. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 239, 651–664 (1989).
Bahcall, J. N. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 24, 577–611 (1986).
Jones, H. R. A., Longmore, A. J., Jameson, R. F. & Mountain, C. M. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 267, 413–423 (1994).
Angel, J. R. P., Cheng, A. Y. S. & Woolf, N. J. Nature 322, 341–343 (1986).
Burke, B. F. Nature 322, 340–341 (1986).
Owen, T. Strategies for the Search for Life in the Universe (ed. Papagiannis, M. D.) 177–185 (Reidel, Dordrecht, 1980).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosenthal, E., Gurwell, M. & Ho, P. Efficient detection of brown dwarfs using methane-band imaging. Nature 384, 243–244 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/384243a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/384243a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.