Abstract
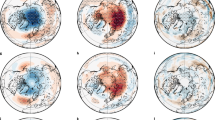
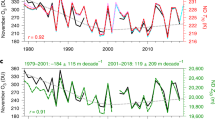
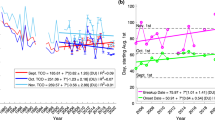
OBSERVATIONS of air temperatures in the lower stratosphere from 1979 to 1990 reveal a cooling trend that varies both spatially and seasonally1. The possible causes of this cooling include changes in concentrations of ozone or of other greenhouse gases2,3, and entirely natural variability, but the relative contributions of such causes are poorly constrained. Here we incorporate the observed decreases in stratospheric ozone concentrations4 over the same period into a general circulation model of the atmosphere, to investigate the role of the ozone losses in affecting patterns of temperature change. We find that the simulated latitudinal pattern of lower-stratospheric cooling for a given month through the decade corresponds well with the pattern of the observed decadal temperature changes. This result confirms the expectation, from simpler model studies2,3,5, that the observed ozone depletion exerts a spatially and seasonally varying fingerprint in the decadal cooling of the lower stratosphere, with the influence of increases in concentrations of other greenhouse gases being relatively small. As anthropogenic halocarbon chemicals are important causes of stratospheric ozone depletion2,3, our study suggests a human influence on the patterns of temperature change in the lower stratosphere over this 11-year period.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Randel, W. J. & Cobb, J. B. J. Geophys. Res. 99, 5433–5447 (1994).
Scientific Assessment of Ozone Depletion: 1991, Global Ozone Research and Monitoring Project Rep. No. 25 Ch. 7 & 8 (WMO, Geneva, Switzerland, 1992).
Scientific Assessment of Stratospheric Ozone Change: 1994, Global Ozone Research and Monitoring Project Rep. No. 37 Ch. 8 (WMO, Geneva, Switzerland, 1995).
Stolarski, R. S., Bloomfield, P., McPeters, R. D. & Herman, J. R. Geophys. Res. Lett. 18, 1015–1018 (1991).
McCormack, P. & Hood, L. L. Geophys. Res. Lett. 21, 1615–1618 (1994).
Ramanathan, V. & Dickinson, R. E. J. Atmos. Sci. 36, 1084–1104 (1979).
Fels, S. B., Mahlman, J. D., Schwarzkopf, M. D. & Sinclair, R. W. J. Atmos. Sci. 37, 2265–2297 (1980).
Shine, K. P. Geophys. Res. Lett. 13, 1331–1334 (1986).
Kiehl, J. T., Boville, B. A. & Briegleb, B. P. Nature 332, 501–504 (1988).
Mahlman, J. D., Pinto, J. P. & Umscheid, L. J. J. Atmos. Sci. 51, 489–508 (1994).
Hansen, J. et al. Clim. Change 30, 103–117 (1995).
Ramaswamy, V., Schwarzkopf, M. D. & Shine, K. P. Nature 355, 810–812 (1992).
Hamilton, K. et al. J. Atmos. Sci. 52, 5–43 (1995).
Lacis, A., Wuebbles, D. & Logan, J. A. J. Geophys. Res. 95, 9971–9981 (1990).
Schwarzkopf, M. D. & Ramaswamy, V. Geophys. Res. Lett. 20, 205–208 (1993).
McCormick, M. P., Veiga, R. E. & Chu, W. P. Geophys. Res. Lett. 18, 1015–1018 (1992).
Randel, W. J. Tech. Note NCA/TN-295 + STR (National Center for Atmospheric Res., Boulder, Colorado, USA, 1987).
Labitzke, K. & van Loon, H. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn 73, 883–889 (1995).
Oort, A. H. & Liu, H. J. Clim. 6, 292–307 (1993).
Labitzke, K. & van Loon, H. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn 72, 1–10 (1994).
Angell, J. K. J. Clim. 1, 1296–1313 (1988).
Ramaswamy, V. & Bowen, M. M. J. Geophys. Res. 99, 18909–18921 (1994).
Shine, K. P., Derwent, R. G., Wuebbles, D. J. & Morcrett, J.-J. in Climate Change: The IPCC Scientific Assessment (eds Houghton, J. T. et al.) 41–68 (Cambridge Univ. Press, 1990).
Scientific Assessment of Stratospheric Ozone Change: 1985, Global Ozone Research and Monitoring project Rep. No. 16 Ch. 15 (WMO, Geneva, Switzerland 1986).
Christy, J. R. Clim. Change 31, 455–474 (1995).
Ramanathan, V., Cicerone, R. J., Singh, H. B. & Kiehl, J. T. J. Geophys. Res. 90, 5547–5566 (1985).
Miller, A. J. et al. Geophys. Res. Lett. 19, 929–932 (1992).
Chanin, M.-L. in The Role of the Stratosphere in Global Change (ed. Chanin, M.-L.) 301–317 (NATO ASI Ser. I, Global Environ. Change, Vol. 8, Springer, Berlin, 1993).
Sun, D.-Z. & Oort, A. H. J. Clim. 8, 1974–1987 (1995).
Santer, B. et al. Nature 382, 39–46 (1996).
Vinnikov, K., Robock, A., Stouffer, R. J. & Manabe, S. Geophys. Res. Lett. 23, 1801–1804 (1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramaswamy, V., Schwarzkopf, M. & Randel, W. Fingerprint of ozone depletion in the spatial and temporal pattern of recent lower-stratospheric cooling. Nature 382, 616–618 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/382616a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/382616a0
This article is cited by
-
To what extent can the ozone valley over the Tibetan Plateau influence the East Asian summer precipitation?
npj Climate and Atmospheric Science (2023)
-
The Role of Ozone Depletion in the Lack of Cooling in the Antarctic Upper Stratosphere during Austral Winter
Advances in Atmospheric Sciences (2023)
-
Surface ocean current variations in the North Pacific related to Arctic stratospheric ozone
Climate Dynamics (2022)
-
Evaluating the Ozone Valley over the Tibetan Plateau in CMIP6 Models
Advances in Atmospheric Sciences (2022)
-
Southern-Hemisphere high-latitude stratospheric warming revisit
Climate Dynamics (2020)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.