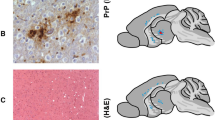
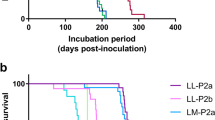
Abstract
ORIGINALLY described by Lugaresi et al. in 1986 (ref. 1), fatal familial insomnia (FFI) is a rare inherited neurological disease characterized by the subacute progression of intractable insomnia and other autonomic abnormalities, cerebellar and pyramidal signs, myoclonus and dementia; neuropathologically, the major feature is severe neuronal loss with associated gliosis in the ventral and mediodorsal thalamic nuclei. The disease has been related to the group of spongiform encephalopathies by virtue of the presence of low levels of proteinase-resistant amyloid protein (PrPres) in the brain2á¤-4, and of a pathogenic single-allele mutation at codon 178 of the PRNP gene that encodes PrF68 (refs 2, 5). Here we report the successful transmission of the disease to experimental animals, placing FFI within the group of infectious cerebral amyloidoses.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lugaresi, E. et al. New Engl. J. Med. 315, 997–1003 (1986).
Medori, R. et al. New Engl. J. Med. 326, 444–449 (1992).
Monari, L. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 91, 2839–2842 (1994).
Brown, P. et al. Ann. Neurol. 38, 245–253 (1995).
Goldfarb, L. G. et al. Science 258, 806–808 (1992).
Bosque, P. J., Vnencak-Jones, C. L., Johnson, M. D., Whitlock, J. A. & McLean, M. J. Neurology 42, 1864–1870 (1992).
Reder, A. T. et al. Neurology 45, 1068–1075 (1995).
Kitamoto, T. et al. Am. J. Path. 140, 1285–1294 (1992).
Muramoto, T., Kitamoto, T., Tateishi, J. & Goto, I. Brain Res. 599, 309–316 (1992).
Tateishi, J. et al. Acta neuropath. 53, 161–163 (1981).
Muramoto, T., Kitamoto, T., Tateishi, J. & Goto, l. Am. J. Path. 140, 1411–1420 (1992).
Little, B., Brown, P. W., Rodgers-Johnson, P., Perl, D. P. & Gajdusek, D. C. Ann. Neurol. 20, 231–239 (1986).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tateishi, J., Brown, P., Kitamoto, T. et al. First experimental transmission of fatal familial insomnia. Nature 376, 434–435 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/376434a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/376434a0
This article is cited by
-
Non-human primates in prion diseases
Cell and Tissue Research (2023)
-
Phenotypic diversity of genetic Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease: a histo-molecular-based classification
Acta Neuropathologica (2021)
-
Huntington’s disease: lessons from prion disorders
Journal of Neurology (2021)
-
Familial human prion diseases associated with prion protein mutations Y226X and G131V are transmissible to transgenic mice expressing human prion protein
Acta Neuropathologica Communications (2018)
-
Lysosomal Quality Control in Prion Diseases
Molecular Neurobiology (2018)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.