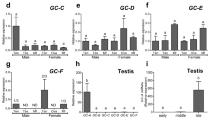
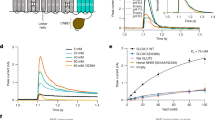
Abstract
Guanylate cyclase has been strongly implicated as a cell-surface receptor on spermatozoa for a chemotactic peptide1, and on various other cells as a receptor for atrial natriuretic peptides2–4. Resact (Cys-Val-Thr-Gly-Ala-Pro-Gly-Cys-Val-Gly-Gly-Gly-Arg-Leu-NH2), the chemotactic peptide released by sea urchin Arbacia punctulata eggs, is specifically crosslinked to A. punctulata spermatozoan guanylate cyclase1. After the binding of the peptide the state of guanylate cyclase phosphorylation modulates enzyme activity1,5,6. We report here that the deduced amino-acid sequence of the spermatozoan membrane form of guanylate cyclase predicts an intrinsic membrane protein of 986 amino acids with an amino-terminal signal sequence. A single transmembrane domain separates the protein into putative extracellular and cytoplasmic-catalytic domains. The cytoplasmic carboxyl-terminal 95 amino acids contain 20% serine, the likely regulatory sites for phosphory-lation. Unexpectedly, the enzyme is homologous to the protein kinase family.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shimotnura, H., Dangott, L. J. & Garbers, D. L. J. biol. Chem. 261, 15778–15782 (1986).
Kuno, T. et al. J. biol. Chem. 261, 5817–5823 (1986).
Paul, A. K., Marala, R. B., Jaiswal, R. K. & Sharma, R. K. Science 235, 1224–1226 (1987).
Takayanagi, R. et al. J. biol. Chem. 262, 12104–12113 (1986).
Bentley, J. K., Shimomura, H. & Garbers, D. L. Cell 45, 281–288 (1986).
Bentley, J. K., Tubb, D. J. & Garbers, D. L. J. biol. Chem. 261, 14859–14862 (1986).
Radany, E. W., Gerzer, R. & Garbers, D. L. J. biol. Chem. 253, 8346–8351 (1983).
IUPAC-IUB Committee on Biochemical Nomenclature, Biochem. J. 113, 1 (1969).
Ward, G. E., Garbers, D. L. & Vacquier, V. D. Science 227, 768–770 (1985).
Suzuki, N. et al. J. biol. Chem. 259, 14874–14879 (1984).
Ward, G. E. & Vacquier, V. D. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80, 5578–5582 (1983).
Kozak, M. Nucleic. Acids Res. 9, 5233–5262 (1981).
Watson, M. E. E. Nucleic Acids Res. 12, 5145–5164 (1984).
Sabatini, D. D., Kreibich, G., Morimoto, T. & Adesnik, M. J. Cell Biol. 92, 1–22 (1982).
Ramarao, C. S. & Garbers, D. L. J. biol. Chem. 263, 1524–1529 (1988).
Kataoka, T., Broek, D. & Wigler, M. Cell 43, 493–505 (1985).
Aiba, H., Mori, K., Tanaka, M., Ooi, T., Roy, A. & Danchin, A. Nucleic Acids Res. 12, 9427–9440 (1984).
Hunter, T. & Cooper, J. A. in The Enzymes (eds Boyer, P. D. & Krebs; E. G.) 17, 191–246 (Academic, New York, 1986).
Hunter, T. Cell 50, 823–829 (1987).
Knopf, J. L. et al. Cell 46, 491–502 (1986).
Yarden, Y. et al. Nature 323, 226–232 (1986).
Roebroek, A. J. M. et al. EMBO J. 4, 2897–2903 (1985).
Watson, R., Oskarsson, M. & Van Woude, G. F. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 4078–3082 (1982).
Hanks, S. K., Quinn, A. M. & Hunter, T. Science 241, 42–52 (1988).
Garbers, D. L. & Murad, F. Adv. Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 10, 57–67 (1979).
McLean, J. W. et al. Nature 330, 132–137 (1987).
Sanger, F., Couison, A. R., Barrell, B. G., Smith, A. J. H. & Roe, B. A. J. molec. Biol. 143, 161–178 (1980).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, S., Lowe, D., Thorpe, D. et al. Membrane guanylate cyclase is a cell-surface receptor with homology to protein kinases. Nature 334, 708–712 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1038/334708a0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/334708a0
This article is cited by
-
Natriuretic peptides appeared after their receptors in vertebrates
BMC Evolutionary Biology (2019)
-
Ca2+ efflux via plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase mediates chemotaxis in ascidian sperm
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Natriuretic peptide type C induces sperm attraction for fertilization in mouse
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Phototaxis and chemotaxis of brown algal swarmers
Journal of Plant Research (2017)
-
Membrane guanylate cyclase is a beautiful signal transduction machine: overview
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2010)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.