Abstract
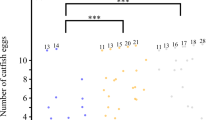
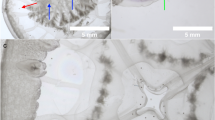
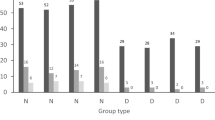
Brood parasitism, where a brood of the parasitic species is fostered by the parents of another species, is well known among birds1. In most cases, such offspring show a complete reliance upon their host parents for food, protection and warmth until their independence. In other vertebrate groups, however, such total dependence upon a host species is unknown. I report here the first example of true brood parasitic behaviour discovered among fishes. In Lake Tanganyika, an endemic mochokid catfish, Synodontis multipunctatus Boulenger, is a brood parasite of mouthbrooding fishes of the family Cichlidae. The eggs of the catfish are incubated in the mouths of any of several host species together with the host's eggs, but hatch earlier. Following absorption of their yolk sacs, the catfish fry feed upon the fry of the host while still in its mouth. Thus the early stages of development of this catfish not only depend upon their hosts for food and protection, but exploit almost their entire parental investment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Payne, R. B. A. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 8, 1–28 (1977).
Keenleyside, M. H. A. Diversity and Adaptation in Fish Behaviour (Springer, Berlin, 1979).
Baerends, G. P. & Baerends-Van-Roon, J. M. Behaviour Suppl. 1 (1950).
Fryer, G. & Iles, T. D The Cichlid Fishes of the Great Lakes of Africa (Oliver & Boyd, Edinburgh, 1972).
Brichard, P. Buntbar. Bull. 74, 10–12 (1979).
Ferguson, J. Buntbar. Bull. 98, 13–16 (1983).
Finley, L. Buntbar. Bull. 98, 17–18 (1983).
Finley, L. Freshwater and Marine Aquarium 7(6), 22–25, 63, 66–75 (1984).
Goff, G. P. Copeia 1984, 149–152 (1984).
McKaye, K. R. Am. Nat. 111, 301–315 (1977).
McKaye, K. R. in Natural Selection and Social Behavior (eds Alexander, R. & Tinkle, D.) 173–183 (Chiron, New York, 1981).
McKaye, K. R. Oecologia 66, 358–363 (1985).
Ribbink, A. J. Nature 267, 243–244 (1977).
Ribbink, A. J., Marsh, A. C., Marsh, B. & Sharp, B. J. S. Afr. J. Zool. 15, 1–6 (1980).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sato, T. A brood parasitic catfish of mouthbrooding cichlid fishes in Lake Tanganyika. Nature 323, 58–59 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1038/323058a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/323058a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.