Abstract
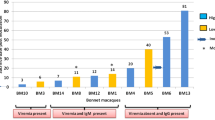
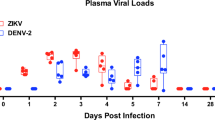
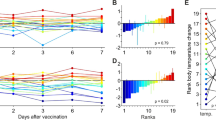
Acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) has become a worldwide epidemic1–6, so the development of vaccines and antiviral agents effective against the causative agent, human T-lymphotropic virus type III (HTLV-III), is vital. This work would be greatly simplified if a suitable animal model could be developed. Here we report the isolation of an HTLV-III-related retrovirus, STLV-III/Delta, from rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta) with transmissible simian AIDS (SAIDS) and from asymptomatic sooty mangabeys (Cercocebus atys). SAIDS was initially diagnosed in several macaques previously inoculated with tissue homogenates of mangabey origin. Western blot analysis of both the mangabey and macaque sera demonstrated the presence of antibody cross-reactive primarily with the HTLV-III proteins p24 and p61. In a related experiment, analysis of these same sera revealed simian antibody to STLV-III/Delta proteins similar, but not identical, to those of HTLV-III with estimated relative molecular masses (Mrs) of 16,000 (16K), 26K, 35K, 45K, 60K and 110K. Infection of the mangabey, an African primate, with an HTLV-III-related virus may provide a clue to the origin of HTLV-III in humans. The apparent difference in susceptibility to SAIDS-like disease between infected macaques and mangabeys suggests that these species may respond differently to STLV-III infection.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gottlieb, M. et al. New Engl. J. Med. 305, 1425–1430 (1981).
Masur, H. et al. New Engl. J. Med. 305, 1431–1438 (1981).
Siegal, F. et al. New Engl. J. Med. 305, 1439–1444 (1981).
Lane, H. et al. New Engl. J. Med. 309, 453–458 (1983).
Ziegler, J. et al. New Engl. J. Med. 311, 565–570 (1984).
Goldsmith, M. F. J. Am. med. Ass. 253, 3369–3384 (1985).
Wolf, R. H. et al. Science 227, 529–531 (1985).
Baskin, G. B. et al. J. natn. Cancer Inst. (in the press).
Hahn, B. H. et al. Nature 312, 166–169 (1984).
Saxinger, C. et al. in Human T-Cell Leukemia/Lymphoma Virus (eds Galio, R. C. et al.) 323–330 (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York, 1983).
Kanki, P. J. et al. Science 228, 1199–1200 (1985).
Daniel, M. D. et al. Science 228, 1201–1204 (1985).
Kanki, P. J. et al. Lancet ii, 1330–1332 (1985).
Kanki, P. J., Alroy, J. & Effex, M. Science 230, 951–954 (1985).
Martin, L. N. et al. Adv. vet. Sci. comp. Med. 28, 201–236 (1984).
Montelaro, R. C., Lohfey, N., Tarekh, B., Blakeney, E. & Issel, C. J. Virol. 42, 1029–1038 (1982).
Montelaro, R. C., Tarekh, B., Orrego, A. & Issel, C. J. biol. Chem. 259, 10539–10544 (1984).
Burnett, W. N. Analyt. Biochem. 112, 195–203 (1981).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murphey-Corb, M., Martin, L., Rangan, S. et al. Isolation of an HTLV-III-related retrovirus from macaques with simian AIDS and its possible origin in asymptomatic mangabeys. Nature 321, 435–437 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1038/321435a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/321435a0
This article is cited by
-
Opioid abuse and SIV infection in non-human primates
Journal of NeuroVirology (2023)
-
Statin treatment prevents the development of pulmonary arterial hypertension in a nonhuman primate model of HIV-associated PAH
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Resistance to simian immunodeficiency virus low dose rectal challenge is associated with higher constitutive TRIM5α expression in PBMC
Retrovirology (2014)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.