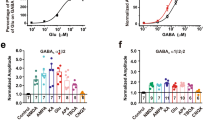
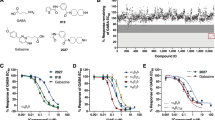
Abstract
L-Glutamic acid (Glu) and L-aspartic acid (Asp) are putative excitatory transmitters in the mammalian central nervous system (CNS)1–3. Receptors at Glu- and Asp-mediated synapses are presumably different4,5, and a prerequisite for the identification and characterisation of such sites is the availability of specific antagonists and agonists. Among various potential Glu and Asp antagonists3–6 Glu diethyl ester (GDEE)7–9 and (D)-α-aminoadipic acid (α-AA)9–13 show some selectivity, the latter particularly towards excitation by N-methyl-Asp. Kainic acid (KA), a structural analogue of Glu, is a powerful excitant of CNS neurones14–16 that seems to interact with only a small proportion of Glu receptors5. Ibotenic acid (Ibo) is a powerful neuronal excitant9,17,18 also structurally related to Glu. Excitation by Ibo, however, is readily antagonised by α-AA, whereas GDEE has little or no effect13, suggesting that Ibo preferentially activates Asp rather than Glu receptors. Furthermore, excitation of neurones by Ibo is followed by a prolonged depression of excitability18,19 which is sensitive to bicuculline methochloride19, indicating that Ibo is probably converted by decarboxylation into muscimol20 during microelectrophoretic ejection near CNS neurones. Thus, neither KA nor Ibo seem to have sufficient specificity to be useful compounds with which to study central Glu or Asp receptors. We describe here a new class of Glu agonist obtained by structural manipulation of Ibo (Table 1). Elongation of the side chain of Ibo by an additional methylene group and introduction of different ring substituents have led to isoxazole amino acids with carboxyl groups resistant to decarboxylation. A further aim of this homologation was to convert the apparent Asp agonist Ibo into a Glu agonist.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
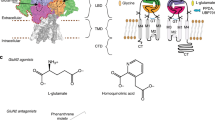
References
Curtis, D. R. & Johnston, G. A. R. Ergebn. Physiol. 69, 97–188 (1974).
Krnjević, K. Physiol. Rev. 54, 418–540 (1974).
Curtis, D. R. in Glutamic Acid: Advances in Biochemistry and Physiology (eds Filer, L. J. Jr et al.) 163–175 (Raven, New York, 1979).
Watkins, J. C. in Kainic Acid as a Tool in Neurobiology (eds McGeer, E. G., Olney, J. W. & McGeer, P. L.) 37–39 (Raven, New York, 1978).
Johnston, G. A. R. in Glutamic Acid: Advances in Biochemistry and Physiology (eds Filer, L. J. Jr et al.) 177–185 (Raven, New York, 1979).
McLennan, H. in Handbook of Psychopharmacology Vol. 4 (eds Iversen, L. L., Iversen, S. D. & Snyder, S. H.) 211–228 (Plenum, New York, 1975).
Curtis, D. R. et al. Brain Res. 41, 283–301 (1972).
Haldeman, S. & McLennan, H. Brain Res. 45, 393–400 (1972).
Hall, J. G., Hicks, T. P., McLennan, H., Richardson, T. L. & Wheal, H. V. J. Physiol., Lond. 286, 29–39 (1979).
Biscoe, T. J. et al. Eur. J. Pharmac. 45, 315–316 (1977).
Biscoe, T. J. et al. Brain Res. 148, 543–548 (1978).
Lodge, D., Headley, P. M. & Curtis, D. R. Brain Res. 153, 603–608 (1978).
McLennan, H. & Lodge, D. Brain Res. 169, 83–90 (1979).
Shinozaki, H. & Konishi, S. Brain Res. 24, 368–371 (1970).
Johnston, G. A. R., Curtis, D. R., Davies, J. & McCulloch, R. M. Nature 248, 804 (1974).
Biscoe, T. J., Evans, R. H., Headley, P. M., Martin, M. R. & Watkins, J. C. Br. J. Pharmac. 58, 373–382 (1976).
Johnston, G. A. R., Curtis, D. R., de Groat, W. C. & Duggan, A. W. Biochem. Pharmac. 17, 2488–2489 (1968).
MacDonald, J. F. & Nistri, A. J. Physiol., Lond. 275, 449–465 (1978).
Curtis, D. R., Lodge, D. & McLennan, H. J. Physiol., Lond. 291, 19–28 (1979).
Eugster, C. H. Fortschr. Chem. org. Natstoffe 27, 261–321 (1969).
Curtis, D. R., Duggan, A. W., Felix, D. & Johnston, G. A. R. Brain Res. 32, 69–96 (1971).
Simon, J. R., Contrera, J. F. & Kuhar, M. J. J. Neurochem. 26, 141–147 (1976).
Krogsgaard-Larsen, P., Hjeds, H., Curtis, D. R., Lodge, D. & Johnston, G. A. R. J. Neurochem. 32, 1717–1724 (1979).
Hansen, J. J. & Krogsgaard-Larsen, P. JCS Commun. 87–88 (1979).
Christensen, S. B. & Krogsgaard-Larsen, P. Acta chem. scand. B32, 27–30 (1978).
Honoré, T. & Lauridsen, J. Acta chem. scand. (in the press).
Krogsgaard-Larsen, P., Johnston, G. A. R., Curtis, D. R., Game, C. J. A. & McCulloch, R. M. J. Neurochem. 25, 803–809 (1975).
Johnston, G. A. R., Kennedy, S. M. E. & Twitchin, B. J. Neurochem. 32, 121–127 (1979).
London, E. D. & Coyle, J. T. Molec. Pharmac. 15, 492–505 (1979).
Balcar, V. J., Johnston, G. A. R. & Stephanson, A. L. Brain Res. 102, 143–151 (1976).
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L. & Randall, R. J. J. biol. Chem. 193, 265–275 (1951).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krogsgaard-Larsen, P., Honoré, T., Hansen, J. et al. New class of glutamate agonist structurally related to ibotenic acid. Nature 284, 64–66 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1038/284064a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/284064a0
This article is cited by
-
The 1980s: d-AP5, LTP and a Decade of NMDA Receptor Discoveries
Neurochemical Research (2019)
-
Transitions between asynchronous and synchronous states: a theory of correlations in small neural circuits
Journal of Computational Neuroscience (2018)
-
Investigating dynamic structural and mechanical changes of neuroblastoma cells associated with glutamate-mediated neurodegeneration
Scientific Reports (2014)
-
Analogues of 3-Hydroxyisoxazole-Containing Glutamate Receptor Ligands Based on the 3-Hydroxypyrazole-Moiety: Design, Synthesis and Pharmacological Characterization
Neurochemical Research (2014)
-
A Metabolomic Approach to Ionotropic Glutamate Receptor Subtype Function: A Nuclear Magnetic Resonance in vitro Investigation
Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism (2006)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.