Abstract
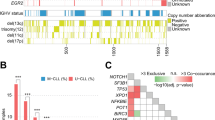
Prognostic predictions in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) at early clinical stage are based on biological disease parameters, such as ZAP-70 and CD38 protein levels, genomic aberrations as well as immunoglobulin variable heavy chain gene (IgVH) mutation status. In the current study, ZAP-70 and CD38 expressions were examined by flow cytometry in 252 patients with B-CLL. Cytoplasmic ZAP-70 expression in more than 20% (ZAP-70+) and surface CD38 expression on more than 30% (CD38+) of B-CLL cells were associated with an unfavorable clinical course. The levels of ZAP-70 and CD38 did not change over time in the majority of patients where sequential samples were available for analysis. Combined analysis of ZAP-70 and CD38 yielded discordant results in 73 patients (29.0%), whereas 120 patients (47.6%) were concordantly negative and 59 patients (23.4%) were concordantly positive for ZAP-70 and CD38 expression. Median treatment-free survival times in patients whose leukemic cells were ZAP-70+CD38+ was 30 months as compared to 130 months in patients with a ZAP-70−CD38− status. In patients with discordant ZAP-70/CD38 results, the median treatment-free survival time was 43 months. Thus, ZAP-70 and CD38 expression analyses provided complementary prognostic information identifying three patient subgroups with good, intermediate and poor prognosis. Over-representation of high-risk genomic aberrations such as 17p deletion or 11q deletion and distribution of the IgVH mutation status in B-CLL discordant for ZAP-70/CD38 pointed toward a distinct biologic background of the observed disease subgroups. This finding was also supported by microarray-based gene expression profiling in a subset of 35 patients. The expression of 37 genes differed significantly between the three groups defined by their expression of ZAP-70 and CD38, including genes that are involved in regulation of cell survival and chemotherapy resistance.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Keating MJ, Chiorazzi N, Messmer B, Damle RN, Allen SL, Rai KR et al. Biology and Treatment of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. ASH Educational Book. The American Society of Hematology: Washington, DC, 2003, pp 153–175.
Dighiero G, Binet JL . When and how to treat chronic lymphocytic leukemia? N Engl J Med 2000; 343: 1799–1802.
Shanafelt TD, Geyer SM, Kay NE . Prognosis at diagnosis: integrating molecular biologic insights into clinical practice for patients with CLL. Blood 2004; 103: 1202–1210.
Rai KR, Sawitsky A, Cronkite EP, Chanana AD, Levy RN, Pasternack BS . Clinical staging of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1975; 46: 219–234.
Binet JL, Auquier A, Dighiero G, Chastang C, Piguet H, Goasguen J et al. A new prognostic classification of chronic lymphocytic leukemia derived from a multivariate survival analysis. Cancer 1981; 48: 198–206.
Hamblin TJ, Davis Z, Gardiner A, Oscier DG, Stevenson FK . Unmutated Ig V(H) genes are associated with a more aggressive form of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1999; 94: 1848–1854.
Damle RN, Wasil T, Fais F, Ghiotto F, Valetto A, Allen SL et al. Ig V gene mutation status and CD38 expression as novel prognostic indicators in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1999; 94: 1840–1847.
Rosenwald A, Alizadeh AA, Widhopf G, Simon R, Davis RE, Yu X et al. Relation of gene expression phenotype to immunoglobulin mutation genotype in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Exp Med 2001; 194: 1639–1647.
Wiestner A, Rosenwald A, Barry TS, Wright G, Davis RE, Henrickson SE et al. ZAP-70 expression identifies a chronic lymphocytic leukemia subtype with unmutated immunoglobulin genes, inferior clinical outcome, and distinct gene expression profile. Blood 2003; 101: 4944–4951.
Chen L, Widhopf G, Huynh L, Rassenti L, Rai KR, Weiss A et al. Expression of ZAP-70 is associated with increased B-cell receptor signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2002; 100: 4609–4614.
Chen L, Apgar J, Huynh L, Dicker F, Giago-McGahan T, Rassenti L et al. ZAP-70 directly enhances IgM signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2005; 105: 2036–2041.
Crespo M, Bosch F, Villamor N, Bellosillo B, Colomer D, Rozman M et al. ZAP-70 expression as a surrogate for immunoglobulin-variable-region mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 1764–1775.
Orchard JA, Ibbotson RE, Davis Z, Wiestner A, Rosenwald A, Thomas PW et al. ZAP-70 expression and prognosis in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Lancet 2004; 363: 105–111.
Rassenti LZ, Huynh L, Toy TL, Chen L, Keating MJ, Gribben JG et al. ZAP-70 compared with immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene mutation status as a predictor of disease progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 2004; 351: 893–901.
Dürig J, Nückel H, Cremer M, Fuhrer A, Halfmeyer K, Fandrey J et al. ZAP-70 expression is a prognostic factor in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2003; 17: 2426–2434.
Schroers R, Pukrop T, Dürig J, Haase D, Dührsen U, Trümper L et al. B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia with aberrant CD8 expression: genetic and immunophenotypic analysis of prognostic factors. Leuk Lymphoma 2004; 45: 1677–1681.
Hamblin TJ, Orchard JA, Ibbotson RE, Davis Z, Thomas PW, Stevenson FK et al. CD38 expression and immunoglobulin variable region mutations are independent prognostic variables in chronic lymphocytic leukemia, but CD38 expression may vary during the course of the disease. Blood 2002; 99: 1023–1029.
Deaglio S, Capobianco A, Bergui L, Dürig J, Morabito F, Dührsen U et al. CD38 is a signaling molecule in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Blood 2003; 102: 2146–2155.
Cheson BD, Bennett JM, Rai KR, Grever MR, Kay NE, Schiffer CA et al. Guidelines for clinical protocols for chronic lymphocytic leukemia: recommendations of the National Cancer Institute-sponsored working group. Am J Hematol 1988; 29: 152–163.
Dürig J, Naschar M, Schmücker U, Renzing-Kohler K, Holter T, Hüttmann A et al. CD38 expression is an important prognostic marker in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Leukemia 2002; 16: 30–35.
Matthews C, Catherwood M, Morris TC, Alexander HD . Routine analysis of IgVH mutational status in CLL patients using BIOMED-2 standardized primers and protocols. Leuk Lymphoma 2004; 45: 1899–1904.
van Dongen JJ, Langerak AW, Bruggemann M, Evans PA, Hummel M, Lavender FL et al. Design and standardization of PCR primers and protocols for detection of clonal immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor gene recombinations in suspect lymphoproliferations: report of the BIOMED-2 Concerted Action BMH4-CT98-3936. Leukemia 2003; 17: 2257–2317.
Dürig J, Nückel H, Huttmann A, Kruse E, Holter T, Halfmeyer K et al. Expression of ribosomal and translation-associated genes is correlated with a favorable clinical course in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2003; 101: 2748–2755.
Tusher VG, Tibshirani R, Chu G . Significance analysis of microarrays applied to the ionizing radiation response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 5116–5121.
Döhner H, Stilgenbauer S, Benner A, Leupolt E, Kröber A, Bullinger L et al. Genomic aberrations and survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 2000; 343: 1910–1916.
Ibrahim S, Keating M, Do KA, O’Brien S, Huh YO, Jilani I et al. CD38 expression as an important prognostic factor in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2001; 98: 181–186.
Ghia P, Guida G, Stella S, Gottardi D, Geuna M, Strola G et al. The pattern of CD38 expression defines a distinct subset of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patients at risk of disease progression. Blood 2003; 101: 1262–1269.
Ghia P, Guida G, Scielzo C, Geuna M, Caligaris-Cappio F . CD38 modifications in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: are they relevant? Leukemia 2004; 18: 1733–1735.
de Veer MJ, Holko M, Frevel M, Walker E, Der S, Paranjape JM et al. Functional classification of interferon-stimulated genes identified using microarrays. J Leukoc Biol 2001; 69: 912–920.
Zaki M, Douglas R, Patten N, Bachinsky M, Lamb R, Nowell P et al. Disruption of the IFN-gamma cytokine network in chronic lymphocytic leukemia contributes to resistance of leukemic B cells to apoptosis. Leuk Res 2000; 24: 611–621.
Friedberg JW, Dong DA, Li S, Kim H, Stephans K, Noonan K et al. Oral fludarabine has significant activity in patients with previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and leads to increased STAT1 levels in vivo. Leuk Res 2004; 28: 139–147.
Frank DA, Mahajan S, Ritz J . B lymphocytes from patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia contain signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) 1 and STAT3 constitutively phosphorylated on serine residues. J Clin Invest 1997; 100: 3140–3148.
Lage H, Perlitz C, Abele R, Tampe R, Dietel M, Schadendorf D et al. Enhanced expression of human ABC-transporter tap is associated with cellular resistance to mitoxantrone. FEBS Lett 2001; 503: 179–184.
Izquierdo MA, Neefjes JJ, Mathari AE, Flens MJ, Scheffer GL, Scheper RJ . Overexpression of the ABC transporter TAP in multidrug-resistant human cancer cell lines. Br J Cancer 1996; 74: 1961–1967.
Acknowledgements
We thank Anja Führer, Ute Schmücker, Barbara Friedmann, Sabrina Becker, Frederike von Bonin and Rainer Steffens for excellent technical assistance and Brigitte Fischer for help with compiling patient data. We thank Dres Söling, Siehl, Burghardt, Nusch, Kalhori, Rudolph, Meyer, Detken and Seraphin for referring patients. This study was in part supported by the ‘Ministerium für Schule, Wissenschaft und Erziehung des Landes Nordrhein-Westfalen’. RS is supported by a grant from the Deutsche Krebshilfe (70-3138-Schr 1, Max-Eder-Programm).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Leukemia website (http://www.nature.com/leu)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schroers, R., Griesinger, F., Trümper, L. et al. Combined analysis of ZAP-70 and CD38 expression as a predictor of disease progression in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 19, 750–758 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2403707
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2403707
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Combined analysis of ZAP-70 and CD38 expression in sudanese patients with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia
BMC Research Notes (2019)
-
Evaluation of CD38 expression in Sudanese patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia
BMC Research Notes (2018)
-
Oncogenic microRNA-155 and its target PU.1: an integrative gene expression study in six of the most prevalent lymphomas
International Journal of Hematology (2015)
-
Autoimmune haemolytic anaemia emerging during Campath treatment in a patient with CD5 negative chronic lymphocytic leukaemia
Indian Journal of Hematology and Blood Transfusion (2014)
-
Serum copper is a simple but valuable prognostic marker in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia
International Journal of Hematology (2014)