Abstract
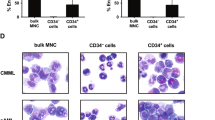
To investigate the mechanisms behind the leukemic expansion of BCR/ABL-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), we examined the cell cycle status of hematopoietic progenitor cells from peripheral blood (PB) and bone marrow (BM) of 37 patients with newly diagnosed BCR/ABL-positive CML. We found a high proportion of 12.51 ± 1.19% of CD34+peripheral blood progenitor cells (PBPC) in S/G2M phase. Comparison of PB and BM from 19 cases revealed similar proliferation rates (10.74 ± 1.41% vs 15.97 ± 1.95%). Furthermore, even primitive CD34+/CD38− PBPC displayed high proliferation rates (17.45 ± 2.98%) in 10 cases examined. In contrast, PBPC from 11 patients with BCR/ABL-negative myeloproliferative disorders were almost noncycling (S/G2M 1.46 ± 0.47%). When matched pairs of PB and BM from six patients with BCR/ABL-negative myeloproliferative disorders were examined, only 0.89 ± 0.41% of the CD34+ PBPC, but 8.29 ± 3.13% CD34+ cells from BM were in S/G2M phase. Consistently, as compared to 19 patients with newly diagnosed BCR/ABL-positive CML, a significantly lower PB/BM ratio of CD34+ cells in S/G2M phase was found in these six patients with BCR/ABL-negative myeloprolifrative disorders. Administration of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor STI571 to 13 patients with CML in chronic phase, accelerated phase, or blast crisis lead to an inhibition of PBPC proliferation within a few days. Interestingly, CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells from BM remained proliferating in five cases examined, indicating that CML PBPC are more easily inhibited by STI571 as compared to CD34+ CML hematopoietic progenitor cells from BM. These data suggest that BCR/ABL leads to an enhanced cell cycle activation of CD34+ cells, which seems to be, at least in part, independent of additional factors provided by the bone marrow microenvironment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fialkow PJ, Gartler SM, Yoshida A . Clonal origin of chronic myelocytic leukemia in man Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1967 58: 1468–1471
Rowley JD . A new consistent chromosomal abnormality in chronic myelogenous leukaemia identified by quinacrine fluorescence and Giemsa staining Nature 1973 243: 290–293
Groffen J, Stephenson JR, Heisterkamp N, De Klein A, Bartram CR, Grosveld G . Philadelphia chromosomal breakpoints are clustered within a limited region, bcr, on chromosome 22 Cell 1984 36: 93–99
Shtivelman E, Lifshitz B, Gale RP, Roe BA, Canaani E . Alternative splicing of RNAs transcribed from the human abl gene and from the bcr-abl fused gene Cell 1986 47: 277–284
Ben-Neriah Y, Daley G, Mes-Masson A-M, Witte O, Baltimore D . The chronic-myelogenous leukemia-specific P210 protein is the product of the bcr-abl hybrid gene Science 1986 233: 212–214
Shtivelman E, Lifshitz B, Gale RP, Canaani E . Fused transcript of abl and bcr genes in chronic myelogenous leukaemia Nature 1985 315: 550–554
Daley GQ, VanEtten RA, Baltimore D . Induction of chronic myelogenous leukemia in mice by the P210 bcr/abl gene of the Philadelphia chromosome Science 1990 247: 824–830
Heisterkamp N, Jenster G, ten Hoeve J, Zovich D, Pattengale P, Jones G . Acute leukemia in bcr/abl transgenic mice Nature 1990 344: 251–253
Bedi A, Zehnbauer BA, Barber JP, Sharkis SJ, Jones RJ . Inhibition of apoptosis by BCR-ABL in chronic myeloid leukemia Blood 1994 83: 2038–2044
McGahon A, Bissonnette R, Schmitt M, Cotter KM, Green DR, Cotter TG . BCR-ABL maintains resistance of chronic myelogenous leukemia cells to apoptotic cell death Blood 1994 83: 1179–1187
Traycoff CM, Halstead B, Rice S, McMahel J, Srour E, Cornetta K . Chronic myelogenous leukaemia CD34+ cells exit G0/G1 phases of the cell cycle more rapidly than normal marrow CD34+ cells Br J Haematol 1998 102: 759–767
Eaves AC, Cashman JD, Gaboury LA, Kalousek DK, Eaves CJ . Unregulated proliferation of primitive chronic myeloid leukemia progenitors in the presence of normal marrow adherent cells Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1986 83: 5306–5310
Emanuel P, Bates L, Castleberry R, Gualtieri R, Zuckerman K . Selective hypersensitivity to granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor by juvenile chronic myeloid leukemia hematopoietic progenitors Blood 1991 77: 925–929
Roberts AW, Metcalf D . Noncycling state of peripheral blood progenitor cells mobilized by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and other cytokines Blood 1995 86: 1600–1605
Lemoli RM, Tafuri A, Fortuna A, Petrucci MT, Ricciardi MR, Catani L, Rondelli D, Fogli M, Leopardi G, Ariola C, Tura S . Cycling status of CD34+ cells mobilized into peripheral blood of healthy donors by recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor Blood 1997 89: 1189–1196
Uchida N, He D, Friera AM, Reitsma M, Sasaki D, Chen B, Tsukamoto A . The unexpected G0/G1 cell cycle status of mobilized hematopoietic stem cells from peripheral blood Blood 1997 89: 465–472
Leitner A, Strobl H, Fischmeister G, Kurz M, Romanakis K, Haas OA, Printz D, Buchinger P, Bauer S, Gadner H, Fritsch G . Lack of DNA synthesis among CD34+ cells in cord blood and in cytokine-mobilized blood Br J Haematol 1996 92: 255–262
Jordan CT, Yamasaki G, Minamoto D . High-resolution cell cycle analysis of defined phenotypic subsets within primitive human hematopoietic cell populations Exp Hematol 1996 24: 1347–1355
Fruehauf S, Veldwijk MR, Krämer A, Haas R, Zeller WJ . Delineation of cell cycle state and correlation to adhesion molecule expression of human CD34+ cells from steady-state bone marrow and peripheral blood mobilized following G-CSF supported chemotherapy Stem Cells 1998 16: 271–279
Thiele J, Wickenhauser C, Baldus SE, Kuemmel T, Zirbes TK, Drebber U, Wirtz R, Thiel A, Hansmann ML, Fischer R . Characterization of CD34+ human hemopoietic progenitor cells from the peripheral blood: enzyme-, carbohydrate- and immunocytochemistry, morphometry, and ultrastructure Leuk Lymphoma 1995 16: 483–491
Morrison SJ, Wright DE, Weissman IL . Cyclophosphamide/granulocyte colony-stimulating factor induces hematopoietic stem cells to proliferate prior to mobilization Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997 94: 1908–1913
To LB, Haylock DN, Simmons PJ, Juttner CA . The biology and clinical uses of blood stem cells Blood 1997 89: 2233–2258
Buchdunger E, Zimmermann J, Mett H, Meyer T, Müller M, Druker BJ, Lydon NB . Inhibition of the Abl protein-tyrosine kinase in vitro and in vivo by a 2-phenylaminopyrimidine derivative Cancer Res 1996 56: 100–104
Druker BJ, Tamura S, Buchdunger E, Ohno S, Segal GM, Fanning S, Zimmermann J, Lydon NB . Effects of a selective inhibitor of the Abl tyrosine kinase on the growth of bcr/abl positive cells Nature Med 1996 2: 561–566
Carroll M, Ohno-Jones S, Tamura S, Buchdunger E, Zimmermann J, Lydon NB, Gilliland DG, Druker BJ . CGP57148, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, inhibits the growth of cells expressing BCR-ABL, TEL-ABL and TEL-PDGFR fusion proteins Blood 1997 90: 4947–4952
Druker BJ, Sawyers CL, Talpaz M, Resta D, Peng B, Ford J . Phase I trial of a specific ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitor, CGP57148, in interferon refractory chronic myelogenous leukemia patients Blood 1998 92: 252a (Abstr.)
Knaan-Shanzer S, Valerio D, van Beusechem V . Cell cycle state, response to hemopoietic growth factors and retroviral vector-mediated transduction of human hemopoietic stem cells Gene Therapy 1996 3: 323–333
Grand FH, Marley SB, Chase A, Titley I, Healy L, Spencer A, Reiter A, Goldman JM, Gordon MY . BCR/ABL-negative progenitors are enriched in the adherent fraction of CD34+ cells circulating in the blood of chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia patients Leukemia 1997 11: 1486–1492
Petzer AL, Eaves CJ, Lansdorp PM, Ponchio L, Barnett MJ, Eaves AC . Characterization of primitive subpopulations of normal and leukemic cells present in the blood of patients with newly diagnosed as well as established chronic myeloid leukemia Blood 1996 88: 2162–2171
Maurer-Schultze B, Siebert M, Bassukas ID . An in vivo study on the synchronizing effect of hydroxyurea Exp Cell Res 1988 174: 230–243
Udomsadki C, Eaves CJ, Swolin B, Reid DS, Barnett MJ, Eaves AC . Rapid decline of chronic myeloid leukemic cells in long-term culture due to a defect at the leukemic stem cell level Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1992 89: 6192–6196
Matulonis U, Salgia R, Okuda K, Druker B, Griffin JD . Interleukin-3 and p210BCR/ABL activate both unique and overlapping pathways of signal transduction in a factor-dependent myeloid cell line Exp Hematol 1993 21: 1460–1466
Laneuville P, Heisterkamp N, Groffen J . Expression of the chronic myelogenous leukaemia-associated p210BCR/ABL oncoprotein in a murine IL-3 dependent myeloid cell line Oncogene 1991 6: 275–282
Jiang X, Lopez A, Holyoake TL, Eaves A, Eaves C . Autocrine production and action of IL-3 and G-CSF on Ph+ CD34+ cells from patients with CML Exp Hematol 1998 26: 800 (Abstr.)
Jonuleit T, Peschel C, Schwab R, van der Kuip H, Buchdunger E, Fischer T, Huber C, Aulitzky WE . Bcr-abl kinase promotes cell cycle entry of primary myeloid CML cells in the absence of growth factors Br J Haematol 1998 100: 295–303
Renshaw MW, McWhirter JR, Wang JYJ . The human leukemia oncogene bcr/abl abrogates the anchorage requirement but not the growth factor requirement for proliferation Mol Cell Biol 1995 15: 1286–1293
Lugo TG, Pendergast AM, Witte ON . Tyrosine kinase activity and transformation potency of bcr-abl gene products Science 1990 247: 1079–1082
Krämer A, Hörner S, Willer A, Frühauf S, Hochhaus A, Hallek M, Hehlmann R . Adhesion to fibronectin stimulates proliferation of wild type and bcr/abl-transfected murine hematopoietic cells Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999 96: 2087–2092
Gordon MY, Dowding CR, Riley GP, Goldman JM, Greaves MF . Altered adhesive interactions with marrow stroma of haematopoietic progenitor cells in chronic myeloid leukaemia Nature 1987 328: 342–344
Verfaillie CM, McCarthy JB, McGlave PB . Mechanisms underlying abnormal trafficking of malignant progenitors in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Decreased adhesion to stroma and fibronectin but increased adhesion to the basement membrane components laminin and collagen type IV J Clin Invest 1992 90: 1232–1241
Terstappen LW, Huang S, Safford M, Landsdorp PM, Coken MR . Sequential generations of hematopoietic colonies derived from single nonlineage-committed CD34+/CD38− progenitor cells Blood 1991 77: 1218–1227
Reems JA, Torok-Storb B . Cell cycle and functional differences between CD34+/CD38hi and CD34+/CD38lo human marrow cells after in vitro cytokine exposure Blood 1995 85: 1480–1487
Hao Q-L, Shah AJ, Thiemann FT, Smogorzewska EM, Crooks GM . A functional comparison of CD34+/CD38− cells in cord blood and bone marrow Blood 1995 86: 3745–3753
Kasper B, Fruehauf S, Schiedlmeier B, Buchdunger E, Ho AD, Zeller WJ . Favorable therapeutic index of a p210BCR-ABL specific tyrosine kinase inhibitor – activity on lineage-committed and primitive chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) progenitors Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 1999 44: 433–438
Gambacorti-Passerini C, le Coutre P, Mologni L, Fanelli M, Bertazzoli C, Marchesi E, di Nicola M, Biondi A, Corneo GM, Belotti D, Pogliani E, Lydon NB . Inhibition of the ABL kinase activity blocks the proliferation of BCR/ABL+ leukemic cells and induces apoptosis Blood Cells Mol Dis 1997 23: 380–394
Dan S, Naito M, Tsuruo T . Selective induction of apoptosis in Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia cells by an inhibitor of BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase, CGP 57148 Cell Death Differ 1998 5: 710–715
Acknowledgements
We thank Ms Susanne Brendel for excellent technical assistance. This work was supported by the Deutsche Krebshilfe (Grant No. 10-1179-Krl) and the Forschungsfonds, Fakultät für Klinische Medizin Mannheim, Universität Heidelberg, Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krämer, A., Löffler, H., Bergmann, J. et al. Proliferating status of peripheral blood progenitor cells from patients with BCR/ABL-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia. Leukemia 15, 62–68 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402005
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402005
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
BMI-1 expression is enhanced through transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation during the progression of chronic myeloid leukemia
Annals of Hematology (2009)
-
Deregulation and cross talk among Sonic hedgehog, Wnt, Hox and Notch signaling in chronic myeloid leukemia progression
Leukemia (2007)
-
The use of isobaric tag peptide labeling (iTRAQ) and mass spectrometry to examine rare, primitive hematopoietic cells from patients with chronic myeloid leukemia
Molecular Biotechnology (2007)