Abstract
OBJECTIVE:
Decreased conjugation is probably more important than hemolysis for causing jaundice in G6PD-deficient neonates. The role of enzyme inducers, like phenobarbital, in G6PD deficiency is unclear. This randomized controlled trial was performed to evaluate Phenobarbital's role in reducing the need for phototherapy among G6PD-deficient neonates.
STUDY DESIGN:
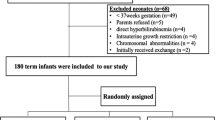
This stratified, randomized, triple-blinded, placebo-controlled trial was conducted in a level III NICU. Consecutive babies with gestation ≥34 weeks and birth weight ≥1800 g were screened from cord blood. G6PD-deficient neonates, who were otherwise healthy, were enrolled. Rh isoimmunization, maternal Phenobarbital use and lack of parental consent were exclusion criteria. Subjects were randomly allocated to receive 5 mg/kg day of oral phenobarbital/ placebo for first 3 days. They were monitored daily for total serum bilirubin (TSB) until declining TSB was documented twice. The primary outcome was requirement for phototherapy and secondary outcomes were duration of phototherapy, need for exchange transfusion, peak TSB and adverse effects. Sample size of 56 could detect a decline in phototherapy requirement from 40 to 5% with 80% power and 5% error.
RESULTS:
Of 2370 babies screened, 63 were G6PD-deficient. Of them, 56 eligible babies were allocated to phenobarbital (n=27) or placebo (n=29). The mean age of administration of the first dose was 18.55±7.3 h. In total, 44% in phenobarbital group and 41% in placebo group required phototherapy (p=1.0). There was no significant difference in exchange transfusion rates (18.5 vs 10%, p=0.46). No baby had adverse reactions.
CONCLUSION:
Prophylactic oral phenobarbital does not decrease the need for phototherapy or exchange transfusions in G6PD-deficient neonates.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jolly JG, Sarup BM, Bhatnagar DP, Maini SC . Glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency in India. J Indian Med Assoc 1972;58:196.
Valaes T, Drummond GS, Kappas A . Control of hyperbilirubinemia in glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase deficient newborns using an inhibitor of bilirubin production, Sn-Mesoporphyrin. Pediatrics 1998;101: http://www.pediatrics.org/cgi/content/full/105/5/el.
Kaplan M, Muraca M, Hammerman C, et al. Bilirubin conjugation reflected by conjugated bilirubin fractions in glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase deficient neonates — a determining factor in the pathogenesis of hyperbilirubinemia. Pediatrics 1998;102: http://www.pediatrics.org/egi/content/full/102/3/e37.
Meloni T, Costa S, Cuuntilo S . Haptoglobin, hemopexin, hemoglobin and haematocrit in newborns with erythrocytes glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency. Acta Hematol 1975;54:284–288.
Valaes T, Karaklis A, Stavrakakis D, Bavela-Stavrakakis K, Perakis A, Doxiadis SA . Incidence and mechanism of neonatal jaundice retated to G6PD deficiency. Pediatr Res 1969;3:448–458.
Kaplan M, Buetller E, Vreman HJ, et al. Neonatal hyperbilirubinemia in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficient heterozygotes. Pediatr 1999;104:68–74.
Meloni T, Cagnazzo G, Dore A, Cuuntillo S . Phenobarbital for prevention of hyperbilirubinemia in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficient newborn infants. J Pediatr 1973;82:1048.
Meloni T, Dore A, Cuuntilo S . The effect of phenobarbitone in the hyperbilirubinemia of neonates with deficiency of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase of the erythrocytes. Helv Pediatr Acta 1972;274:197 [German].
Gall JC, Brewer GJ, Dern RJ . Studies of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity of individual erythrocytes: the methemoglobin elution test for identification of female heterozygotes for G6PD deficiency. Am J Hum Genet. 1965;17:359.
Valaes TN, Harvey-Wilkes K . Pharmacologic approaches to the prevention and treatment of neonatal hyperbilirubinemia. Clin Perinatol 1990;17:245–273.
National Neonatology Forum. The National Neonatal–Perinatal Database, India. Report for the Year 2000; p. 39.
Cockington RA . A guide to the use of phototherapy in the management of neonatal hyperbilirubinemia. J Pediatr 1979;95:281–285.
American Academy of Pediatrics: Practice parameter: Management of hyperbilirubinemia in the healthy term newborn. Pediatrics 1994;94:558–565.
Bhutani VK, Johnson L, Sivieri EM . Predictive ability of a pre-discharge hour specific serum bilirubin for subsequent significant hyperbilirubinemia in healthy term and near term newborns. Pediatrics 1999;103:6–14.
Kaplan M, Renbaum P, Levy-Lahad E, Hammerman C, Lahad A, Beutler E . Gilbert syndrome and glucose-6-phosphate deficiency: a dose-dependent genetic interaction crucial to neonatal hyperbilirubinemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci 1997;94:12128–12132.
Iolascon A, Faienza MF, Perrotta S, Meloni GF, Ruggiu G, del Giudice EM . Gilbert's syndrome and jaundice in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficient neonates. Haematologica 1999;84:99–102.
Beutler E . G6PD deficiency. Blood 1994;84:3613–3636.
Mohanty D, Mukherjee MB, Colah RB . Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency in India. Indian J Pediatr 2004;71:525–529.
Kaplan M, Algur N, Hammerman C . Onset of jaundice in glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase deficient neonates. Pediatrics 2001;108:956–959.
Kumar R, Narang A, Kumar P, Garewal G . Study of postnatal phenobarbitone prophylaxis for neonatal jaundice in babies with birth weight 1000–1499 grams. Indian Pediatr 2002;39:945–951.
Cuuntilo S, Meloni T, Dore A . Effect of orotic acid upon serum bilirubin in newborn infants with erythrocyte G6PD deficiency. Acta Paediatr Scand 1974;63:143–146.
Kappas A, Drummond GS, Valaes T . A single dose of Sn-Mesoporphyrin prevents development of severe hyperbilirubinemia in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficient newborns. Pediatrics 2001;108:25–30.
Meloni T, Forteleoni G, Dore A, Cutillo S . Neonatal hyperbilirubinemia in heterozygous glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficient females. Br J Haematol 1983;53:241–246.
Weng YH, Chou YH, Lien RI . Hyperbilirubinemia in healthy neonates with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency. Early Hum Dev 2003;71:129–136.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Sources of financial assistance: None.
Conflict of interest: None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murki, S., Dutta, S., Narang, A. et al. A Randomized, Triple-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Prophylactic Oral Phenobarbital to Reduce the Need for Phototherapy in G6PD-Deficient Neonates. J Perinatol 25, 325–330 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7211258
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7211258
This article is cited by
-
The side effects of phototherapy for neonatal jaundice: what do we know? What should we do?
European Journal of Pediatrics (2011)
-
Prophylactic Oral Phenobarbital
Journal of Perinatology (2005)