Abstract
Objective:
To determine the effect of drastic weight loss on arterial compliance, inflammatory and metabolic parameters in patients with morbid obesity with and without cardiovascular risk factors who underwent laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding (LAGB).
Design:
Open prospective study, morbidly obese subjects divided into low- and high-risk group were evaluated before and 4 months after LAGB.
Subjects:
Forty-one Caucasian subjects aged between 16 and 55 years, with morbid (grade 3) obesity (20 low- risk and 21 high-risk subjects) who underwent LAGB and completed a 16-week follow-up.
Measurments:
Patients were evaluated at baseline and 4 months after LAGB for body mass index (BMI), arterial blood pressure (BP), metabolic factors including lipid profile, HbA1C, insulin, C-peptide, fibrinogen, hs-C reactive protein (CRP) and Homeostasis model assessment-insulin resistance (HOMA-IR). Arterial elasticity of large and small arteries was evaluated using pulse-wave contour analysis method (HDI CR 2000, Eagan, Minnesota) at baseline and after 4 months.
Results:
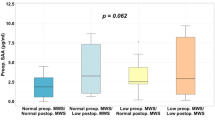
Body mass index reduction induced by LABG, from 43.55±5.11 to 35.10±4.87 in low-risk patients and from 42.90±3.22 to 35.00±3.24 in high-risk patients, significantly improved small artery elasticity (SAE) from 6.30±2.74 to 7.25±1.85, in morbidly obese patients with multiple cardiovascular risk factors (high-risk group). Improvement in SAE was accompanied by improvement of arterial BP, glucose and lipid metabolism, and reduction of CRP values.
Conclusion:
Although dramatic weight reduction induced by surgical intervention was associated with similar changes in body weight and significant improvement of metabolic and inflammatory parameters in two groups of obese patients, SAE improved only in high-risk patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kopelman PG . Obesity as a medical problem. Nature 2000; 404: 635–643.
National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. Clinical guidelines on the identification, evaluation, and treatment of overweight and obesity in adults: the evidence report. Obes Res 1998; 6: 51S–209S.
National Task Force on the Prevention and Treatment of Obesity. Overweight, obesity, and health risk. Arch Intern Med 2000; 160: 898–904.
Wildman RP, Mackey RH, Bostom A, Thompson T, Sutton-Tyrrell K . Measures of obesity are associated with vascular stiffness in young and older adults. Hypertension 2003; 42: 468–473.
Sutton-Tyrrell K, Newman A, Simonsick EM, Havlik R, Pahor M, Lakatta E et al. Aortic stiffness is associated with visceral adiposity in older adults enrolled in the study of health, aging, and body composition. Hypertension 2001; 38: 429–433.
Woo KS, Chook P, Yu CW, Sung RYT, Qiao M, Leung SSF et al. Overweight in children is associated with arterial endothelial dysfunction and intima–media thickening. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2004; 28: 852–857.
Cohn JN, Finkelstein S, McVeigh G, Morgan D, LeMay I, Robinson J et al. Non-invasive pulse wave analysis for the detection of arterial vascular disease. Hypertension 1995; 26: 503–508.
van Popele NM, Grobbee DE, Bots ML, Asmar R, Topouchian J, Reneman RS et al. Association between arterial stiffness and atherosclerosis: the Rotterdam Study. Stroke 2001; 32: 454–460.
Blacher J, Guerin AP, Pannier B, Marchais SJ, Safar ME, London GM . Impact of aortic stiffness on survival in end-stage renal disease. Circulation 1999; 99: 2434–2439.
Laurent S, Boutouyrie P, Asmar R, Gautier I, Laloux B, Guize L et al. Aortic stiffness is an independent predictor of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in hypertensive patients. Hypertension 2001; 37: 1236–1241.
Cruickshank K, Riste L, Anderson SG, Wright JS, Dunn G, Gosling RG . Aortic pulse-wave velocity and its relationship to mortality in diabetes and glucose intolerance. An integrated index of vascular function? Circulation 2002; 106: 2085–2090.
Zieman SJ, Melenovsky V, Kass DA . Mechanisms, pathophysiology, and therapy of arterial stiffness. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2005; 25: 932–943.
Paganelli M, Giacomelli M, Librenti MC, Pontiroli AE, Ferla G . Thirty months experience with laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding. Obes Surg 2000; 10: 269–271.
Pontiroli AE, Pizzocri P, Librenti MC, Vedani P, Marchi M, Cucchi E et al. Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding for the treatment of morbid (grade 3) obesity and its metabolic complication: a three-year study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002; 87: 3555–3561.
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turmer RC . Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and β-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985; 28: 412–419.
Zimlichman R, Shargorodsky M, Boaz M, Duprez D, Rahn KH, Rizzoni D et al. Determination of arterial compliance using blood pressure waveform analysis with the CR-2000 system. Am J Hypertens 2005; 18: 65–71.
Shargorodsky M, Leibovitz E, Lubimov L, Gavish D, Zimlichman R . Prolonged treatment with the AT1 receptor blocker, valsartan, increases small and large artery compliance in uncomplicated essential arterial hypertension. Am J Hypertens 2002; 15: 1087–1091.
Leibovitz E, Hazanov N, Zimlichman R, Shargorodsky M, Gavish D . Treatment with atorvastatin improves small artery compliance in patients with severe hypercholesterolemia. Am J Hypertens 2001; 14: 1096–1098.
Cohn JN . Vascular wall function as a risk marker for cardiovascular disease. Am J Hypertens 1999; 17: S41–S42.
Sato H, Hayashi J, Harashima K, Shimazu H, Kitamoto K . A population-based study of arterial stiffness index in relation to cardiovascular risk factors. J Atheroscler Thromb 2005; 12: 175–180.
Benetos A, Waeber B, Izzo J, Mitchell G, Resnic L, Asmar R et al. Influence of age, riskfactors, and cardiovascular and renal disease on arterial stiffness: clinical applications. Am J Hypertens 2002; 15: 1101–1108.
Mc Veigh G, Brennan G, Hayes R, Cohn J, Finkelstein S, Johnston D . Vascular abnormalities in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus identified arterial waveform analysis. Am J Med 1993; 95: 424–430.
Ferreira I, Twisk JW, van Mechelen W, Kemper HC, Seidell JC, Stehouwer CD . Current and adolescent body fatness and fat distribution: relationships with carotid intima–media thickness and large artery stiffness at the age of 36 years. J Hypertens 2004; 22: 145–155.
Montagnani M, Quon MJ . Insulin action in vascular endothelium: potential mechanisms linking insulin resistance with hypertension. Diabetes Obes Metab 2000; 2: 285–292.
Nickenig G, Roling J, Strehlow K, Schnabel P, Bohm M . Insulin induces upregulation of vascular AT1 receptor gene expression by posttranscriptional mechanisms. Circulation 1998; 98: 2453–2460.
Brownlee M, Cerami A, Vlassara H . Advanced glycosylation end products in tissue and the biochemical basis of diabetic complications. N Engl J Med 1988; 318: 1315–1321.
Rizzoni D, Porteri E, Guelfi D, Muiesan ML, Valentini U, Cimino A et al. Structural alterations in subcutaneous small arteries of normotensive and hypertensive patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Circulation 2001; 103: 1238–1244.
Oda A, Taniguchi T, Yokoyama M . Leptin stimulates rat aortic smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration. Kobe J Med Sci 2001; 47: 141–150.
Sierra-Honigmann MR, Nath AK, Murakami C, Garcia-Cardena G, Papa-petropoulos A, Sessa WC et al. Biological action of leptin as an angiogenic factor. Science 1998; 281: 1683–1686.
Balkestein EJ, Aggel-Leijssen DP, van Baak MA, Struijker-Boudier HA, van Bortel LM . The effect of weight loss with or without exercise training on large artery compliance in healthy obese men. J Hypertens 1999; 17: 1831–1835.
Sorensen TIA, Rissanen A, Korkeila M, Kaprio J . Intention to lose weight, weight changes, and 18-y mortality in overweight individuals without co-morbidities. Plos Med 2005; 2: e171.
Grey E, Bratteli C, Glasser SP, Alinder C, Finkelstein SM, Lindgren BP . Reduced small artery but not large artery elasticity is an independent risk marker for cardiovascular events. Am J Hypertens 2003; 16: 265–269.
Mc Veigh GE, Allen PB, Morgan DR, Hanratty CG, Silke B . Nitric oxide modulation of blood vessel tone identified by arterial waveform analysis. Clin Sci 2001; 100: 387–393.
Cohn JN, Quyyumi AA, Hollenberg NK, Kenneth AJ . Surrogate markers for cardiovascular disease. Circulation 2004; 109: 31–46.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shargorodsky, M., Fleed, A., Boaz, M. et al. The effect of a rapid weight loss induced by laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding on arterial stiffness, metabolic and inflammatory parameters in patients with morbid obesity. Int J Obes 30, 1632–1638 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0803320
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0803320
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Short- and Long-Term Effects of Bariatric Surgery on Vascular Phenotype
Obesity Surgery (2019)
-
Immune cell-mediated inflammation and the early improvements in glucose metabolism after gastric banding surgery
Diabetologia (2013)
-
Effect of Laparoscopic Adjustable Gastric Banding on Modifiable Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Extremely Obese Adolescents
Obesity Surgery (2012)
-
One Year Improvements in Cardiovascular Risk Factors: a Comparative Trial of Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass vs. Adjustable Gastric Banding
Obesity Surgery (2010)
-
Effect of diet-induced energy deficit and body fat reduction on high-sensitive CRP and other inflammatory markers in obese subjects
International Journal of Obesity (2009)