Abstract
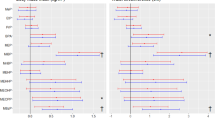
BACKGROUND: Body weight loss occurring after a hypoenergetic diet or a gastroplasty could be followed by an increase in blood concentration of potentially toxic pollutants that can interfere with the hormonal system (endocrine disrupters).
DESIGN: Thirty obese individuals recruited for gastroplasty were compared before and after treatment with 45 normal-weight people.
MEASUREMENTS: Blood samples were analyzed for DDT, DDE, HCB and PCBs no. 28, 52, 101, 118, 138, 153 and 180, by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry.
RESULTS: The results indicate clearly that body weight loss occurring after gastroplasty increases plasma concentration of lipophilic pollutants.
CONCLUSION: Gastroplasty increases plasma concentration of organochlorine pesticides and PCBs, which could be a risk factor of endocrine disruption. Future longitudinal research will have to determine if the advantages of body weight loss are reduced by this potentially harmful effect.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
National Academy of Sciences. Principles of plant and animals pest control Publication no. 1695 National Academy Press: Washington, DC 1969 3 pp
Boersma ER . Environmental exposure to polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and dioxine Acta Pathologica Microbiologica et Immunologica Scandinavica 2001 109 (Suppl 103): S243–S253.
Jouannet P, Wang C, Eustache F, Kold-Jensen T, Auger J . Semen quality and male reproductive health: the controversy about human sperm concentration decline Acta Pathologica Microbiologica et Immunologica Scandinavica 2001 109: 333–344.
Aliva A, Spira A, Multigner L . Contribution of environmental factors to the risk of male infertility Hum Reprod 2001 16: 1768–1776.
Krstevska-Konstantinova M, Charlier C, Craen M, Du Caju M, Heinrichs C, de Beaufort C, Plomteux G, Bourguignon JP . Sexual precocity after immigration from developing countries to Belgium: evidence of previous exposure to organochlorine pesticides Hum Reprod 2001 16: 1020–1026.
Partsch C-J, Sippell W . Pathogenesis and epidemiology of precocious puberty. Effects of exogenous oestrogens Hum Reprod Update 2001 7: 292–302.
Hoyer AP, Jorgensen T, Brock JW, Grandjean P . Organochlorine exposure and breast cancer survival J Clin Epidemiol 2000 53: 323–330.
Lucena R, Allan M, Costabeber I, Villarejo M, Navajas R . Breast cancer risk factors: PCB congeners Eur J Cancer Prev 2001 10: 117–119.
Dewailly E, Dodin S, Verreault R, Ayotte P, Sauvé L, Morin J, Brisson J . High organochlorine body burden in women with estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer J Natl Cancer Inst 1994 86: 232–234.
Zheng T, Holford TR, Tessari J, Mayne ST, Owens PH, Ward B, Carter D, Boyle P, Dubrow R, Archibeque-Engle S, Zahm SH . Breast cancer risk associated with congeners of polychlorinated biphenyls Am J Epidemiol 2000 152: 50–58.
Minelli EV, Ribeiro ML . Quantitative method for the determination of organochlorine pesticides in serum J Anal Toxicol 1996 20: 23–26.
Laden F, Hankinson SE, Wolff M, Colditz G, Willett W, Speizer F, Hunter D . Plasma organochlorine levels and the risk of breast cancer: an extended follow-up in the Nurses' Health Study Int J Cancer 2001 91: 568–574.
Chevrier J, Dewailly E, Ayotte P, Mauriège P, Desprès J-P, Tremblay A . Body weight loss increases plasma and adipose tissue concentrations of potentially toxic pollutants in obese individuals Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2000 24: 1272–1278.
Ahmiya Y, Nakai K . Effect of starvation on excretion, distribution and metabolism of DDT in mice Tohoku J Exp Med 1977 122: 143–153.
Bigsby R, Caperell-Grant A, Madhukar V . Xenobiotics released from fat during fasting produce estrogenic effects in ovariectomized mice Cancer Res 1997 57: 865–869.
Flechtner-Mors M, Ditschuneit H, Johnson T, Suchard M, Adler G . Metabolic and weight loss effects on long-term dietary intervention in obese patients: four-year results Obes Res 2000 8: 399–402.
Capella JF, Capella RF . The weight reduction operation of choice: vertical banded gastroplasty or gastric by-pass Am J Surg 1996 171: 74–79.
Belachew M, Legrand M, Vincent V, Lismonde M, Le Docte N, Deschamps V . Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding World J Surg 1998 22: 955–963.
Charlier C, Plomteux G . Determination of organochlorines pesticide residues in blood of healthy individuals Clin Chem Lab Med 2002 40: 361–364.
Patterson DG, Isaacs SG, Alexander LR, Turner WE, Hampton L, Bernert JT, Needham LL . Method 6: determination of specific polychlorinated dibenzo-P-dioxins and dibenzofurans in blood and adipose tissue by isotope dilution–high resolution mass spectrometry IARC Sci Publ 1991 108: 299–342.
Carson R . Silent spring Houghton Aifflin: Boston, MA 1962.
Ashby J . Getting the problem of endocrine disruption into focus: the need for a pause for thought APMIS 2000 108: 805–813.
Lipsett MB . Hormones, medications and cancer Cancer 1983 51: 2426–2429.
Doll R, Peto R . The causes of cancer: quantitative estimates of avoidable risks in the United States today J Natl Cancer Inst 1981 66: 1191–1303.
Dale WE, Gaines TB, Hayes WJ . Storage and excretion of DDT in starved rate Toxicol Appl Pharmac 1962 4: 89–106.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Charlier, C., Desaive, C. & Plomteux, G. Human exposure to endocrine disrupters: consequences of gastroplasty on plasma concentration of toxic pollutants. Int J Obes 26, 1465–1468 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802144
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802144
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Environmental neglect: endocrine disruptors as underappreciated but potentially modifiable diabetes risk factors
Diabetologia (2019)
-
Treatment of persistent organic pollutants in wastewater using hydrodynamic cavitation in synergy with advanced oxidation process
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2018)
-
TCDD exposure estimation for workers at a New Zealand 2,4,5-T manufacturing facility based on serum sampling data
Journal of Exposure Science & Environmental Epidemiology (2010)
-
Increased Risk of Relapse After Breast Cancer With Exposure to Organochlorine Pollutants
Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology (2007)
-
Thermogenesis and weight loss in obese individuals: a primary association with organochlorine pollution
International Journal of Obesity (2004)