Abstract
OBJECTIVE: To investigate the relationship between polymorphisms in the OB-R and OB genes and metabolic markers for obesity and glucose intolerance in a population of Nauruan men. In addition, we examined the effect of the simultaneous presence of the three polymorphisms on the phenotype of individuals in this population.
DESIGN AND SUBJECTS: This study was conducted in a population from the Pacific Island of Nauru. Populations in this region have some of the highest recorded rates of obesity and type 2 diabetes and are therefore of great interest in the genetic analysis of these diseases. Two hundred and thirty-two male subjects were examined in this cross-sectional study. All subjects were non-diabetic and the group had a mean age of 31 y and a mean body weight of 104 kg.
MEASUREMENTS: Several phenotypic measures of body fatness and fat distribution (anthropometry), fasting plasma insulin, glucose and leptin concentrations, blood pressure and 2 h plasma glucose concentration, genotypes of subjects for the Gln223Arg, PRO1019pro (OB-R gene) and OB gene polymorphisms.
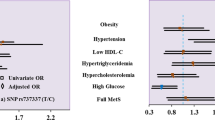
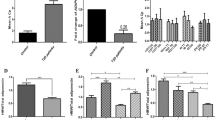
RESULTS: Individually, the OB gene and Gln223Arg OB-R polymorphisms were not associated with the obese or glucose-intolerant phenotype in this population. Individuals with the PRO1019pro polymorphism were found to have elevated insulin concentrations and diastolic blood pressure (Pc=0.04). In addition, individuals found to simultaneously exhibit homozygosity of the common allele of all three polymorphisms (genotypes: Arg/Arg, pro/pro and II/II) exhibited significantly elevated fasting insulin levels (Pc=0.03).
CONCLUSIONS: Pacific Island populations exhibit a remarkably high prevalence rate of obesity and type 2 diabetes and represent a unique population for genetic studies of obesity. In the present study we have revealed that a specific combination of alleles in OB and OB-R, two candidate genes for obesity, may confer an increased risk for the development of insulin resistance in Nauruan males.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Silva, A., Walder, K., Aitman, T. et al. Combination of polymorphisms in OB-R and the OB gene associated with insulin resistance in Nauruan males. Int J Obes 23, 816–822 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0800931
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0800931
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The association of insertions/deletions (INDELs) and variable number tandem repeats (VNTRs) with obesity and its related traits and complications
Journal of Physiological Anthropology (2017)
-
The Q223R polymorphism in LEPR is associated with obesity in Pacific Islanders
Human Genetics (2010)
-
Functional Consequences of the Human Leptin Receptor (LEPR) Q223R Transversion
Obesity (2009)
-
Association analysis of genes involved in the leptin-signaling pathway with obesity in Brazil
International Journal of Obesity (2002)
-
Genetic factors as predictors of weight gain in young adult Dutch men and women
International Journal of Obesity (2002)