Volume 28
-
No. 12 December 2021
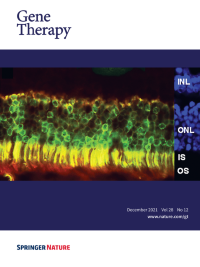
Cover Credit:Suprachoroidal injection provides a new, noninvasive route of delivery for ocular gene therapy. Two weeks after suprachoroidal injection of 7.8x109 genome copies of AAV2tYF-GRK1-GFP in Brown Norway rats, an ocular section shows strong GFP fluorescence (green) and immunostaining for GFP (red) in photoreceptor cell bodies (outer nuclear layer, ONL), inner segments (IS) and outer segments (OS). GRK1 is the photoreceptor-specific rhodopsin kinase promoter.
-
No. 10-11 November 2021
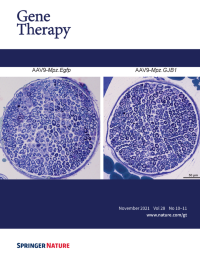
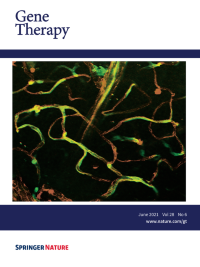
Cover Credit:Femoral motor nerves of Gjb1-null mice following post-onset intrathecal delivery of the AAV9-Mpz.GJB1 vector. AAV9-Mpz. GJB1 injected mice show improved myelination compared to mock-treated littermates with fewer demyelinated and remyelinated fibers as well as fewer foamy macrophages. See paper by Kagiava et al. in this issue of Gene Therapy.
-
No. 9 September 2021
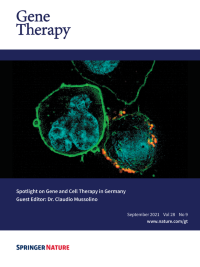
Cover Credit:A multiple myeloma cancer cell interacting with a SLAMF7-specific CAR-T cell. The remarkable clinical benefit achieved using CAR T cells to defeat B cells malignancies has prompted the use of these “living drugs” to target other types of cancer. Virus-free methods, such as transposons, can be used to equip T cells with cancer-specific CAR molecules thus potentially simplifying manufacturing and reducing toxicity. Theimageshows the interaction between a SLAMF7-specific CAR T cell (orange), generated using the Sleeping Beauty transposon technology, and a multiple myeloma target cell (green).See paper by Prommersberger et al. in this issue of Gene Therapy.
-
No. 7-8 August 2021
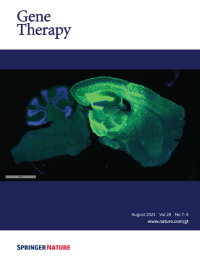
Cover Credit:Enhanced brain transduction efficiency in MPS IIIB mice with neonatal 6 site intra-parenchymal injection of a total of 1.4 x 1010 vector genomes of AAV8 triple capsid mutant expressing GFP.
-
No. 6 June 2021
Cover Credit:Small and cell-type restricted promoters are important tools for basic and preclinical research, and clinical delivery of gene therapies. Human-DNA MiniPromoter Ple32 (CLDN5, 1,670 bp) was developed for specifi c expression in the endothelial cells of the bloodretina and blood-brain barrier. The image shows Ple32 driving emerald GFP expression (green), co-labeled with anti-CD31 an endothelial cell marker (red), confi rming blood vessel expression in the target endothelial cells that create the barrier. See paper by Korecki et al. in this issue of Gene Therapy.
-
No. 5 May 2021
Cover Credit:To celebrate our Gene therapy for the Eye special edition, members of the EiC’s lab consented to show off their diverse ‘vision’. Photo credit: Dr Jerolen Naidoo, Bioengineering and Integrated Genomics Research Group, CSIR, SouthAfrica.
-
No. 3-4 April 2021
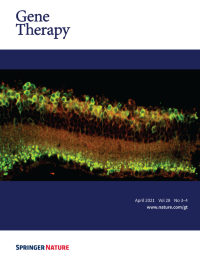
Cover Credit:Intravitreal injection of AAV-carried Ambient-light activatable Multi-Characteristic Opsin (MCO) led to ON-bipolar cell (green) specific expression (red, reporter mCherry) in rd10 mice retina with complete loss of natural photoreceptors.Gene therapy-based treatment such as optogenetics offers a potentially powerful way to bypass damaged photoreceptors in retinal degenerative diseases and use the remaining retinal cells for functionalization to achieve photosensitivity.This issue of Gene Therapy describes the use of ambient-light activatable Broadband Multi-Characteristic Opsin (MCO) for photosensitizing ON Bipolar cells to restore vision in mice with severe photoreceptor degeneration, mimicking human disease of severe Retinitis Pigmentosa (RP). Theimageshows robust expression of MCO in soma and axonal terminals of bipolar cells of the retina,16 weeks after intravitreal injection of AAV-carriedMCO.See paper by Batabyal et al. in this issue of Gene Therapy.
-
No. 1-2 February 2021
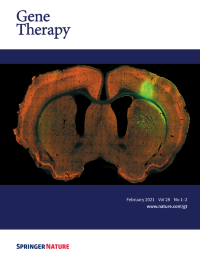
Cover legend: Adeno-associated viral vector-mediated transduction of the corticospinal tract. Adeno-associated viral vectors (AAVs) are widely used as vehicles for gene transfer to the nervous system. The choice of promoter is an essential aspect of the design of AAVs. The image shows a coronal brain section of a rat injected with AAV1-SYN-eGFP in the right sensory-motor cortex. Transduction with AAV1 harbouring a human synapsin promoter leads to neuron-specific and strong transgene expression. The promoter comparison study by Nieuwenhuis et al., is now published in this issue of Gene Therapy.