Abstract
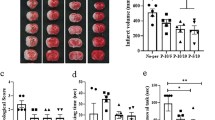
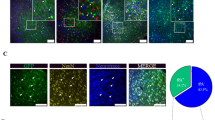
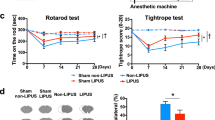
Acute cerebral ischemia causes hypoxic neuronal cell death by necrosis and apoptosis. Expression of anti-apoptotic transgenes in ischemic brain may provide a useful therapeutic strategy for alleviation of postischemic damage. The present study investigates liposome-mediated transfer of the human bcl-2 protein in a rat model of focal transient ischemia due to middle cerebral artery (MCA) occlusion. Two different types of plasmid vectors were used for bcl-2 expression: one driven by the constitutive cytomegalovirus promoter (pCMV) and another based on the hypoxia-inducible human vascular endothelial growth factor promoter (pHRE). Cationic liposome/plasmid DNA complexes (lipoplexes) were injected directly into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of rats immediately after MCA occlusion. The brains of treated and control animals were analyzed 48 h later. Infarct volumes and numbers of apoptotic cells were quantified. Occlusion of the MCA resulted in ipsilateral cerebral infarcts in all study animals. Transfer of the bcl-2 gene resulted in high level widespread protein expression in the case of the pCMV-bcl2 plasmid, while animals treated with the pHRE-bcl2 vector showed lower expression levels of bcl2 which were in addition limited to the ischemic area. Treatment with pCMV-bcl2, but not with pHRE-bcl2, was able to significantly reduce the infarct volume, which was 109 ± 8 mm3 for pCMV-bcl2, 152 ± 29 mm3 for pHRE-bcl2, and 155 ± 18 mm3 for control animals. Animals transfected with either vector showed a significant reduction in numbers of apoptotic cells in the infarct and penumbra area compared with controls. There were no short-term neurological side-effects of the CSF injection of lipoplexes or of bcl-2 expression. In conclusion, the hypoxia-inducible bcl-2 expression mediated by intrathecal lipoplexes may represent a novel, biologically safe and lesion-selective therapeutic approach for neuroprotection after acute cerebral ischemia.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lipton P. . Ischemic cell death in brain neurons Physiol Rev 1999 79: 1431 1431
Mattson M.P., Culmsee C., Yu Z.F. . Apoptostic and antiapoptotic mechanisms in stroke Cell Tissue Res 2000 301: 173 173
Tsujimoto Y., Shimizu S. . Bcl-2 family: life-or-death switch FEBS Lett 2000 466: 6 6
Guo Q. et al. Alzheimer's presenillin mutation sensitizes neural cells to apoptosis induced by trophic factor withdrawal and amyloid β-peptide: involvement of calcium and oxyradicals J Neurosci 1997 17: 4212 4212
Kruman I. et al. Evidence that 4-hydroxynonenal mediates oxidative stress-induced neuronal apoptosis J Neurosci 1997 17: 5089 5089
Cao Y.J., Shibata T., Rainov N.G. . Hypoxia-inducible transgene expression in differentiated human NT2N neurons – a cell culture model for gene therapy of postischemic neuronal loss Gene Therapy 2000 18: 1357 1357
Linnik M.D. et al. Expression of bcl-2 from a defective herpes simplex virus-1 vector limits neuronal death in focal cerebral ischemia Stroke 1995 26: 1670 1670
Lawrence M.S. et al. Herpes simplex viral vectors expressing Bcl-2 are neuroprotective when delivered after a stroke J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1997 17: 740 740
Antonawich F.J., Federoff H.J., Davis J.N. . Bcl-2 transduciton, using a herpes simplex virus amplicon protects hippocampal neurons from transient global ischemia Exp Neurol 1999 156: 130 130
Shimazaki K. et al. Adeno-associated virus vector-mediated bcl-2 gene transfer into post-ischemic gerbil brain in vivo: prospects for gene therapy of ischemia-induced neuronal death Gene Therapy 2000 7: 1244 1244
Betz A.L., Yang G.Y., Davidson B.L. . Attenuation of stroke size in rats using an adenoviral vector to induce overexpression of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in brain J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1995 15: 547 547
Dokka S. et al. Inhibition of endotoxin-induced lung inflammation by interleukin-10 gene transfer in mice Am J Physiol 2000 279: L872 L872
Zou L.L. et al. Liposome-mediated NGF gene transfection following neuronal injury: potential therapeutic applications Gene Therapy 1999 6: 994 994
McLachlan G. et al. Evaluation in vitro and in vivo of cationic liposome-expression construct complexes for cystic fibrosis gene therapy Gene Therapy 1995 2: 614 614
Porteous D.J. et al. Evidence for safety and efficacy of DOTAP cationic liposome mediated CFTR gene transfer to the nasal epithelium of patients with cystic fibrosis Gene Therapy 1997 4: 210 210
Shibata T., Giaccia A.J., Brown J.M. . Development of a hypoxia-responsive vector for tumor specific gene therapy Gene Therapy 2000 7: 493 493
Deininger M.H. et al. Antiapoptotic Bcl-2 family protein expression increases with progression of oligodendroglioma Cancer 1999 86: 1832 1832
Nor J.E. et al. Up-regulation of Bcl-2 in microvascular endothelial cells enhances intratumoral angiogenesis and accelerates tumor growth Cancer Res 2001 61: 2183 2183
Thorsell A., Fox E., Heilig M. . Lipid mediated gene delivery in the adult rat brain: quantitative analysis of expression Neurochem Int 1999 35: 65 65
Yang G.Y. et al. Overexpression of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in the mouse brain reduces ischemic brain injury Brain Res 1997 751: 181 181
Ooboshi H. et al. Adenovirus-mediated gene transfer in vivo to cerebral blood vessels and perivascular tissue Circ Res 1995 77: 7 7
Kramm C.M. et al. Long-term survival in a rodent model of disseminated brain tumors by combined intrathecal delivery of herpes vectors and ganciclovir treatment Hum Gene Ther 1996 7: 1989 1989
Meuli-Simmen C. et al. Gene expression along the cerebral-spinal axis after regional gene delivery Hum Gene Ther 1999 10: 2689 2689
Hayashi K. et al. Gene therapy for preventing neuronal death using hepatocyte growth factor: in vivo gene transfer of HGF to subarachnoid space prevents delayed neuronal death in gerbil hippocampal CA1 neurons Gene Therapy 2001 8: 1167 1167
Prentice H. et al. Regulated expression of a foreign gene targeted to the ischaemic myocardium Cardiovasc Res 1997 35: 567 567
Vinall P.E. et al. Temporal changes in sensitivity of rats to cerebral ischemic insult J Neurosurg 2000 93: 82 82
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant from the E-Kröner-Fresenius Foundation (NGR), and in parts by grants Ra 705/4-1 from the German Research Council (DFG) and 2794A/0087H and 3067A/0029G from the Federal State of Saxony-Anhalt, and a grant from the Bartling Foundation Hannover (all to NGR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, YJ., Shibata, T. & Rainov, N. Liposome-mediated transfer of the bcl-2 gene results in neuroprotection after in vivo transient focal cerebral ischemia in an animal model. Gene Ther 9, 415–419 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301676
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301676
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Changes in the Expression of Bcl-2 Protein in Neurons in the Hippocampal Fields after Use of Ischemic Postconditioning of the Brain
Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology (2016)
-
Temporal Regulation of Apoptotic and Anti-apoptotic Molecules After Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion Followed by Reperfusion
Molecular Neurobiology (2014)
-
Bcl-2 enhances the formation of newborn striatal long-projection neurons in adult rat brain after a transient ischemic stroke
Neuroscience Bulletin (2012)
-
Increased Expression of a Proline-Rich Akt Substrate (PRAS40) in Human Copper/Zinc-Superoxide Dismutase Transgenic Rats Protects Motor Neurons from Death after Spinal Cord Injury
Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism (2008)
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Apoptosis in Cerebral Ischemia: Multiple Neuroprotective Opportunities
Molecular Neurobiology (2008)