Abstract
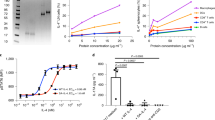
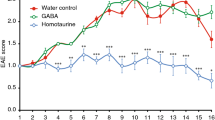
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an immune-mediated inflammatory disease of the central nervous system (CNS) that might benefit from anti-inflammatory therapies. However, systemic delivery of anti-inflammatory drugs in MS patients has so far been disappointing, mostly due to the limited capacity of these molecules to enter the CNS. We injected into the cisterna magna (i.c.) of Biozzi AB/H mice affected by a relapsing–remitting form of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), the animal model of MS, a non-replicative herpes simplex virus (HSV) type-1-derived vector containing the interleukin (IL)-4 gene (d120:LacZ:IL-4). CNS delivery of the d120:LacZ:IL-4 vector, after EAE onset, induced the in situ production of IL-4 by CNS-resident cells facing the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) spaces and reduced by 47% (P < 0.02) the disease-related deaths. compared with mice treated with the control d120:lacz vector, il-4-treated mice also showed a shorter duration of the first eae attack, a longer inter-relapse period, and a reduction in the severity and duration of the first relapse. protection from eae progression in il-4-treated mice was associated with activation of microglia in spinal cord areas where mrna content of the pro-inflammatory chemokines, macrophage chemoattractant protein-1 (mcp-1) and rantes, was reduced and that of the anti-inflammatory cytokine il-4 was increased. finally, cns-infiltrating mononuclear cells from il-4-treated mice produced lower levels of mcp-1 mrna compared with control mice. our results, showing that il-4 gene delivery using hsv-1 vectors induces protection from eae by in situ modulating the cytokine/chemokine-mediated circuits sustaining effector cell functions, indicate that the intrathecal ‘therapeutic’ use of nonreplicative hsv-1-derived vectors containing anti-inflammatory molecules might represent an alternative strategy in inflammatory diseases of the cns.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Steinman L . A few autoreactive cells in an autoimmune infiltrate control a vast population of nonspecific cells: a tale of smart bombs and the infantry Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996 93: 2253–2256
Martino G, Hartung HP . Immunopathogenesis of multiple sclerosis: the role of T cells Curr Opin Neurol 1999 12: 309–321
Kieseier B et al. Effector pathways in immune mediated central nervous system demyelination Curr Opin Neurol 1999 12: 323–336
Selmaj KW, Raine CS . Tumor necrosis factor mediates myelin and oligodendrocyte damage in vitro Ann Neurol 1998 23: 339–346
The IFNB Multiple Sclerosis Study Group . Interferon beta-1b is effective in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. I. Clinical results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial Neurology 1993 43: 655–661
The IFNB Multiple Sclerosis Study Group and the University of British Columbia MS/MRI Analysis Group . Neutralizing antibodies during treatment of multiple sclerosis with interferon beta-1b: experience during the first three years Neurology 1996 47: 889–894
Calabresi PA et al. Phase 1 trial of transforming growth factor beta 2 in chronic progressive MS Neurology 1998 51: 289–292
The Lenercept Multiple Sclerosis Study Group and University of British Columbia MS/MRI Analysis Group ., TNF neutralization in MS: results of a randomized, placebo-controlled multicenter study Neurology 1999 53: 457–465
Khan OA et al. Interferon beta-1b serum levels in multiple sclerosis patients following subcutaneous administration Neurology 1996 46: 1639–1643
Martino G et al. Cytokine gene therapy of autoimmune demyelination revisited using herpes simplex virus type-1-derived vectors Gene Therapy 2000 7: 1087–1093
Furlan R et al. Central nervous system delivery of interleukin-4 by a non replicative herpes simplex type I viral vector ameliorates autoimmune demyelination Hum Gene Ther 1998 9: 2605–2617
Mattner F et al. Inhibition of Th1 development and treatment of chronic-relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis by a non-hypercalcemic analogue of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 Eur J Immunol 2000 30: 498–508
Racke MK et al. Cytokine-induced immune deviation as a therapy for inflammatory autoimmune disease J Exp Med 1994 180: 1961–1966
Inobe JI, Chen Y, Weiner HL . In vivo administration of IL-4 induces TGF-beta-producing cells and protects animals from experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis Ann NY Acad Sci 1996 778: 390–392
Brocke S et al. Treatment of experimental encephalomyelitis with a peptide analogue of myelin basic protein Nature 1996 379: 343–346
Storch M, Lassmann H . Pathology and pathogenesis of demyelinating diseases Curr Opin Neurol 1997 10: 186–192
Reiseter BS, Miller GT, Happ MP, Kasaian MT . Treatment of murine experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis with a myelin basic protein peptide analog alters the cellular composition of leukocytes infiltrating the cerebrospinal fluid J Neuroimmunol 1998 91: 156–170
Aloisi F, Ria F, Adorini L . Regulation of T-cell responses by CNS antigen-presenting cells: different role for microglia and astrocytes Immunol Today 2000 21: 141–147
Matsukawa A et al. Production and regulation of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in lipopolysaccharide- or monosodium urate crystal-induced arthritis in rabbits: roles of tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin-1, and interleukin-8 Lab Invest 1998 78: 973–985
Weiss JM, Downie SA, Lyman WD, Berman JW . Astrocyte-derived monocyte-chemoattractant protein-1 directs the transmigration of leukocytes across a model of the human blood–brain barrier J Immunol 1998 161: 6896–6903
Korner H et al. Critical points of tumor necrosis factor action in central nervous system autoimmune inflammation defined by gene targeting J Exp Med 1997 186: 1585–1590
Liedtke W et al. Effective treatment of models of multiple sclerosis by matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors Ann Neurol 1998 44: 35–46
Suzumura A, Sawada M, Itoh Y, Marunouchi T . Interleukin-4 induces proliferation and activation of microglia but suppresses their induction of class II major histocompatibility complex antigen expression J Neuroimmunol 1994 53: 209–218
Brodie C, Goldreich N, Haiman T, Kazimirsky G . Functional IL-4 receptors on mouse astrocytes: IL-4 inhibits astrocyte activation and induces NGF secretion J Neuroimmunol 1998 81: 20–30
Liu JSH, Amaral TD, Brosnan CF, Lee SC . IFNs are critical regulators of IL-1 receptor antagonist and IL-1 expression in human microglia J Immunol 1998 161: 1989–1996
Serot J, Bene MC, Foliguet B, Faure GC . Monocyte-derived IL-10-secreting dendritic cells in choroid plexus epithelium J Neuroimmunol 2000 105: 115–119
Abbas AK, Murphy KM, Sher A . Functional diversity of helper T lymphocytes Nature 1996 383: 787–793
DeLuca NA, McCarthy AM, Schaffer PA . Isolation and characterization of deletion mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1 in the gene encoding immediate–early regulatory protein ICP4 J Virol 1985 56: 558–570
Allen SJ et al. Isolation and characterization of cells infiltrating the spinal cord during the course of chronic relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the Biozzi AB/H mouse Cell Immunol 1993 146: 335–350
Furlan R et al. Caspase-1 regulates the inflammatory process leading to autoimmune demyelination J Immunol 1999 163: 2403–2409
Acknowledgements
This work was in part supported by Telethon (Italy), Italian Multiple Sclerosis Society (AISM) and MURST.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Furlan, R., Poliani, P., Marconi, P. et al. Central nervous system gene therapy with interleukin-4 inhibits progression of ongoing relapsing–remitting autoimmune encephalomyelitis in Biozzi AB/H mice. Gene Ther 8, 13–19 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301357
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301357
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Intracisternal delivery of PEG-coated gold nanoparticles results in high brain penetrance and long-lasting stability
Journal of Nanobiotechnology (2019)
-
IL-4 mediated by HSV vector suppresses morphine withdrawal response and decreases TNFα, NR2B, and pC/EBPβ in the periaqueductal gray in rats
Gene Therapy (2017)
-
IL4 induces IL6-producing M2 macrophages associated to inhibition of neuroinflammation in vitro and in vivo
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2016)
-
A comparative study of experimental mouse models of central nervous system demyelination
Gene Therapy (2014)
-
Effect of herpes simplex virus vector-mediated interleukin-4 gene therapy on bladder overactivity and nociception
Gene Therapy (2013)