Abstract
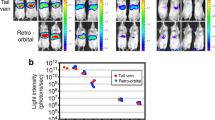
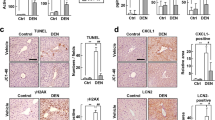
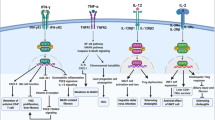
Drug-inducible systems allow modulation of the duration and intensity of cytokine expression in liver immuno-based gene therapy protocols. However, the biological activity of the transgene may influence their function. We have analyzed the kinetics of interleukin-12 (IL-12) expression controlled by the doxycycline (Dox)- and the mifepristone (Mif)-dependent systems using two long-term expressing vectors directed to liver: a plasmid administered by hydrodynamic injection and a high-capacity adenoviral vector. Daily administration of Dox or Mif was associated with a progressive loss of inducibility and a decrease of murine IL-12 production. This inhibition occurred at the transcriptional level and was probably caused by an interferon (IFN)-γ-mediated downmodulation of liver-specific promoters that control the expression of transactivators in these systems. Genome-wide expression microarrays studies revealed a parallel downregulation of liver-specific genes in mice overexpressing murine IL-12. However, a promoter naturally induced by IL-12 was also inhibited by this cytokine when placed in a plasmid vector. Interestingly, treatment with sodium butyrate, a class I/II histone deacetylase inhibitor, was able to rescue liver-specific promoter activity solely in the vector. We conclude that biologically active IL-12 can transiently inhibit the function of drug-inducible systems in non-integrative DNA vectors by reducing promoter activity, probably through IFN-γ and protein deacetylation-dependent mechanisms.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Prieto J, Qian C, Hernandez-Alcoceba R, Gonzalez-Aseguinolaza G, Mazzolini G, Sangro B et al. Gene therapy of liver diseases. Expert Opin Biol Ther 2004; 4: 1073–1091.
Sangro B, Mazzolini G, Ruiz J, Herraiz M, Quiroga J, Herrero I et al. Phase I trial of intratumoral injection of an adenovirus encoding interleukin-12 for advanced digestive tumors. J Clin Oncol 2004; 22: 1389–1397.
Penuelas I, Mazzolini G, Boan JF, Sangro B, Marti-Climent J, Ruiz M et al. Positron emission tomography imaging of adenoviral-mediated transgene expression in liver cancer patients. Gastroenterology 2005; 128: 1787–1795.
Zabala M, Wang L, Hernandez-Alcoceba R, Hillen W, Qian C, Prieto J et al. Optimization of the Tet-on system to regulate interleukin 12 expression in the liver for the treatment of hepatic tumors. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 2799–2804.
Wang L, Hernandez-Alcoceba R, Shankar V, Zabala M, Kochanek S, Sangro B et al. Prolonged and inducible transgene expression in the liver using gutless adenovirus: a potential therapy for liver cancer. Gastroenterology 2004; 126: 278–289.
Burcin MM, Schiedner G, Kochanek S, Tsai SY, O'Malley BW . Adenovirus-mediated regulable target gene expression in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96: 355–360.
Aurisicchio L, De Tomassi A, La Monica N, Ciliberto G, Traboni C, Palombo F . Regulated and liver-specific tamarin alpha interferon gene delivery by a helper-dependent adenoviral vector. J Virol 2005; 79: 6772–6780.
Brunda MJ, Luistro L, Hendrzak JA, Fountoulakis M, Garotta G, Gately MK . Role of interferon-gamma in mediating the antitumor efficacy of interleukin-12. J Immunother Emphasis Tumor Immunol 1995; 17: 71–77.
Su AI, Wiltshire T, Batalov S, Lapp H, Ching KA, Block D et al. A gene atlas of the mouse and human protein-encoding transcriptomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 6062–6067.
Kramer MG, Barajas M, Razquin N, Berraondo P, Rodrigo M, Wu C et al. In vitro and in vivo comparative study of chimeric liver-specific promoters. Mol Ther 2003; 7: 375–385.
Nagae Y, Muller-Eberhard U . Identification of an interleukin-6 responsive element and characterization of the proximal promoter region of the rat hemopexin gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1992; 185: 420–429.
Presky DH, Minetti LJ, Gillessen S, Wilkinson VL, Wu CY, Gubler U et al. Analysis of the multiple interactions between IL-12 and the high affinity IL-12 receptor complex. J Immunol 1998; 160: 2174–2179.
Ramana CV, Gil MP, Schreiber RD, Stark GR . Stat1-dependent and -independent pathways in IFN-gamma-dependent signaling. Trends Immunol 2002; 23: 96–101.
Yu J, Wei M, Becknell B, Trotta R, Liu S, Boyd Z et al. Pro- and antiinflammatory cytokine signaling: reciprocal antagonism regulates interferon-gamma production by human natural killer cells. Immunity 2006; 24: 575–590.
Bolden JE, Peart MJ, Johnstone RW . Anticancer activities of histone deacetylase inhibitors. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2006; 5: 769–784.
Joseph J, Mudduluru G, Antony S, Vashistha S, Ajitkumar P, Somasundaram K . Expression profiling of sodium butyrate (NaB)-treated cells: identification of regulation of genes related to cytokine signaling and cancer metastasis by NaB. Oncogene 2004; 23: 6304–6315.
Yamano T, Ura K, Morishita R, Nakajima H, Monden M, Kaneda Y . Amplification of transgene expression in vitro and in vivo using a novel inhibitor of histone deacetylase. Mol Ther 2000; 1: 574–580.
Ying M, Xu R, Wu X, Zhu H, Zhuang Y, Han M et al. Sodium butyrate ameliorates histone hypoacetylation and neurodegenerative phenotypes in a mouse model for DRPLA. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 12580–12586.
Egorin MJ, Yuan ZM, Sentz DL, Plaisance K, Eiseman JL . Plasma pharmacokinetics of butyrate after intravenous administration of sodium butyrate or oral administration of tributyrin or sodium butyrate to mice and rats. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 1999; 43: 445–453.
Lui VW, Falo Jr LD, Huang L . Systemic production of IL-12 by naked DNA mediated gene transfer: toxicity and attenuation of transgene expression in vivo. J Gene Med 2001; 3: 384–393.
Leoni F, Zaliani A, Bertolini G, Porro G, Pagani P, Pozzi P et al. The antitumor histone deacetylase inhibitor suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid exhibits antiinflammatory properties via suppression of cytokines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 2995–3000.
Leoni F, Fossati G, Lewis EC, Lee JK, Porro G, Pagani P et al. The histone deacetylase inhibitor ITF2357 reduces production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in vitro and systemic inflammation in vivo. Mol Med 2005; 11: 1–15.
Castell JV, Gomez-Lechon MJ, David M, Andus T, Geiger T, Trullenque R et al. Interleukin-6 is the major regulator of acute phase protein synthesis in adult human hepatocytes. FEBS Lett 1989; 242: 237–239.
Qian X, Samadani U, Porcella A, Costa RH . Decreased expression of hepatocyte nuclear factor 3 alpha during the acute-phase response influences transthyretin gene transcription. Mol Cell Biol 1995; 15: 1364–1376.
Sung RS, Qin L, Bromberg JS . TNFalpha and IFNgamma induced by innate anti-adenoviral immune responses inhibit adenovirus-mediated transgene expression. Mol Ther 2001; 3: 757–767.
Qin L, Ding Y, Pahud DR, Chang E, Imperiale MJ, Bromberg JS . Promoter attenuation in gene therapy: interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibit transgene expression. Hum Gene Ther 1997; 8: 2019–2029.
Marks PA, Richon VM, Miller T, Kelly WK . Histone deacetylase inhibitors. Adv Cancer Res 2004; 91: 137–168.
Riu E, Chen ZY, Xu H, He CY, Kay MA . Histone modifications are associated with the persistence or silencing of vector-mediated transgene expression in vivo. Mol Ther 2007; 15: 1348–1355.
Dion LD, Goldsmith KT, Tang DC, Engler JA, Yoshida M, Garver Jr RI . Amplification of recombinant adenoviral transgene products occurs by inhibition of histone deacetylase. Virology 1997; 231: 201–209.
Gorman CM, Howard BH, Reeves R . Expression of recombinant plasmids in mammalian cells is enhanced by sodium butyrate. Nucleic Acids Res 1983; 11: 7631–7648.
Keslacy S, Tliba O, Baidouri H, Amrani Y . Inhibition of tumor necrosis factor-alpha-inducible inflammatory genes by interferon-gamma is associated with altered nuclear factor-kappaB transactivation and enhanced histone deacetylase activity. Mol Pharmacol 2007; 71: 609–618.
Klampfer L, Huang J, Swaby LA, Augenlicht L . Requirement of histone deacetylase activity for signaling by STAT1. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 30358–30368.
Nusinzon I, Horvath CM . Interferon-stimulated transcription and innate antiviral immunity require deacetylase activity and histone deacetylase 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 14742–14747.
Chang HM, Paulson M, Holko M, Rice CM, Williams BR, Marie I et al. Induction of interferon-stimulated gene expression and antiviral responses require protein deacetylase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 9578–9583.
Ocker M, Alajati A, Ganslmayer M, Zopf S, Luders M, Neureiter D et al. The histone-deacetylase inhibitor SAHA potentiates proapoptotic effects of 5-fluorouracil and irinotecan in hepatoma cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2005; 131: 385–394.
Takimoto R, Kato J, Terui T, Takada K, Kuroiwa G, Wu J et al. Augmentation of antitumor effects of p53 gene therapy by combination with HDAC inhibitor. Cancer Biol Ther 2005; 4: 421–428.
Gonzalez-Aseguinolaza G, Van Kaer L, Bergmann CC, Wilson JM, Schmieg J, Kronenberg M et al. Natural killer T cell ligand alpha-galactosylceramide enhances protective immunity induced by malaria vaccines. J Exp Med 2002; 195: 617–624.
Zhang G, Budker V, Wolff JA . High levels of foreign gene expression in hepatocytes after tail vein injections of naked plasmid DNA. Hum Gene Ther 1999; 10: 1735–1737.
Crettaz J, Berraondo P, Mauleon I, Ochoa L, Shankar V, Barajas M et al. Intrahepatic injection of adenovirus reduces inflammation and increases gene transfer and therapeutic effect in mice. Hepatology 2006; 44: 623–632.
Berasain C, Garcia-Trevijano ER, Castillo J, Erroba E, Santamaria M, Lee DC et al. Novel role for amphiregulin in protection from liver injury. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 19012–19020.
Irizarry RA, Bolstad BM, Collin F, Cope LM, Hobbs B, Speed TP . Summaries of Affymetrix GeneChip probe level data. Nucleic Acids Res 2003; 31: e15.
Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA, Astrand M, Speed TP . A comparison of normalization methods for high density oligonucleotide array data based on variance and bias. Bioinformatics 2003; 19: 185–193.
Tusher VG, Tibshirani R, Chu G . Significance analysis of microarrays applied to the ionizing radiation response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 5116–5121.
Benjamini Y, Drai D, Elmer G, Kafkafi N, Golani I . Controlling the false discovery rate in behavior genetics research. Behav Brain Res 2001; 125: 279–284.
Murtagh F . Multidimensional clustering algorithms. COMPSTAT Lectures 4. Physica-Verlag: Wuerzburg, 1985, pp 131.
Acknowledgements
We thank Gloria Gonzalez-Aseguinolaza (Division Hepatology and Gene Therapy, University of Navarra, Spain) for the IFN-γ R−/− knockout mice. We appreciate scientific feedback obtained from Ricky Johnstone (Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre, Australia) and Howard Young (National Cancer Institute, USA). This project was founded through the UTE project CIMA, DIGNA Biotech and Grants from Education Department, Gobierno de Navarra and Fondo de Investigacion Sanitaria (FIS) and CIBERehd. RHA is a recipient of Ramon y Cajal research contract. MGK is a recipient of an FIS research contract. IM is a recipient of a Torres Quevedo contract.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reboredo, M., Zabala, M., Mauleon, I. et al. Interleukin-12 inhibits liver-specific drug-inducible systems in vivo. Gene Ther 15, 277–288 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3303073
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3303073
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Development of a Liver-specific Tet-On Inducible System for AAV Vectors and Its Application in the Treatment of Liver Cancer
Molecular Therapy (2011)
-
Inhibition of nuclear delivery of plasmid DNA and transcription by interferon γ: hurdles to be overcome for sustained gene therapy
Gene Therapy (2011)
-
Intensive Pharmacological Immunosuppression Allows for Repetitive Liver Gene Transfer With Recombinant Adenovirus in Nonhuman Primates
Molecular Therapy (2010)