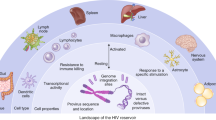
Abstract
The current treatment regimen for HIV-infected individuals combines two or more drugs targeting different viral proteins such as RT and gag. Resistance to conventional drugs can develop quickly, and typically persists. The prospect of longer, continuous antiretroviral therapy brings with it the need for new antiretroviral drugs and approaches. In this context, gene therapies have the potential to prolong life and quality of life as an additional therapeutic class and may serve as an adjuvant to traditional treatments. This review focuses on RNA-based hematopoietic cell gene therapy for treatment of HIV infection. Recent advances in our understanding of RNA interference (RNAi) make this an especially attractive candidate for anti-HIV gene therapy although ribozyme and RNA decoy/aptamer approaches can be combined with RNAi to make a combinatorial therapy akin to highly active anti-retroviral therapy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Podlekareva D, Mocroft A, Dragsted UB, Ledergerber B, Beniowski M, Lazzarin A et al. Factors associated with the development of opportunistic infections in HIV-1-infected adults with high CD4+ cell counts: a EuroSIDA study. J Infect Dis 2006; 194: 633–641.
Deeks SG . Antiretroviral treatment of HIV infected adults. BMJ 2006; 332: 1489–1493.
Phillips AN, Gazzard BG, Clumeck N, Losso MH, Lundgren JD . When should antiretroviral therapy for HIV be started? BMJ 2007; 334: 76–78.
Stevens M, De Clercq E, Balzarini J . The regulation of HIV-1 transcription: molecular targets for chemotherapeutic intervention. Med Res Rev 2006; 26: 595–625.
Sharma A, Awasthi S, Harrod CK, Matlock EF, Khan S, Xu L et al. The Werner syndrome helicase is a cofactor for HIV-1 long terminal repeat transactivation and retroviral replication. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 12048–12057.
Hetzer C, Bisgrove D, Cohen MS, Pedal A, Kaehlcke K, Speyerer A et al. Recruitment and Activation of RSK2 by HIV-1 Tat. PLoS ONE 2007; 2: e151.
Haase AD, Jaskiewicz L, Zhang H, Laine S, Sack R, Gatignol A et al. TRBP, a regulator of cellular PKR and HIV-1 virus expression, interacts with Dicer and functions in RNA silencing. EMBO Rep 2005; 6: 961–967.
Bennasser Y, Yeung ML, Jeang KT . HIV-1 TAR RNA subverts RNA interference in transfected cells through sequestration of TAR RNA-binding protein, TRBP. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 27674–27678.
Triboulet R, Mari B, Lin YL, Chable-Bessia C, Bennasser Y, Lebrigand K et al. Suppression of microRNA-silencing pathway by HIV-1 during virus replication. Science 2007; 315: 1579–1582.
Christensen HS, Daher A, Soye KJ, Frankel LB, Alexander MR, Laine S et al. Small Interfering RNAs against the TAR RNA Binding Protein, TRBP, a Dicer Cofactor, Inhibit Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Long Terminal Repeat Expression and Viral Production. J Virol 2007; 81: 5121–5131.
Bannwarth S, Laine S, Daher A, Grandvaux N, Clerzius G, Leblanc AC et al. Cell-specific regulation of TRBP1 promoter by NF-Y transcription factor in lymphocytes and astrocytes. J Mol Biol 2006; 355: 898–910.
Ong CL, Thorpe JC, Gorry PR, Bannwarth S, Jaworowski A, Howard JL et al. Low TRBP levels support an innate human immunodeficiency virus type 1 resistance in astrocytes by enhancing the PKR antiviral response. J Virol 2005; 79: 12763–12772.
Wu W, Sun M, Zou GM, Chen J . MicroRNA and cancer: current status and prospective. Int J Cancer 2007; 120: 953–960.
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP, Anderson TA . MicroRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol 2007; 302: 1–12.
Osada H, Takahashi T . MicroRNAs in biological processes and carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 2007; 28: 2–12.
Rinaldi A, Poretti G, Kwee I, Zucca E, Catapano CV, Tibiletti MG et al. Concomitant MYC and microRNA cluster miR-17-92 (C13orf25) amplification in human mantle cell lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma 2007; 48: 410–412.
Matsubara H, Takeuchi T, Nishikawa E, Yanagisawa K, Hayashita Y, Ebi H et al. Apoptosis induction by antisense oligonucleotides against miR-17-5p and miR-20a in lung cancers overexpressing miR-17-92. Oncogene [E-pub ahead of print: 26 March 2007; doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210425].
Venturini L, Battmer K, Castoldi M, Schultheis B, Hochhaus A, Muckenthaler MU et al. Expression of the miR-17-92 polycistron in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) CD34+cells. Blood 2007; 109: 4399–4405.
Omoto S, Fujii YR . Cloning and detection of HIV-1-encoded microRNA. Methods Mol Biol 2006; 342: 255–265.
Bennasser Y, Le SY, Yeung ML, Jeang KT . MicroRNAs in human immunodeficiency virus-1 infection. Methods Mol Biol 2006; 342: 241–253.
Mattes J, Yang M, Foster PS . Regulation of microRNA by antagomirs: a new class of pharmacological antagonists for the specific regulation of gene function? Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2007; 36: 8–12.
Puerta-Fernandez E, Barroso-del Jesus A, Romero-Lopez C, Tapia N, Martinez MA, Berzal-Herranz A . Inhibition of HIV-1 replication by RNA targeted against the LTR region. AIDS 2005; 19: 863–870.
Gu S, Ji J, Kim JD, Yee JK, Rossi JJ . Inhibition of infectious human immunodeficiency virus type 1 virions via lentiviral vector encoded short antisense RNAs. Oligonucleotides 2006; 16: 287–295.
Barroso-DelJesus A, Puerta-Fernandez E, Tapia N, Romero-Lopez C, Sanchez-Luque FJ, Martinez MA et al. Inhibition of HIV-1 replication by an improved hairpin ribozyme that includes an RNA decoy. RNA Biol 2005; 2: 75–79.
Sood V, Unwalla H, Gupta N, Chakraborti S, Banerjea AC . Potent knock down of HIV-1 replication by targeting HIV-1 Tat/Rev RNA sequences synergistically with catalytic RNA and DNA. AIDS 2007; 21: 31–40.
Qureshi A, Zheng R, Parlett T, Shi X, Balaraman P, Cheloufi S et al. Gene silencing of HIV chemokine receptors using ribozymes and single-stranded antisense RNA. Biochem J 2006; 394: 511–518.
Sajic R, Lee K, Asai K, Sakac D, Branch DR, Upton C et al. Use of modified U1 snRNAs to inhibit HIV-1 replication. Nucleic Acids Res 2007; 35: 247–255.
Yan H, Zareen N, Levinger L . Naturally occurring mutations in human mitochondrial pre-tRNASer(UCN) can affect the transfer ribonuclease Z cleavage site, processing kinetics, and substrate secondary structure. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 3926–3935.
Kovrigina E, Yang L, Pfund E, Altman S . Regulated expression of functional external guide sequences in mammalian cells using a U6 RNA polymerase III promoter. RNA 2005; 11: 1588–1595.
Li H, Trang P, Kim K, Zhou T, Umamoto S, Liu F . Effective inhibition of human cytomegalovirus gene expression and growth by intracellular expression of external guide sequence RNA. RNA 2006; 12: 63–72.
Yang YH, Li H, Zhou T, Kim K, Liu F . Engineered external guide sequences are highly effective in inducing RNase P for inhibition of gene expression and replication of human cytomegalovirus. Nucleic Acids Res 2006; 34: 575–583.
Barnor JS, Endo Y, Habu Y, Miyano-Kurosaki N, Kitano M, Yamamoto H et al. Effective inhibition of HIV-1 replication in cultured cells by external guide sequences and ribonuclease P. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2004; 14: 4941–4944.
Ikeda M, Habu Y, Miyano-Kurosaki N, Takaku H . Suppression of HIV-1 replication by a combination of endonucleolytic ribozymes (RNase P and tRNnase ZL). Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2006; 25: 427–437.
Boden D, Pusch O, Lee F, Tucker L, Ramratnam B . Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 escape from RNA interference. J Virol 2003; 77: 11531–11535.
Das AT, Brummelkamp TR, Westerhout EM, Vink M, Madiredjo M, Bernards R et al. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 escapes from RNA interference-mediated inhibition. J Virol 2004; 78: 2601–2605.
Sabariegos R, Gimenez-Barcons M, Tapia N, Clotet B, Martinez MA . Sequence homology required by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 to escape from short interfering RNAs. J Virol 2006; 80: 571–577.
Westerhout EM, Ooms M, Vink M, Das AT, Berkhout B . HIV-1 can escape from RNA interference by evolving an alternative structure in its RNA genome. Nucleic Acids Res 2005; 33: 796–804.
Nishitsuji H, Kohara M, Kannagi M, Masuda T . Effective suppression of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 through a combination of short- or long-hairpin RNAs targeting essential sequences for retroviral integration. J Virol 2006; 80: 7658–7666.
Chang LJ, Liu X, He J . Lentiviral siRNAs targeting multiple highly conserved RNA sequences of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Gene Therapy 2005; 12: 1133–1144.
Berkhout B, Haasnoot J . The interplay between virus infection and the cellular RNA interference machinery. FEBS Lett 2006; 580: 2896–2902.
Wilson JA, Richardson CD . Hepatitis C virus replicons escape RNA interference induced by a short interfering RNA directed against the NS5b coding region. J Virol 2005; 79: 7050–7058.
Kim DH, Rossi JJ . Strategies for silencing human disease using RNA interference. Nat Rev Genet 2007; 8: 173–184.
Akashi H, Miyagishi M, Yokota T, Watanabe T, Hino T, Nishina K et al. Escape from the interferon response associated with RNA interference using vectors that encode long modified hairpin-RNA. Mol Biosyst 2005; 1: 382–390.
Weinberg MS, Ely A, Barichievy S, Crowther C, Mufamadi S, Carmona S et al. Specific inhibition of HBV replication in vitro and in vivo with expressed long hairpin RNA. Mol Ther 2007; 15: 534–541.
Strat A, Gao L, Utsuki T, Cheng B, Nuthalapaty S, Mathis JM et al. Specific and nontoxic silencing in mammalian cells with expressed long dsRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 2006; 34: 3803–3810.
Watanabe T, Sudoh M, Miyagishi M, Akashi H, Arai M, Inoue K et al. Intracellular-diced dsRNA has enhanced efficacy for silencing HCV RNA and overcomes variation in the viral genotype. Gene Therapy 2006; 13: 883–892.
Konstantinova P, ter Brake O, Haasnoot J, de Haan P, Berkhout B . Trans-inhibition of HIV-1 by a long hairpin RNA expressed within the viral genome. Retrovirology 2007; 4: 1–14.
Konstantinova P, de Vries W, Haasnoot J, ter Brake O, de Haan P, Berkhout B . Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 by RNA interference using long-hairpin RNA. Gene Therapy 2006; 13: 1403–1413.
An DS, Qin FX, Auyeung VC, Mao SH, Kung SK, Baltimore D et al. Optimization and functional effects of stable short hairpin RNA expression in primary human lymphocytes via lentiviral vectors. Mol Ther 2006; 14: 494–504.
Grimm D, Streetz KL, Jopling CL, Storm TA, Pandey K, Davis CR et al. Fatality in mice due to oversaturation of cellular microRNA/short hairpin RNA pathways. Nature 2006; 441: 537–541.
Scherer LJ, Frank R, Rossi JJ . Optimization and characterization of tRNA-shRNA expression constructs. Nucleic Acids Res 2007; 35: 2620–2628.
ter Brake O, Konstantinova P, Ceylan M, Berkhout B . Silencing of HIV-1 with RNA interference: a multiple shRNA approach. Mol Ther 2006; 14: 883–892.
Garcia-Sastre A, Biron CA . Type 1 interferons and the virus-host relationship: a lesson in detente. Science 2006; 312: 879–882.
de Veer MJ, Sledz CA, Williams BR . Detection of foreign RNA: implications for RNAi. Immunol Cell Biol 2005; 83: 224–228.
Karpala AJ, Doran TJ, Bean AG . Immune responses to dsRNA: implications for gene silencing technologies. Immunol Cell Biol 2005; 83: 211–216.
Robbins MA, Li M, Leung I, Li H, Boyer DV, Song Y et al. Stable expression of shRNAs in human CD34+ progenitor cells can avoid induction of interferon responses to siRNAs in vitro. Nat Biotechnol 2006; 24: 566–571.
Kim DH, Villeneuve LM, Morris KV, Rossi JJ . Argonaute-1 directs siRNA-mediated transcriptional gene silencing in human cells. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2006; 13: 793–797.
Janowski BA, Corey DR . Inhibiting transcription of chromosomal DNA using antigene RNAs. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser (Oxf) 2005: 367–368.
Janowski BA, Hu J, Corey DR . Silencing gene expression by targeting chromosomal DNA with antigene peptide nucleic acids and duplex RNAs. Nat Protoc 2006; 1: 436–443.
Janowski BA, Huffman KE, Schwartz JC, Ram R, Hardy D, Shames DS et al. Inhibiting gene expression at transcription start sites in chromosomal DNA with antigene RNAs. Nat Chem Biol 2005; 1: 216–222.
Janowski BA, Huffman KE, Schwartz JC, Ram R, Nordsell R, Shames DS et al. Involvement of AGO1 and AGO2 in mammalian transcriptional silencing. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2006; 13: 787–792.
Janowski BA, Kaihatsu K, Huffman KE, Schwartz JC, Ram R, Hardy D et al. Inhibiting transcription of chromosomal DNA with antigene peptide nucleic acids. Nat Chem Biol 2005; 1: 210–215.
Janowski BA, Younger ST, Hardy DB, Ram R, Huffman KE, Corey DR . Activating gene expression in mammalian cells with promoter-targeted duplex RNAs. Nat Chem Biol 2007; 3: 166–173.
Martianov I, Ramadass A, Serra Barros A, Chow N, Akoulitchev A . Repression of the human dihydrofolate reductase gene by a non-coding interfering transcript. Nature 2007; 445: 666–670.
Li M, Rossi JJ . Lentiviral vector delivery of siRNA and shRNA encoding genes into cultured and primary hematopoietic cells. Methods Mol Biol 2005; 309: 261–272.
Bahner I, Sumiyoshi T, Kagoda M, Swartout R, Peterson D, Pepper K et al. Lentiviral vector transduction of a dominant-negative Rev gene into human CD34(+) hematopoietic progenitor cells potently inhibits human immunodeficiency virus-1 replication. Mol Ther 2007; 15: 76–85.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scherer, L., Rossi, J. & Weinberg, M. Progress and prospects: RNA-based therapies for treatment of HIV infection. Gene Ther 14, 1057–1064 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302977
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302977
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Surface modification of TPGS-b-(PCL-ran-PGA) nanoparticles with polyethyleneimine as a co-delivery system of TRAIL and endostatin for cervical cancer gene therapy
Nanoscale Research Letters (2013)
-
Functional In Vivo Delivery of Multiplexed Anti-HIV-1 siRNAs via a Chemically Synthesized Aptamer With a Sticky Bridge
Molecular Therapy (2013)
-
Co-delivery of docetaxel and endostatin by a biodegradable nanoparticle for the synergistic treatment of cervical cancer
Nanoscale Research Letters (2012)
-
Therapeutic Potential of Aptamer-siRNA Conjugates for Treatment of HIV-1
BioDrugs (2012)
-
Systemic Administration of Combinatorial dsiRNAs via Nanoparticles Efficiently Suppresses HIV-1 Infection in Humanized Mice
Molecular Therapy (2011)