Abstract
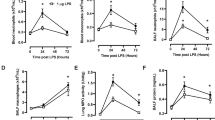
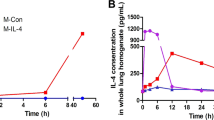
Targeted expression of interleukin-10 (IL-10) has been proposed as a means to suppress acute and chronic inflammation. We explored the capacity of targeted adenoviral expression of human or viral IL-10 to improve outcome in a zymosan-induced model of acute lung injury and multisystem organ failure. Intratracheal administration of adenovirus expressing either human or viral IL-10 prior to zymosan administration significantly improved survival at a dose of 107 particles (P<0.01), whereas the same recombinant vectors were ineffective at 108 particles and increased mortality at 109 particles. Improved survival after administration of 107 particles of adenovirus expressing viral or human IL-10 was associated with local tissue expression of IL-10 (100–300 pg/g wet wt). In contrast, mortality after administration of 109 particles was associated with markedly elevated IL-10 expression, both in the lung (10 000–70 000 pg/g wet wt) and systemically (1000–3000 pg/ml plasma), with evidence of an exaggerated systemic inflammatory response (plasma IL-6 and TNFα). Targeted gene expression of IL-10 can be used to treat acute inflammatory processes, but increased doses resulting in its systemic release are not associated with improvements in outcome, and may actually exacerbate acute inflammatory processes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Crystal RG . The gene as the drug. Nat Med 1995; 1: 15–17.
Moldawer LL, Edwards PD, Josephs M, Minter RM, Copeland III EM, MacKay SL . Application of gene therapy to acute inflammatory diseases. Shock 1999; 12: 83–101.
Factor P . Gene therapy for acute diseases. Mol Ther 2001; 4: 515–524.
St George JA . Gene therapy progress and prospects: adenoviral vectors. Gene Therapy 2003; 10: 1135–1141.
Volpers C, Kochanek S . Adenoviral vectors for gene transfer and therapy. J Gene Med 2004; 6 (Suppl 1): S164–S171.
Doerschug K, Sanlioglu S, Flaherty DM, Wilson RL, Yarovinsky T, Monick MM et al. First-generation adenovirus vectors shorten survival time in a murine model of sepsis. J Immunol 2002; 169: 6539–6545.
Oberholzer C, Oberholzer A, Tschoeke SK, Minter RM, Bahjat FR, LaFace D et al. Influence of recombinant adenovirus on liver injury in endotoxicosis, and its modulation by IL-10 expression. J Endot Res 2004; 10: 393–401.
Margolis DJ, Crombleholme T, Herlyn M . Clinical protocol: Phase I trial to evaluate the safety of H5.020CMV.PDGF-B for the treatment of a diabetic insensate foot ulcer. Wound Repair Regen 2000; 8: 480–493.
Sangro B, Mazzolini G, Ruiz J, Herraiz M, Quiroga J, Herrero I et al. Phase I trial of intratumoral injection of an adenovirus encoding interleukin-12 for advanced digestive tumors. J Clin Oncol 2004; 22: 1389–1397.
Evans CH . Gene therapies for osteoarthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep 2004; 6: 31–40.
Minter RM, Rectenwald JE, Fukuzuka K, Tannahill CL, La Face D, Tsai V et al. TNF-alpha receptor signaling and IL-10 gene therapy regulate the innate and humoral immune responses to recombinant adenovirus in the lung. J Immunol 2000; 164: 443–451.
Minter RM, Ferry MA, Rectenwald JE, Bahjat FR, Oberholzer A, Oberholzer C et al. Extended lung expression and increased tissue localization of viral IL-10 with adenoviral gene therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 277–282.
Minter RM, Ferry MA, Murday ME, Tannahill CL, Bahjat FR, Oberholzer C et al. Adenoviral delivery of human and viral IL-10 in murine sepsis. J Immunol 2001; 167: 1053–1059.
Standiford TJ, Wilkowski JM, Sisson TH, Hattori N, Mehrad B, Bucknell KA et al. Intrapulmonary tumor necrosis factor gene therapy increases bacterial clearance and survival in murine gram-negative pneumonia. Hum Gene Ther 1999; 10: 899–909.
Chen GH, Reddy RC, Newstead MW, Tateda K, Kyasapura BL, Standiford TJ . Intrapulmonary TNF gene therapy reverses sepsis-induced suppression of lung antibacterial host defense. J Immunol 2000; 165: 6496–6503.
Goris RJ, Boekholtz WK, van Bebber IP, Nuytinck JK, Schillings PH . Multiple-organ failure and sepsis without bacteria. An experimental model. Arch Surg 1986; 121: 897–901.
Pittet JF, Griffiths MJ, Geiser T, Kaminski N, Dalton SL, Huang X et al. TGF-beta is a critical mediator of acute lung injury. J Clin Invest 2001; 107: 1537–1544.
Oberholzer A, Oberholzer C, Moldawer LL . Interleukin-10: A complex role in the pathogenesis of sepsis syndromes and its potential as an anti-inflammatory drug. Crit Care Med 2002; 30: S58–S63.
Walley KR, Lukacs NW, Standiford TJ, Strieter RM, Kunkel SL . Balance of inflammatory cytokines related to severity and mortality of murine sepsis. Infect Immun 1996; 64: 4733–4738.
van der Poll T, Marchant A, Buurman WA, Berman L, Keogh CV, Lazarus DD et al. Endogenous IL-10 protects mice from death during septic peritonitis. J Immunol 1995; 155: 5397–5401.
Steinhauser ML, Hogaboam CM, Kunkel SL, Lukacs NW, Strieter RM, Standiford TJ . IL-10 is a major mediator of sepsis-induced impairment in lung antibacterial host defense. J Immunol 1999; 162: 392–399.
Lyons A, Kelly JL, Rodrick ML, Mannick JA, Lederer JA . Major injury induces increased production of interleukin-10 by cells of the immune system with a negative impact on resistance to infection. Ann Surg 1997; 226: 450–458; discussion 458–460.
Peng Y, Trevejo J, Zhou J, Marino MW, Crystal RG, Falck-Pedersen E et al. Inhibition of tumor necrosis factor alpha by an adenovirus-encoded soluble fusion protein extends transgene expression in the liver and lung. J Virol 1999; 73: 5098–5109.
Zhang HG, Zhou T, Yang P, Edwards III CK, Curiel DT, Mountz JD . Inhibition of tumor necrosis factor alpha decreases inflammation and prolongs adenovirus gene expression in lung and liver. Hum Gene Ther 1998; 9: 1875–1884.
Neidhardt R, Keel M, Steckholzer U, Safret A, Ungethuem U, Trentz O et al. Relationship of interleukin-10 plasma levels to severity of injury and clinical outcome in injured patients. J Trauma 1997; 42: 863–870; discussion 870–861.
Oldenburg HS, Burress Welborn M, Pruitt JH, Boelens PG, Seeger JM, Martin TD et al. Interleukin-10 appearance following thoraco-abdominal and abdominal aortic aneurysm repair is associated with the duration of visceral ischaemia. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 2000; 20: 169–172.
Ertel W, Keel M, Bonaccio M, Steckholzer U, Gallati H, Kenney JS et al. Release of anti-inflammatory mediators after mechanical trauma correlates with severity of injury and clinical outcome. J Trauma 1995; 39: 879–885; discussion 885-877.
Jansen MJ, Hendriks T, de Man BM, van der Meer JW, Goris RJ . Interleukin 10 mitigates the development of the zymosan-induced multiple organ dysfunction syndrome in mice. Cytokine 1999; 11: 713–721.
von Asmuth EJ, Maessen JG, van der Linden CJ, Buurman WA . Tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin 6 in a zymosan-induced shock model. Scand J Immunol 1990; 32: 313–319.
Jansen MJ, Hendriks T, Hermsen R, Van der Meer JW, Goris RJ . A monoclonal antibody against tumour necrosis factor-alpha improves survival in experimental multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Cytokine 1998; 10: 904–910.
Lauw FN, Pajkrt D, Hack CE, Kurimoto M, van Deventer SJ, van der Poll T . Proinflammatory effects of IL-10 during human endotoxemia. J Immunol 2000; 165: 2783–2789.
Adib-Conquy M, Petit AF, Marie C, Fitting C, Cavaillon JM . Paradoxical priming effects of IL-10 on cytokine production. Int Immunol 1999; 11: 689–698.
Kelly JL, Lyons A, Soberg CC, Mannick JA, Lederer JA . Anti-interleukin-10 antibody restores burn-induced defects in T-cell function. Surgery 1997; 122: 146–152.
Graham FL, Prevec L . Methods for construction of adenovirus vectors. Mol Biotechnol 1995; 3: 207–220.
Vieira P, de Waal-Malefyt R, Dang MN, Johnson KE, Kastelein R, Fiorentino DF et al. Isolation and expression of human cytokine synthesis inhibitory factor cDNA clones: homology to Epstein-Barr virus open reading frame BCRFI. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1991; 88: 1172–1176.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by Grants R01 GM-63021-03, awarded by the National Institute of General Medical Sciences. PM and PE were supported by a training Grant T32 GM-08235-05, in burns and trauma research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McAuliffe, P., Murday, M., Efron, P. et al. Dose-dependent improvements in outcome with adenoviral expression of interleukin-10 in a murine model of multisystem organ failure. Gene Ther 13, 276–282 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302600
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302600
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Effect of recombinant IL-10 on cultured fetal rat alveolar type II cells exposed to 65%-hyperoxia
Respiratory Research (2011)
-
Clinical Review: Gene-based therapies for ALI/ARDS: where are we now?
Critical Care (2011)