Abstract
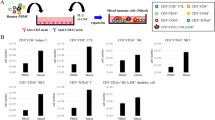
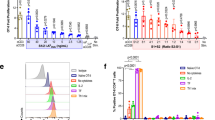
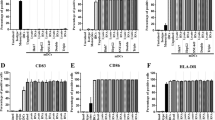
The maturation state of dendritic cells (DCs) is an important determinant for the initiation and regulation of adaptive immune responses. In this study, we wanted to assess whether functional activation of human monocyte-derived DCs can be achieved by electroporation of an activation signal in the form of double-stranded (ds) RNA and whether simultaneous electroporation of the dsRNA with tumor antigen encoding mRNA can lead to the induction of a cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) response. Electroporation of immature DCs with poly(I:C12U), a dsRNA analogue, resulted in phenotypic as well as functional changes, indicative of DC maturation. Co-electroporation of DCs with both poly(I:C12U) and Melan-A/MART-1 encoding mRNA induced strong anti-Melan-A/MART-1 CD8+ T-cell responses in vitro. Higher numbers of Melan-A/MART-1-specific CTLs were consistently obtained with poly(I:C12U)-activated DCs compared to DCs matured in the presence of an inflammatory cytokine cocktail. These results indicate that DC co-electroporation with both dsRNA and tumor antigen encoding mRNA induces fully activated and antigen-loaded DCs that promote antigen-specific CTL responses and may provide the basis for future immunotherapeutic strategies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Janeway Jr CA . Approaching the asymptote? Evolution and revolution in immunology. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 1989; 54 (Part 1): 1–13.
Alexopoulou L, Holt AC, Medzhitov R, Flavell RA . Recognition of double-stranded RNA and activation of NF-kappaB by Toll-like receptor 3. Nature 2001; 413: 732–738.
Matsumoto M, Funami K, Tanabe M, Oshiumi H, Shingai M, Seto Y et al. Subcellular localization of Toll-like receptor 3 in human dendritic cells. J Immunol 2003; 171: 3154–3162.
Williams BR . Signal integration via PKR. Sci STKE 2001; 89: RE2.
Diebold SS, Montoya M, Unger H, Alexopoulou L, Roy P, Haswell LE et al. Viral infection switches non-plasmacytoid dendritic cells into high interferon producers. Nature 2003; 424: 324–328.
Stark GR, Kerr IM, Williams BR, Silverman RH, Schreiber RD . How cells respond to interferons. Annu Rev Biochem 1998; 67: 227–264.
Yoneyama M, Kikuchi M, Natsukawa T, Shinobu N, Imaizumi T, Miyagishi M et al. The RNA helicase RIG-I has an essential function in double-stranded RNA-induced innate antiviral responses. Nat Immunol 2004; 5: 730–737.
Sallusto F, Lanzavecchia A . Efficient presentation of soluble antigen by cultured human dendritic cells is maintained by granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor plus interleukin 4 and downregulated by tumor necrosis factor alpha. J Exp Med 1994; 179: 1109–1118.
Gallucci S, Lolkema M, Matzinger P . Natural adjuvants: endogenous activators of dendritic cells. Nat Med 1999; 5: 1249–1255.
Luft T, Pang KC, Thomas E, Hertzog P, Hart DN, Trapani J et al. Type I IFNs enhance the terminal differentiation of dendritic cells. J Immunol 1998; 161: 1947–1953.
Le Bon A, Schiavoni G, D'Agostino G, Gresser I, Belardelli F, Tough DF . Type I interferons potently enhance humoral immunity and can promote isotype switching by stimulating dendritic cells in vivo. Immunity 2001; 14: 461–470.
Lebre MC, Antons JC, Kalinski P, Schuitemaker JH, van Capel TM, Kapsenberg ML et al. Double-stranded RNA-exposed human keratinocytes promote Th1 responses by inducing a type-1 polarized phenotype in dendritic cells: role of keratinocyte-derived tumor necrosis factor alpha, type I interferons, and interleukin-18. J Invest Dermatol 2003; 120: 990–997.
Romani N, Reider D, Heuer M, Ebner S, Kampgen E, Eibl B et al. Generation of mature dendritic cells from human blood. An improved method with special regard to clinical applicability. J Immunol Methods 1996; 196: 137–151.
Jonuleit H, Kuhn U, Muller G, Steinbrink K, Paragnik L, Schmitt E et al. Pro-inflammatory cytokines and prostaglandins induce maturation of potent immunostimulatory dendritic cells under fetal calf serum-free conditions. Eur J Immunol 1997; 27: 3135–3142.
Verdijk RM, Mutis T, Esendam B, Kamp J, Melief CJ, Brand A et al. Polyriboinosinic polyribocytidylic acid (poly(I:C)) induces stable maturation of functionally active human dendritic cells. J Immunol 1999; 163: 57–61.
Cella M, Salio M, Sakakibara Y, Langen H, Julkunen I, Lanzavecchia A . Maturation, activation, and protection of dendritic cells induced by double-stranded RNA. J Exp Med 1999; 189: 821–829.
de Jong EC, Vieira PL, Kalinski P, Schuitemaker JH, Tanaka Y, Wierenga E et al. Microbial compounds selectively induce Th1 cell-promoting or Th2 cell-promoting dendritic cells in vitro with diverse Th cell-polarizing signals. J Immunol 2002; 168: 1704–1709.
Kapsenberg ML . Dendritic-cell control of pathogen-driven T-cell polarization. Nat Rev Immunol 2003; 3: 984–993.
Reis e Sousa C . Activation of dendritic cells: translating innate into adaptive immunity. Curr Opin Immunol 2004; 16: 21–25.
Adams M, Navabi H, Jasani B, Man S, Fiander A, Evans AS et al. Dendritic cell (DC) based therapy for cervical cancer: use of DC pulsed with tumour lysate and matured with a novel synthetic clinically non-toxic double stranded RNA analogue poly [I]:poly [C(12)U] (Ampligen R). Vaccine 2003; 21: 787–790.
Ponsaerts P, Van den Bosch G, Cools N, Van Driessche A, Nijs G, Lenjou M et al. Messenger RNA electroporation of human monocytes, followed by rapid in vitro differentiation, leads to highly stimulatory antigen-loaded mature dendritic cells. J Immunol 2002; 169: 1669–1675.
Scandella E, Men Y, Gillessen S, Forster R, Groettrup M . Prostaglandin E2 is a key factor for CCR7 surface expression and migration of monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Blood 2002; 100: 1354–1361.
Luft T, Jefford M, Luetjens P, Toy T, Hochrein H, Masterman KA et al. Functionally distinct dendritic cell (DC) populations induced by physiologic stimuli: prostaglandin E(2) regulates the migratory capacity of specific DC subsets. Blood 2002; 100: 1362–1372.
Jacobs BL, Langland JO . When two strands are better than one: the mediators and modulators of the cellular responses to double-stranded RNA. Virology 1996; 219: 339–349.
Horng T, Barton GM, Medzhitov R . TIRAP: an adapter molecule in the Toll signaling pathway. Nat Immunol 2001; 2: 835–841.
Kato H, Sato S, Yoneyama M, Yamamoto M, Uematsu S, Matsui K et al. Cell type-specific involvement of RIG-I in antiviral response. Immunity 2005; 23: 19–28.
Siegal FP, Kadowaki N, Shodell M, Fitzgerald-Bocarsly PA, Shah K, Ho S et al. The nature of the principal type I interferon-producing cells in human blood. Science 1999; 284: 1835–1837.
Cella M, Jarrossay D, Facchetti F, Alebardi O, Nakajima H, Lanzavecchia A et al. Plasmacytoid monocytes migrate to inflamed lymph nodes and produce large amounts of type I interferon. Nat Med 1999; 5: 919–923.
Kalinski P, Vieira PL, Schuitemaker JH, de Jong EC, Kapsenberg ML . Prostaglandin E(2) is a selective inducer of interleukin-12 p40 (IL-12p40) production and an inhibitor of bioactive IL-12p70 heterodimer. Blood 2001; 97: 3466–3469.
Van Tendeloo VF, Ponsaerts P, Lardon F, Nijs G, Lenjou M, Van Broeckhoven C et al. Highly efficient gene delivery by mRNA electroporation in human hematopoietic cells: superiority to lipofection and passive pulsing of mRNA and to electroporation of plasmid cDNA for tumor antigen loading of dendritic cells. Blood 2001; 98: 49–56.
Tuyaerts S, Michiels A, Corthals J, Bonehill A, Heirman C, de Greef C et al. Induction of Influenza Matrix Protein 1 and MelanA-specific T lymphocytes in vitro using mRNA-electroporated dendritic cells. Cancer Gene Ther 2003; 10: 696–706.
Bonehill A, Heirman C, Tuyaerts S, Michiels A, Zhang Y, van der Bruggen P et al. Efficient presentation of known HLA class II-restricted MAGE-A3 epitopes by dendritic cells electroporated with messenger RNA encoding an invariant chain with genetic exchange of class II-associated invariant chain peptide. Cancer Res 2003; 63: 5587–5594.
Michiels A, Tuyaerts S, Bonehill A, Corthals J, Breckpot K, Heirman C et al. Electroporation of immature and mature dendritic cells: implications for dendritic cell-based vaccines. Gene Therapy 2005; 12: 772–782.
Grunebach F, Kayser K, Weck MM, Muller M, Appel S, Brossart P . Cotransfection of dendritic cells with RNA coding for HER-2/neu and 4-1BBL increases the induction of tumor antigen specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Cancer Gene Ther 2005; 12: 749–756.
Dannull J, Nair S, Su Z, Boczkowski D, DeBeck C, Yang B et al. Enhancing the immunostimulatory function of dendritic cells by transfection with mRNA encoding OX40 ligand. Blood 2005; 105: 3206–3213.
Mailliard RB, Wankowicz-Kalinska A, Cai Q, Wesa A, Hilkens CM, Kapsenberg ML et al. alpha-type-1 polarized dendritic cells: a novel immunization tool with optimized CTL-inducing activity. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 5934–5937.
Gautier G, Humbert M, Deauvieau F, Scuiller M, Hiscott J, Bates EE et al. A type I interferon autocrine-paracrine loop is involved in Toll-like receptor-induced interleukin-12p70 secretion by dendritic cells. J Exp Med 2005; 201: 1435–1446.
Napolitani G, Rinaldi A, Bertoni F, Sallusto F, Lanzavecchia A . Selected Toll-like receptor agonist combinations synergistically trigger a T helper type 1-polarizing program in dendritic cells. Nat Immunol 2005; 6: 769–776.
Valmori D, Fonteneau JF, Lizana CM, Gervois N, Lienard D, Rimoldi D et al. Enhanced generation of specific tumor-reactive CTL in vitro by selected Melan-A/MART-1 immunodominant peptide analogues. J Immunol 1998; 160: 1750–1758.
Acknowledgements
We thank Erna Borms, Christine Huysmans and Jan Volkaert for help with DC cultures, Elsy Vaeremans and Peggy Verbuyst for mRNA preparations, Roger Andries and Jos Theunissen for their helpful technical suggestions and Daniel Powell and Gregory Lizée for critical reading of the manuscript. This work was supported by grants to Kris Thielemans from the Fund for Scientific Research-Flanders (FWO-Vlaanderen), the Ministry of Science (IUAP/PAI IV), the Fortis Bank, the Belgische Federatie voor Kankerbestrijding and BruCells. JL Aerts was supported by a return grant from the Belgian Science Policy (BELSPO).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Michiels, A., Breckpot, K., Corthals, J. et al. Induction of antigen-specific CD8+ cytotoxic T cells by dendritic cells co-electroporated with a dsRNA analogue and tumor antigen mRNA. Gene Ther 13, 1027–1036 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302750
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302750
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
An autologous dendritic cell vaccine polarizes a Th-1 response which is tumoricidal to patient-derived breast cancer cells
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy (2019)
-
Long-term clinical outcome of melanoma patients treated with messenger RNA-electroporated dendritic cell therapy following complete resection of metastases
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy (2015)
-
Dendritic Cells Loaded With mRNA Encoding Full-length Tumor Antigens Prime CD4+ and CD8+ T Cells in Melanoma Patients
Molecular Therapy (2012)
-
A Short Pulse of IL-4 Delivered by DCs Electroporated With Modified mRNA Can Both Prevent and Treat Autoimmune Diabetes in NOD Mice
Molecular Therapy (2010)
-
Enhancing the T-cell Stimulatory Capacity of Human Dendritic Cells by Co-electroporation With CD40L, CD70 and Constitutively Active TLR4 Encoding mRNA
Molecular Therapy (2008)