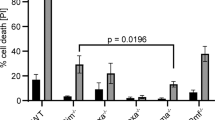
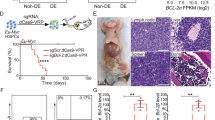
Abstract
Bcl-XL is a Bcl-2-related survival protein that is essential for normal development. Bcl-XL expression is rapidly induced by a wide range of survival signals and many cancer cells constitutively express high levels. The Bcl-X gene has a complex organization with multiple promoters giving rise to RNAs with alternate 5′ non-coding exons. Here we have investigated the mechanisms that control basal and induced expression of Bcl-XL in B-lymphoma cells. Antisense experiments demonstrated that Bcl-XL was essential for survival of Akata6 B-lymphoma cells. The levels of RNAs containing the IB Bcl-X non-coding exon, derived from the distal 1B promoter, correlated with basal expression of Bcl-XL in primary malignant B cells and this promoter was highly active in B-cell lines. The activity of this promoter was largely dependent on a single Ets binding site and Ets family proteins were bound at this promoter in intact cells. CD40 ligand (CD40L)-induced cell survival was associated with increased Bcl-XL expression and accumulation of exon IA-containing RNAs, derived from the proximal 1A promoter. Nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB) inhibition prevented induction of Bcl-XL protein and exon IA-containing RNAs by CD40L. Therefore, the distal Bcl-X 1B promoter plays a critical role in driving constitutive expression-mediated via Ets family proteins in malignant B cells, whereas NF-κB plays a central role in the induction of Bcl-XL in response to CD40 signalling via the proximal 1A promoter.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andjelic S, Hsia C, Suzuki H, Kadowaki T, Koyasu S, Liou HC . (2000). Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and NF-kappa B/Rel are at the divergence of CD40-mediated proliferation and survival pathways. J Immunol 165: 3860–3867.
Ban J, Eckhart L, Weninger W, Mildner M, Tschachler E . (1998). Identification of a human cDNA encoding a novel Bcl-x isoform. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 248: 147–152.
Biroccio A, Benassi B, D'Agnano C, Buglioni S, Mottolese M, Ricciotti A et al. (2001). c-Myb and Bcl-x overexpression predicts poor prognosis in colorectal cancer: clinical and experimental findings. Am J Pathol 158: 1289–1299.
Boise LH, Gonzalez-Garcia M, Postema CE, Ding L, Lindsten T, Turka LA et al. (1993). Bcl-x, a bcl-2 related gene that functions as a dominant regulator of apoptotic cell death. Cell 74: 597–608.
Brimmell M, Mendiola R, Mangion J, Packham G . (1998). BAX frameshift mutations in cell lines derived from human haemopoietic malignancies are associated with resistance to apoptosis and microsatellite instability. Oncogene 16: 1803–1812.
Chao DT, Korsmeyer SJ . (1998). BCL-2 family: regulators of cell death. Annu Rev Immunol 16: 395–419.
Chen C, Edelstein LC, Gelinas C . (2000). The Rel/NF-kappaB family directly activates expression of the apoptosis inhibitor Bcl-x(L). Mol Cell Biol 20: 2687–2695.
Choi MS, Boise LH, Gottschalk AR, Quintans J, Thompson CB, Klaus GG . (1995). The role of bcl-XL in CD40-mediated rescue from anti-mu-induced apoptosis in WEHI-231 B lymphoma cells. Eur J Immunol 25: 1352–1357.
Dallman C, Packham G . (2005). Purification of primary malignant B-cells and immunoblot analysis of bcl-2 family proteins. Methods Mol Med 115: 1–13.
Deng G, Lane C, Kornblau S, Goodacre A, Snell V, Andreeff M et al. (1998). Ratio of bcl-xshort to bcl-xlong is different in good- and poor-prognosis subsets of acute myeloid leukemia. Mol Med 4: 158–164.
de Nigris F, Mega T, Berger N, Barone MV, Santoro M, Viglietto G et al. (2001). Induction of ETS-1 and ETS-2 transcription factors is required for thyroid cell transformation. Cancer Res 61: 2267–2275.
Derenne S, Monia B, Dean NM, Taylor JK, Rapp MJ, Harousseau JL et al. (2002). Antisense strategy shows that Mcl-1 rather than Bcl-2 or Bcl-x(L) is an essential survival protein of human myeloma cells. Blood 100: 194–199.
Deverman BE, Cook BL, Manson SR, Niederhoff RA, Langer EM, Rosova I et al. (2002). Bcl-xL deamidation is a critical switch in the regulation of the response to DNA damage. Cell 111: 51–62.
Dumon S, Santos SC, Debierre-Grockiego F, Gouilleux-Gruart V, Cocault L, Boucheron C et al. (1999). IL-3 dependent regulation of Bcl-xL gene expression by STAT5 in a bone marrow derived cell line. Oncogene 18: 4191–4199.
Fennell DA, Corbo MV, Dean NM, Monia BP, Cotter FE . (2001). In vivo suppression of Bcl-XL expression facilitates chemotherapy-induced leukaemia cell death in a SCID/NOD-Hu model. Br J Haematol 112: 706–713.
Friess H, Lu Z, Andren-Sandberg A, Berberat P, Zimmermann A, Adler G et al. (1998). Moderate activation of the apoptosis inhibitor bcl-xL worsens the prognosis in pancreatic cancer. Ann Surg 228: 780–787.
Glasgow JN, Wood T, Perez-Polo JR . (2000). Identification and characterization of nuclear factor kappaB binding sites in the murine bcl-x promoter. J Neurochem 75: 1377–1389.
Grad JM, Zeng XR, Boise LH . (2000). Regulation of Bcl-xL: a little bit of this and a little bit of STAT. Curr Opin Oncol 12: 543–549.
Grillot DA, Gonzalez-Garcia M, Ekhterae D, Duan L, Inohara N, Ohta S et al. (1997). Genomic organization, promoter region analysis, and chromosome localization of the mouse bcl-x gene. J Immunol 158: 4750–4757.
Heere-Ress E, Thallinger C, Lucas T, Schlagbauer-Wadl H, Wacheck V, Monia BP et al. (2002). Bcl-X(L) is a chemoresistance factor in human melanoma cells that can be inhibited by antisense therapy. Int J Cancer 99: 29–34.
Hsu T, Trojanowska M, Watson DK . (2004). Ets proteins in biological control and cancer. J Cell Biochem 91: 896–903.
Inman GJ, Binne UK, Parker GA, Farrell PJ, Allday MJ . (2001). Activators of the Epstein–Barr virus lytic program concomitantly induce apoptosis, but lytic gene expression protects from cell death. J Virol 75: 2400–2410.
Irvin BJ, Wood LD, Wang L, Fenrick R, Sansam CG, Packham G et al. (2003). TEL, a putative tumor suppressor, induces apoptosis and represses transcription of Bcl-XL. J Biol Chem 278: 46378–46386.
Ishida T, Kobayashi N, Tojo T, Ishida S, Yamamoto T, Inoue J . (1995). CD40 signaling-mediated induction of Bcl-XL, CdK4, and CdK6. Implication of their co-operation in selective B cell growth. J Immunol 155: 5527–5535.
Jazirehi AR, Vega MI, Chatterjee D, Goodglick L, Bonavida B . (2004). Inhibition of the Raf-MEK1/2-ERK1/2 signaling pathway, Bcl-xL down-regulation, and chemosensitization of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma B cells by Rituximab. Cancer Res 64: 7117–7126.
Kirito K, Watanabe T, Sawada K, Endo H, Ozawa K, Komatsu N . (2002). Thrombopoietin regulates Bcl-xL gene expression through Stat5 and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation pathways. J Biol Chem 277: 8329–8337.
Krajewska M, Fenoglio-Preiser CM, Krajewski S, Song K, Macdonald JS, Stemmerman G et al. (1996a). Immunohistochemical analysis of Bcl-2 family proteins in adenocarcinomas of the stomach. Am J Pathol 149: 1449–1457.
Krajewska M, Moss SF, Krajewski S, Song K, Holt PR, Reed JC . (1996b). Elevated expression of Bcl-X and reduced Bak in primary colorectal adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res 56: 2422–2427.
Lee HH, Dadgostar H, Cheng Q, Shu J, Cheng G . (1999). NF-kappa B-mediated up-regulation of Bcl-x and Bfl-1/A1 is required for CD40 survival signaling in B lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 9136–9141.
Lee JH, Koo TH, Hwang BY, Lee JJ . (2002). Kaurane diterpene, Kamebakaurin, inhibits NF-kappa B by directly targeting the DNA-binding activity of p50 and blocks the expression of antiapoptotic NF-kappa B target genes. J Biol Chem 277: 18411–18420.
Lohmann CM, League AA, Clark WS, Lawson D, DeRose PB, Cohen C . (2000). Bcl-2: bax and bcl-2: Bcl-x ratios by image cytometric quantitation of immunohistochemical expression in ovarian carcinoma: correlation with prognosis. Cytometry 42: 61–66.
MacCarthy-Morrogh L, Wood L, Brimmell M, Johnson PW, Packham G . (2000). Identification of a novel human BCL-X promotor and exon. Oncogene 19: 5534–5538.
Michels J, O'Neill JW, Dallman CL, Mouzakiti A, Habens F, Brimmell M et al. (2004). Mcl-1 is required for Akata6 B-lymphoma cell survival and is converted to a cell death molecule by efficient caspase-mediated cleavage. Oncogene 23: 4818–4827.
Motoyama N, Wang F, Roth KA, Sawa H, Nakayama K, Nakayama K et al. (1995). Massive cell death of immature hematopoietic cells and neurons in Bcl-x-deficient mice. Science 267: 1506–1510.
Naik P, Karrim J, Hanahan D . (1996). The rise and fall of apoptosis during multistage tumorigenesis: down-modulation contributed to tumor progression from angiogenic progenitors. Genes Dev 10: 2105–2116.
Olopade OI, Adeyanju MO, Safa AR, Hagos F, Mick R, Thompson CB et al. (1997). Overexpressing of BCL-x protein in primary breast cancer is associated with high tumor grade and nodal metastases. Cancer J Sci Am 3: 230–237.
Packham G, White EL, Eischen CM, Yang H, Parganas E, Ihle JN et al. (1998). Selective regulation of Bcl-XL by a Jak kinase-dependent pathway is bypassed in murine hematopoietic malignancies. Genes Dev 12: 2475–2487.
Pallis M, Zhu YM, Russell NH . (1997). Bcl-x(L) is heterogenously expressed by acute myeloblastic leukemia cells and is associated with autonomous growth in vitro and with P-glycoprotein expression. Leukemia 11: 945–949.
Pecci A, Viegas LR, Baranao JL, Beato M . (2001). Promotor choice influences alternative splicing and determines the balanced isoforms expressed from the mouse bcl-x gene. J Biol Chem 276: 21062–21069.
Pena JC, Rudin CM, Thompson CB . (1998). A Bcl-xL transgene promotes malignant conversion of chemically initiated skin papillomas. Cancer Res 58: 2111–2116.
Seth A, Watson DK . (2005). ETS transcription factors and their emerging role in human cancer. Eur J Cancer 41: 2462–2478.
Sevilla L, Aperlo C, Dulic V, Chambard JC, Boutonnet C, Pasquier O et al. (1999). The Ets2 transcription factor inhibits apoptosis induced by colony-stimulating factor 1 deprivation of macrophages through a Bcl-xL-dependent mechanism. Mol Cell Biol 19: 2624–2634.
Sevilla L, Zaldumbide A, Pognonec P, Boulukos KE . (2001). Transcriptional regulation of the bcl-x gene encoding the anti-apoptotic Bcl-xL protein by Ets, Rel/NfkappaB, STAT and AP1 transcription factor families. Histol Histopathol 16: 595–601.
Spender LC, Cannell EJ, Hollyoake M, Wensing B, Gawn JM, Brimmell M et al. (1999). Control of cell cycle entry and apoptosis in B lymphocytes infected by Epstein–Barr virus. J Virol 73: 4678–4688.
Takada K, Horinouchi K, Ono Y, Aya T, Osato T, Takahashi M et al. (1991). An Epstein–Barr virus-producer line Akata: establishment of the cell line and analysis of viral DNA. Virus Genes 5: 147–156.
Tamir A, Howard J, Higgins RR, Li YJ, Berger L, Zacksenhaus E et al. (1999). Fli-1, an Ets-related transcription factor, regulates erythropoietin-induced erythroid proliferation and differentiation: evidence for direct transcriptional repression of the Rb gene during differentiation. Mol Cell Biol 19: 4452–4464.
Taylor JK, Zhang QQ, Monia BP, Marcusson EG, Dean NM . (1999). Inhibition of Bcl-xL expression sensitizes normal human keratinocytes and epithelial cells to apoptotic stimuli. Oncogene 18: 4495–4504.
Tian C, Gregoli P, Bondurant M . (2003). The function of the bcl-x promoter in erythroid progenitor cells. Blood 101: 2235–2242.
Tuscano JM, Druey KM, Riva A, Pena J, Thompson CB, Kehrl JH . (1996). Bcl-x rather than Bcl-2 mediates CD40-dependent centrocyte survival in the germinal center. Blood 88: 1359–1364.
Tu Y, Renner S, Xu F, Fleishman A, Taylor J, Weisz J et al. (1998). BCL-X expression in multiple myeloma: possible indicator of chemoresistance. Cancer Res 58: 256–262.
Vega MI, Huerta-Yepez S, Jazirehi AR, Garban H, Bonavida B . (2005). Rituximab (chimeric anti-CD20) sensitizes B-NHL cell lines to Fas-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 24: 8114–8127.
Viegas LR, Vicent GP, Baranao JL, Beato M, Pecci A . (2004). Steroid hormones induce bcl-X gene expression through direct activation of distal promoter. J Biol Chem 279: 9831–9839.
Wang Z, Karras JG, Howard RG, Rothstein TL . (1995). Induction of bcl-x by CD40 engagement rescues Sig-induced apoptosis in murine B cells. J Immunol 155: 3722–3725.
Wu LX, La Rose J, Chen L, Neale C, Mak T, Okkenhaug K et al. (2005). CD28 regulates the translation of Bcl-xL via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway. J Immunol 174: 180–194.
Xerri L, Parc P, Brousset P, Schlaifer D, Hassoun J, Reed JC et al. (1996). Predominant expression of the long isoform of Bcl-x (Bcl-xL) in human lymphomas. Br J Haematol 92: 900–906.
Acknowledgements
We thank Paul Townsend for his helpful comments. We thank Professor Paul Farrell for the kind gift of Akata6 cells and Immunex Corp., USA for the kind gift of CD40L. This work was supported by the Leukaemia Research Fund and Cancer Research UK.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Habens, F., Lapham, A., Dallman, C. et al. Distinct promoters mediate constitutive and inducible Bcl-XL expression in malignant lymphocytes. Oncogene 26, 1910–1919 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209979
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209979
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
TGF-β induces apoptosis in human B cells by transcriptional regulation of BIK and BCL-XL
Cell Death & Differentiation (2009)