Abstract
Objective: To study significant factors associated with the risk of hypertension among obese women, with and without a history of weight cycling (WC).
Design: Case–control study.
Setting: Obesity Clinic of Chieti University, Italy.
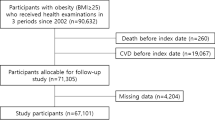
Subjects: A group of 258 obese women aged 25–64 y (103 cases with hypertension and 155 controls) were recruited. All obese subjects had the same clinical characteristics, were without a family history for hypertension, were non-smokers, had normal lipidemic profiles and normal glucose tolerance, were not taking any medication and were otherwise healthy.
Intervention: In the weight cycling women, the history of WC was established on the basis of at least five weight losses in the previous 5 y due to dieting, with a weight loss of at least 4.5 kg per cycle. A logistic regression model adjusted for confounding variables such as waist-to-hip ratio (WHR) and weight cycling history parameters was used and the odds ratio (OR) with 95% confidence intervals was calculated.
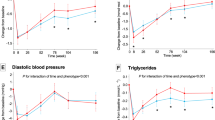
Results: The risk of hypertension increases in subjects with larger WHR (OR 7.8; 95% CI 3.4–17.9) and with a positive history for WC (OR 4.1; 95% CI 2.4–6.9). Further, in obese patients with WC, the weight cycling index and the sum of the weight regained are also important risk factors for hypertension.
Conclusions: These findings could support the hypothesis that it is the combined exposure of central-type obesity and WC that strongly raises the risk of hypertension.
Sponsorship: This work has been financially supported by a grant of Ministero dell’Università e della Ricerca Scientifica e Tecnologica.
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2000) 54, 356–360
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Guarantor: Sergio Sensi.
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guagnano, M., Ballone, E., Pace-Palitti, V. et al. Risk factors for hypertension in obese women. The role of weight cycling. Eur J Clin Nutr 54, 356–360 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1600963
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1600963
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The association between diabetes and hypertension with the number and extent of weight cycles determined from 6 million participants
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Weight fluctuations and risk for metabolic syndrome in an adult cohort
International Journal of Obesity (2008)
-
Weight cycling during growth and beyond as a risk factor for later cardiovascular diseases: the ‘repeated overshoot’ theory
International Journal of Obesity (2006)
-
Associations of short-term weight changes and weight cycling with incidence of essential hypertension in the EPIC-Potsdam Study
Journal of Human Hypertension (2005)
-
THE ASSOCIATION BETWEEN WEIGHT FLUCTUATION AND MORTALITY: RESULTS FROM A POPULATION-BASED COHORT STUDY
Journal of Community Health (2005)