Abstract
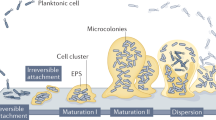
Multicellular bacterial communities (biofilms) abound in nature, and their successful formation and survival is likely to require cell–cell communication — including quorum sensing — to co-ordinate appropriate gene expression. The only mode of quorum sensing that is shared by both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria involves the production of the signalling molecule autoinducer 2 by LuxS. A survey of the current literature reveals that luxS contributes to biofilm development in some bacteria. However, inconsistencies prevent biofilm development being attributed to the production of AI2 in all cases.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Palmer, R. J. Jr, Kazmerzak, K., Hansen, M. C. & Kolenbrander, P. E. Mutualism versus independence: strategies of mixed-species oral biofilms in vitro using saliva as the sole nutrient source. Infect. Immun. 69, 5794–5804 (2001).
Costerton, J. W., Stewart, P. S. & Greenberg, E. P. Bacterial biofilms: a common cause of persistent infections. Science 284, 1318–1322 (1999).
Tan, L. & Darby, C. A movable surface: formation of Yersinia sp. biofilms on motile Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Bacteriol. 186, 5087–5092 (2004).
Williams, P., Winzer, K., Chan, W. C. & Cámara, M. Look who's talking: communication and quorum sensing in the bacterial world. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 362, 1119 (2007).
Hense, B. A. et al. Does efficiency sensing unify diffusion and quorum sensing? Nature Rev. Microbiol. 5, 230 (2007).
Egland, P. G., Palmer, R. J. Jr & Kolenbrander, P. E. Interspecies communication in Streptococcus gordonii–Veillonella atypica biofilms: signaling in flow conditions requires juxtaposition. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 101, 16917–16922 (2004).
Vendeville, A., Winzer, K., Heurlier, K., Tang, C. M. & Hardie, K. R. Making 'sense' of metabolism: autoinducer-2, luxS and pathogenic bacteria. Nature Rev. Microbiol. 3, 383 (2005).
Winzer, K. et al. LuxS: its role in central metabolism and the in vitro synthesis of 4-hydroxy-5-methyl-3(2H)-furanone. Microbiology 148, 909–922 (2002).
Bassler, B. L. & Losick, R. Bacterially speaking. Cell 125, 237 (2006).
Spoering, A. L. & Gilmore, M. S. Quorum sensing and DNA release in bacterial biofilms. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 9, 133–137 (2006).
Lebeer, S. et al. Functional analysis of luxS in the probiotic strain Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG reveals a central metabolic role important for growth and biofilm formation. J. Bacteriol. 189, 860–871 (2007).
Shao, H., Lamont, R. J. & Demuth, D. R. Autoinducer 2 is required for biofilm growth of Aggregatibacter (Actinobacillus) actinomycetemcomitans. Infect. Immun. 75, 4211–4218 (2007).
Krin, E. et al. Pleiotropic role of quorum-sensing autoinducer 2 in Photorhabdus luminescens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72, 6439–6451 (2006).
Wen, Z. T. & Burne, R. A. Functional genomics approach to identifying genes required for biofilm development by Streptococcus mutans. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 68, 1196–1203 (2002).
Merritt, J., Qi, F., Goodman, S. D., Anderson, M. H. & Shi, W. Mutation of luxS affects biofilm formation in Streptococcus mutans. Infect. Immun. 71, 1972–1979 (2003).
Wen, Z. T. & Burne, R. A. LuxS-mediated signaling in Streptococcus mutans is involved in regulation of acid and oxidative stress tolerance and biofilm formation. J. Bacteriol. 186, 2682–2691 (2004).
Yoshida, A., Ansai, T., Takehara, T. & Kuramitsu, H. K. LuxS-based signaling affects Streptococcus mutans biofilm formation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71, 2372–2380 (2005).
Balestrino, D., Haagensen, J. A. J., Rich, C. & Forestier, C. Characterization of type 2 quorum sensing in Klebsiella pneumoniae and relationship with biofilm formation. J. Bacteriol. 187, 2870–2880 (2005).
De Keersmaecker, S. C. J. et al. Chemical synthesis of (S)-4,5-dihydroxy-2,3-pentanedione, a bacterial signal molecule precursor, and validation of its activity in Salmonella typhimurium. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 19563–19568 (2005).
van Houdt, R., Moons, P., Jansen, A., Vanoirbeek, K. & Michiels, C. W. Isolation and functional analysis of luxS in Serratia plymuthica RVH1. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 262, 201–209 (2006).
Li, J. et al. Quorum sensing in Escherichia coli is signaled by AI-2/LsrR: effects on small RNA and biofilm architecture. J. Bacteriol. 189, 6011–6020 (2007).
Gonzalez Barrios, A. F. et al. Autoinducer 2 controls biofilm formation in Escherichia coli through a novel motility quorum-sensing regulator (MqsR, B3022). J. Bacteriol. 188, 305–316 (2006).
Lu, L., Hume, M. E. & Pillai, S. D. Autoinducer-2-like activity on vegetable produce and its potential involvement in bacterial biofilm formation on tomatoes. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2, 242–249 (2005).
Tannock, G. W. et al. Ecological behavior of Lactobacillus reuteri 100-23 is affected by mutation of the luxS gene. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71, 8419–8425 (2005).
Sela, S., Frank, S., Belausov, E. & Pinto, R. A mutation in the luxS gene influences Listeria monocytogenes biofilm formation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72, 5653–5658 (2006).
Challan Belval, S. et al. Assessment of the roles of LuxS, S-ribosyl homocysteine, and autoinducer 2 in cell attachment during biofilm formation by Listeria monocytogenes EGD-e. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72, 2644–2650 (2006).
Rickard, A. H. et al. Autoinducer 2: a concentration-dependent signal for mutualistic bacterial biofilm growth. Mol. Microbiol. 60, 1446–1456 (2006).
Lombardia, E., Rovetto, A. J., Arabolaza, A. L. & Grau, R. R. A LuxS-dependent cell-to-cell language regulates social behavior and development in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 188, 4442–4452 (2006).
Reeser, R. J., Medler, R. T., Billington, S. J., Jost, B. H. & Joens, L. A. Characterization of Campylobacter jejuni biofilms under defined growth conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 73, 1908–1913 (2007).
Xu, L. et al. Role of the luxS quorum-sensing system in biofilm formation and virulence of Staphylococcus epidermidis. Infect. Immun. 74, 488–496 (2006).
Auger, S., Krin, E., Aymerich, S. & Gohar, M. Autoinducer 2 affects biofilm formation by Bacillus cereus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72, 937–941 (2006).
Herzberg, M., Kaye, I. K., Peti, W. & Wood, T. K. YdgG (TqsA) controls biofilm formation in Escherichia coli K-12 through autoinducer 2 transport. J. Bacteriol. 188, 587–598 (2006).
Kendall, M. M., Rasko, D. A. & Sperandio, V. Global effects of the cell-to-cell signaling molecules autoinducer-2, autoinducer-3, and epinephrine in a luxS mutant of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 75, 4875–4884 (2007).
Schneider, R., Lockatell, C. V., Johnson, D. & Belas, R. Detection and mutation of a luxS-encoded autoinducer in Proteus mirabilis. Microbiology 148, 773–782 (2002).
Kim, M. Y. et al. Swarming differentiation of Vibrio vulnificus downregulates the expression of the vvhBA hemolysin gene via the LuxS quorum-sensing system. J. Microbiol. 44, 226–232 (2006).
Jeon, B., Itoh, K., Misawa, N. & Ryu, S. Effects of quorum sensing on flaA transcription and autoagglutination in Campylobacter jejuni. Microbiol. Immunol. 47, 833–839 (2003).
Elvers, K. T. & Park, S. F. Quorum sensing in Campylobacter jejuni: detection of a luxS encoded signalling molecule. Microbiology 148, 1475–1481 (2002).
Schembri, M. A., Kjaergaard, K. & Klemm, P. Global gene expression in Escherichia coli biofilms. Mol. Microbiol. 48, 253–267 (2003).
Beloin, C. et al. Global impact of mature biofilm lifestyle on Escherichia coli K-12 gene expression. Mol. Microbiol. 51, 659–674 (2004).
Geier, H., Mostowy, S., Cangelosi, G. A., Behr, M. A. & Ford, T. E. Autoinducer-2 triggers the oxidative stress response in Mycobacterium avium, leading to biofilm formation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 74, 1798–1804 (2008).
Domka, J., Lee, J. & Wood, T. K. YliH (BssR) and YceP (BssS) regulate Escherichia coli K-12 biofilm formation by influencing cell signaling. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72, 2449–2459 (2006).
Fernandes, R. et al. Magnetic nanofactories: localized synthesis and delivery of quorum-sensing signaling molecule autoinducer-2 to bacterial cell surfaces. Metab. Eng. 9, 228–239 (2007).
McLean, J. S., Ona, O. N. & Majors, P. D. Correlated biofilm imaging, transport and metabolism measurements via combined nuclear magnetic resonance and confocal microscopy. ISME J. 2, 121–131 (2007).
Winzer, K., Hardie, K. R. & Williams, P. Bacterial cell-to-cell communication: sorry, can't talk now — gone to lunch! Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 5, 216 (2002).
Xavier, K. B. et al. Phosphorylation and processing of the quorum-sensing molecule autoinducer-2 in enteric bacteria. ACS Chem. Biol. 2, 128–136 (2007).
Lee, J., Bansal, T., Jayaraman, A., Bentley, W. E. & Wood, T. K. Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli biofilms are inhibited by 7-hydroxyindole and stimulated by isatin. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 73, 4100–4109 (2007).
Azakami, H. et al. Characterization of autoinducer 2 signal in Eikenella corrodens and its role in biofilm formation. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 102, 110–117 (2006).
Cole, S. P., Harwood, J., Lee, R., She, R. & Guiney, D. G. Characterization of monospecies biofilm formation by Helicobacter pylori. J. Bacteriol. 186, 3124–3132 (2004).
Blehert, D. S., Palmer, R. J. Jr, Xavier, J. B., Almeida, J. S. & Kolenbrander, P. E. Autoinducer 2 production by Streptococcus gordonii DL1 and the biofilm phenotype of a luxS mutant are influenced by nutritional conditions. J. Bacteriol. 185, 4851–4860 (2003).
Petersen, F. C., Ahmed, N. A., Naemi, A. & Scheie, A. A. LuxS-mediated signalling in Streptococcus anginosus and its role in biofilm formation. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 90, 109–121 (2006).
McNab, R. et al. LuxS-based signaling in Streptococcus gordonii: autoinducer 2 controls carbohydrate metabolism and biofilm formation with Porphyromonas gingivalis. J. Bacteriol. 185, 274–284 (2003).
Beloin, C. et al. The transcriptional antiterminator RfaH represses biofilm formation in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 188, 1316–1331 (2006).
Daines, D. A. et al. Haemophilus influenzae luxS mutants form a biofilm and have increased virulence. Microb. Pathog. 39, 87 (2005).
Doherty, N., Holden, M. T. G., Qazi, S. N., Williams, P. & Winzer, K. Functional analysis of luxS in Staphylococcus aureus reveals a role in metabolism but not quorum sensing. J. Bacteriol. 188, 2885–2897 (2006).
Sperandio, V., Torres, A. G. & Kaper, J. B. Quorum sensing Escherichia coli regulators B and C (QseBC): a novel two-component regulatory system involved in the regulation of flagella and motility by quorum sensing in E. coli. Mol. Microbiol. 43, 809–821 (2002).
Sircili, M. P., Walters, M., Trabulsi, L. R. & Sperandio, V. Modulation of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli virulence by quorum sensing. Infect. Immun. 72, 2329–2337 (2004).
Rader, B. A., Campagna, S. R., Semmelhack, M. F., Bassler, B. L. & Guillemin, K. The quorum-sensing molecule autoinducer 2 regulates motility and flagellar morphogenesis in Helicobacter pylori. J. Bacteriol. 189, 6109–6117 (2007).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank N. Doherty and N. Halliday for help in the preparation of figure 1 and The Wellcome Trust for funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Related links
Related links
DATABASES
Entrez Genome Project
Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans
Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium
FURTHER INFORMATION
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hardie, K., Heurlier, K. Establishing bacterial communities by 'word of mouth': LuxS and autoinducer 2 in biofilm development. Nat Rev Microbiol 6, 635–643 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro1916
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro1916
This article is cited by
-
Biofilm—a Syntrophic Consortia of Microbial Cells: Boon or Bane?
Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology (2023)
-
Clostridioides difficile LuxS mediates inter-bacterial interactions within biofilms
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
A Multiscale Agent-Based Model for the Investigation of E. coli K12 Metabolic Response During Biofilm Formation
Bulletin of Mathematical Biology (2018)
-
Subtilosin Prevents Biofilm Formation by Inhibiting Bacterial Quorum Sensing
Probiotics and Antimicrobial Proteins (2017)
-
FabR regulates Salmonella biofilm formation via its direct target FabB
BMC Genomics (2016)