Abstract
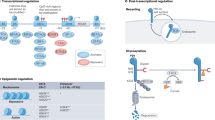
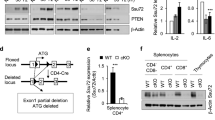
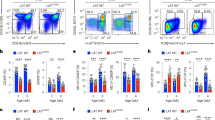
The activation of T cells is vital to the successful elimination of pathogens, but can also have a deleterious role in autoimmunity and transplant rejection. Various signalling pathways are triggered by the T-cell receptor; these have key roles in the control of the T-cell response and represent interesting targets for therapeutic immunomodulation. Recent findings define MALT1 (mucosa-associated-lymphoid-tissue lymphoma-translocation gene 1) as a protein with proteolytic activity that controls T-cell activation by regulating key molecules in T-cell-receptor-induced signalling pathways.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ruland, J., Duncan, G. S., Wakeham, A. & Mak, T. W. Differential requirement for Malt1 in T and B cell antigen receptor signaling. Immunity 19, 749–758 (2003).
Ruefli-Brasse, A. A., French, D. M. & Dixit, V. M. Regulation of NF-κB-dependent lymphocyte activation and development by paracaspase. Science 302, 1581–1584 (2003).
Wegener, E. & Krappmann, D. CARD–Bcl10–Malt1 signalosomes: missing link to NF-κB. Sci. STKE 2007, pe21 (2007).
Ruland, J. et al. Bcl10 is a positive regulator of antigen receptor-induced activation of NF-κB and neural tube closure. Cell 104, 33–42 (2001).
Uren, A. G. et al. Identification of paracaspases and metacaspases: two ancient families of caspase-like proteins, one of which plays a key role in MALT lymphoma. Mol. Cell 6, 961–967 (2000).
Lucas, P. C. et al. Bcl10 and MALT1, independent targets of chromosomal translocation in MALT lymphoma, cooperate in a novel NF-κB signaling pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 19012–19019 (2001).
Ferch, U. et al. MALT1 directs B cell receptor-induced canonical nuclear factor-κB signaling selectively to the c-Rel subunit. Nature Immunol. 8, 984–991 (2007).
Akagi, T. et al. A novel gene, MALT1 at 18q21, is involved in t(11;18) (q21;q21) found in low-grade B-cell lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue. Oncogene 18, 5785–5794 (1999).
Dierlamm, J. et al. The apoptosis inhibitor gene API2 and a novel 18q gene, MLT, are recurrently rearranged in the t(11;18)(q21;q21) associated with mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphomas. Blood 93, 3601–3609 (1999).
Morgan, J. A. et al. Breakpoints of the t(11;18)(q21;q21) in mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma lie within or near the previously undescribed gene MALT1 in chromosome 18. Cancer Res. 59, 6205–6213 (1999).
Isaacson, P. G. & Du, M. Q. MALT lymphoma: from morphology to molecules. Nature Rev. Cancer 4, 644–653 (2004).
Lucas, P. C., McAllister-Lucas, L. M. & Nunez, G. NF-κB signaling in lymphocytes: a new cast of characters. J. Cell. Sci. 117, 31–39 (2004).
Ngo, V. N. et al. A loss-of-function RNA interference screen for molecular targets in cancer. Nature 441, 106–110 (2006).
Jost, P., Peschel, C. & Ruland, J. The Bcl10/Malt1 signaling pathway as a drug target in lymphoma. Curr. Drug Targets 7, 1335–1340 (2006).
Thome, M. CARMA1, BCL-10 and MALT1 in lymphocyte development and activation. Nature Rev. Immunol. 4, 348–359 (2004).
Gross, O. et al. Multiple ITAM-coupled NK cell receptors engage the Bcl10/Malt1 complex via Carma1 for NF-κB and MAPK activation to selectively control cytokine production. Blood 11 January 2008 (doi:10.1182/blood-2007-11-123513).
Gross, O. et al. Card9 controls a non-TLR signalling pathway for innate anti-fungal immunity. Nature 442, 651–656 (2006).
Hara, H. et al. The adaptor protein CARD9 is essential for the activation of myeloid cells through ITAM-associated and Toll-like receptors. Nature Immunol. 8, 619–629 (2007).
Klemm, S. et al. The Bcl10–Malt1 complex segregates FcɛRI-mediated nuclear factor κB activation and cytokine production from mast cell degranulation. J. Exp. Med. 203, 337–347 (2006).
Dong, W. et al. The IRAK-1–BCL10–MALT1–TRAF6–TAK1 cascade mediates signaling to NF-κB from Toll-like receptor 4. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 26029–26040 (2006).
Hsu, Y.-M. S. et al. The adaptor protein CARD9 is required for innate immune responses to intracellular pathogens. Nature Immunol. 8, 198–205 (2007).
Uren, A. G. et al. Identification of paracaspases and metacaspases: two ancient families of caspase-like proteins, one of which plays a key role in MALT lymphoma. Mol. Cell 6, 961–967 (2000).
Rawlings, D. J., Sommer, K. & Moreno-García, M. E. The CARMA1 signalosome links the signalling machinery of adaptive and innate immunity in lymphocytes. Nature Rev. Immunol. 6, 799–812 (2006).
Hacker, H. & Karin, M. Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases. Sci STKE 2006, re13 (2006).
Zhou, H., Du, M. Q. & Dixit, V. M. Constitutive NF-κB activation by the t(11;18)(q21;q21) product in MALT lymphoma is linked to deregulated ubiquitin ligase activity. Cancer Cell 7, 425–431 (2005).
Che, T. et al. MALT1/paracaspase is a signaling component downstream of CARMA1 and mediates T cell receptor-induced NF-κB activation. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 15870–15876 (2004).
Sun, L., Deng, L., Ea, C. K., Xia, Z. P. & Chen, Z. J. The TRAF6 ubiquitin ligase and TAK1 kinase mediate IKK activation by BCL10 and MALT1 in T lymphocytes. Mol. Cell 14, 289–301 (2004).
Noels, H. et al. A Novel TRAF6 binding site in MALT1 defines distinct mechanisms of NF-κB activation by API2–MALT1 fusions. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 10180–10189 (2007).
Yoneda, T. et al. Regulatory mechanisms of TRAF2-mediated signal transduction by Bcl10, a MALT lymphoma-associated protein. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 11114–11120 (2000).
Oeckinghaus, A. et al. Malt1 ubiquitination triggers NF-κB signaling upon T-cell activation. EMBO J. 26, 4634–4645 (2007).
Wu, C. J. & Ashwell, J. D. NEMO recognition of ubiquitinated Bcl10 is required for T cell receptor-mediated NF-κB activation. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 105, 3023–3028 (2008).
Stilo, R. et al. Physical and functional interaction of CARMA1 and CARMA3 with Iκkinaseγ–NFκB essential modulator. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 34323–34331 (2004).
Shambharkar, P. B. et al. Phosphorylation and ubiquitination of the IκB kinase complex by two distinct signaling pathways. EMBO J. 26, 1794–1805 (2007).
Snipas, S. J. et al. Characteristics of the caspase-like catalytic domain of human paracaspase. Biol. Chem. 385, 1093–1098 (2004).
Coornaert, B. et al. T cell antigen receptor stimulation induces MALT1 paracaspase-mediated cleavage of the NF-κB inhibitor A20. Nature Immunol. 9, 263–271 (2008).
Rebeaud, F. et al. The proteolytic activity of the paracaspase MALT1 is key in T cell activation. Nature Immunol. 9, 272–281 (2008).
Vercammen, D., Declercq, W., Vandenabeele, P. & Van Breusegem, F. Are metacaspases caspases? J. Cell Biol. 179, 375–380 (2007).
Heyninck, K. & Beyaert, R. A20 inhibits NF-κB activation by dual ubiquitin-editing functions. Trends Bioch. Sci. 30, 1–4 (2005).
Klinkenberg, M., Van Huffel, S., Heyninck, K. & Beyaert, R. Functional redundancy of the zinc fingers of A20 for inhibition of NF-κB activation and protein–protein interactions. FEBS Lett. 498, 93–97 (2001).
Kinashi, T. Intracellular signalling controlling integrin activation in lymphocytes. Nature Rev. Immunol. 5, 546–559 (2005).
Lu, T. T. & Cyster, J. G. Integrin-mediated long-term B cell retention in the splenic marginal zone. Science 297, 409–412 (2002).
Rueda, D. et al. Bcl10 controls TCR- and FcγR-induced actin polymerization. J. Immunol. 178, 4373–4384 (2007).
Zhou, H. et al. Bcl10 activates the NF-κB pathway through ubiquitination of NEMO. Nature 427, 167–171 (2004).
Acknowledgements
I would like to thank members of my laboratory for critical comments on the manuscript. Our work is supported by grants from the Swiss National Science Foundation, the Swiss Cancer League and the Novartis and Vontobel Foundations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Related links
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thome, M. Multifunctional roles for MALT1 in T-cell activation. Nat Rev Immunol 8, 495–500 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nri2338
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nri2338
This article is cited by
-
Expanding the Clinical and Immunological Phenotypes and Natural History of MALT1 Deficiency
Journal of Clinical Immunology (2022)
-
N4BP1 restricts HIV-1 and its inactivation by MALT1 promotes viral reactivation
Nature Microbiology (2019)
-
Novel MALT1 Mutation Linked to Immunodeficiency, Immune Dysregulation, and an Abnormal T Cell Receptor Repertoire
Journal of Clinical Immunology (2019)
-
Metacaspases versus caspases in development and cell fate regulation
Cell Death & Differentiation (2017)
-
Central role of myeloid MCPIP1 in protecting against LPS-induced inflammation and lung injury
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2017)