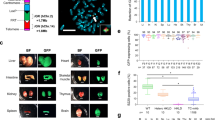
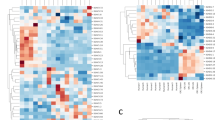
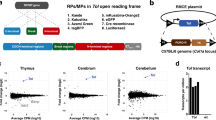
Abstract
HUMAN sequence monoclonal antibodies, which in theory combine high specificity with low immunogenicity, represent a class of potential therapeutic agents. But nearly 20 years after Köhler and Milstein first developed methods for obtaining mouse antibodies1, no comparable technology exists for reliably obtaining high-affinity human antibodies directed against selected targets. Thus, rodent antibodies2, and in vitro modified derivatives of rodent antibodies3–5, are still being used and tested in the clinic. The rodent system has certain clear advantages; mice are easy to immunize, are not tolerant to most human antigens, and their B cells form stable hybridoma cell lines. To exploit these advantages, we have developed transgenic mice that express human IgM, IgG and Igκ in the absence of mouse IgM or Igκ. We report here that these mice contain human sequence transgenes that undergo V(D)J joining, heavy-chain class switching, and somatic mutation to generate a repertoire of human sequence immunoglobulins. They are also homozygous for targeted mutations that disrupt V(D)J rearrangement at the endogenous heavy- and κ light-chain loci. We have immunized the mice with human proteins and isolated hybridomas secreting human IgGκ antigen-specific antibodies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Köhler, G. & Milstein, C. Nature 256, 495–497 (1975).
Goldstein, G. et al. New Engl. J. Med. 313, 337–342 (1985).
Winter, W. & Milstein, C. Nature 349, 293–299 (1991).
Queen, C. Nature 351, 501–502 (1991).
Waldmann, T. A. A. Rev. Immun. 10, 675–704 (1992).
Pettersson, S., Cook, G. P., Brüggemann, M., Williams, G. T. & Neuberger, M. S. Nature 344, 165–168 (1990).
Meyer, K. B. & Neuberger, M. S. EMBO J. 8, 1959–1964 (1989).
Judde, J.-G. & Max, E. E. Molec. cell. Biol. 12, 5206–5216 (1992).
Pieper, F. R. et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 20, 1259–1264 (1992).
Chen, J. et al. Int. Immun. 5, 647–656 (1993).
Chen, J. et al. EMBO J. 12, 821–830 (1993).
Hyakawa, K., Hardy, R. R., Stall, A., Herzenberg, L. A. & Herzenberg, L. A. Eur. J. Immun. 16, 1313–1316 (1986).
Taylor, L. D. et al. Int. Immun. 6, 579–591 (1994).
Durdik, J. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86, 2346–2350 (1989).
Gerstein, R. M. et al. Cell 63, 537–548 (1990).
Morel, P., Nicolas, J. F., Wijdenes, J. & Revillard, J. P. Clin. Immun. Immunopath. 64, 248–253 (1992).
Taylor, L. D. et al. Nuclelc Acids Res. 20, 6287–6295 (1992).
Hogan, B., Costantini, F. & Lacy, E. Methods of Manipulating the Mouse Embryo (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York, 1986).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lonberg, N., Taylor, L., Harding, F. et al. Antigen-specific human antibodies from mice comprising four distinct genetic modifications. Nature 368, 856–859 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1038/368856a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/368856a0
This article is cited by
-
Insights from a 30-year journey: function, regulation and therapeutic modulation of PD1
Nature Reviews Immunology (2023)
-
Cytokines and cytokine receptors as targets of immune-mediated inflammatory diseases—RA as a role model
Inflammation and Regeneration (2022)
-
Efficacy and mechanism of the anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody Daratumumab against primary effusion lymphoma
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy (2022)
-
Development of therapeutic antibodies for the treatment of diseases
Journal of Biomedical Science (2020)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.