Abstract
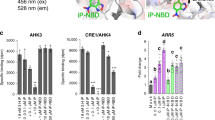
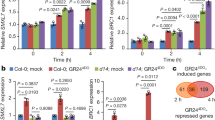
Cytokinins are essential plant hormones that are involved in shoot meristem and leaf formation, cell division, chloroplast biogenesis and senescence. Although hybrid histidine protein kinases have been implicated in cytokinin perception in Arabidopsis, the action of histidine protein kinase receptors and the downstream signalling pathway has not been elucidated to date. Here we identify a eukaryotic two-component signalling circuit that initiates cytokinin signalling through distinct hybrid histidine protein kinase activities at the plasma membrane. Histidine phosphotransmitters act as signalling shuttles between the cytoplasm and nucleus in a cytokinin-dependent manner. The short signalling circuit reaches the nuclear target genes by enabling nuclear response regulators ARR1, ARR2 and ARR10 as transcription activators. The cytokinin-inducible ARR4, ARR5, ARR6 and ARR7 genes encode transcription repressors that mediate a negative feedback loop in cytokinin signalling. Ectopic expression in transgenic Arabidopsis of ARR2, the rate-limiting factor in the response to cytokinin, is sufficient to mimic cytokinin in promoting shoot meristem proliferation and leaf differentiation, and in delaying leaf senescence.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davies, P. J. Plant Hormones; Physiology, Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (ed. Davies, P. J.) (Kluwer Academic, The Netherlands, 1995).
Mok, D. W. & Mok, M. C. Cytokinin metabolism and action. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 52, 89–118 (2001).
Kakimoto, T. CKI1, a histidine kinase homolog implicated in cytokinin signal transduction. Science 274, 982–985 (1996).
Kiba, T. et al. Differential expression of genes for response regulators in response to cytokinins and nitrate in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. 40, 767–771 (1999).
D'Agostino, I. B., Deruere, J. & Kieber, J. J. Characterization of the response of the Arabidopsis response regulator gene family to cytokinin. Plant Physiol. 124, 1706–1717 (2000).
Inoue, T. et al. Identification of CRE1 as a cytokinin receptor from Arabidopsis. Nature 409, 1060–1063 (2001).
Sakakibara, H., Taniguchi, M. & Sugiyama, T. His-Asp phosphorelay signaling: a communication avenue between plants and their environment. Plant Mol. Biol. 42, 273–278 (2000).
Stock, A. M., Robinson, V. L. & Goudreau, P. N. Two-component signal transduction. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 69, 183–215 (2000).
Thomason, P. & Kay, R. Eukaryotic signal transduction via histidine-aspartate phosphorelay. J. Cell Sci. 113, 3141–3150 (2000).
Wurgler-Murphy, S. M. & Saito, H. Two-component signal transducers and MAPK cascades. Trends Biochem. Sci. 22, 172–176 (1997).
Urao, T., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. & Shinozaki, K. Two-component systems in plant signal transduction. Trends Plant Sci. 5, 67–74 (2000).
D'Agostino, I. B. & Kieber, J. J. Phosphorelay signal transduction: the emerging family of plant response regulators. Trends Biochem. Sci. 24, 452–456 (1999).
Yeh, K. C. & Lagarias, J. C. Eukaryotic phytochromes: light-regulated serine/threonine protein kinases with histidine kinase ancestry. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 13976–13981 (1998).
Urao, T. et al. A transmembrane hybrid-type histidine kinase in Arabidopsis functions as an osmosensor. Plant Cell 11, 1743–1754 (1999).
Bleecker, A. B. & Kende, H. Ethylene: a gaseous signal molecule in plants. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 16, 1–18 (2000).
Maeda, T., Wurgler-Murphy, S. M. & Saito, H. A two-component system that regulates an osmosensing MAP kinase cascade in yeast. Nature 369, 242–245 (1994).
Posas, F. et al. Yeast HOG1 MAP kinase cascade is regulated by a multistep phosphorelay mechanism in the SLN1-YPD1-SSK1 ‘two-component’ osmosensor. Cell 86, 865–875 (1996).
Posas, F. & Saito, H. Activation of the yeast SSK2 MAP kinase kinase kinase by the SSK1 two-component response regulator. EMBO J. 17, 1385–1394 (1998).
Clark, K. L., Larsen, P. B., Wang, X. & Chang, C. Association of the Arabidopsis CTR1 Raf-like kinase with the ETR1 and ERS ethylene receptors. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 5401–5406 (1998).
Gamble, R. L., Coonfield, M. L. & Schaller, G. E. Histidine kinase activity of the ETR1 ethylene receptor from Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 7825–7829 (1998).
Suzuki, T. et al. The Arabidopsis sensor his-kinase, ahk4, can respond to cytokinins. Plant Cell Physiol. 42, 107–113 (2001).
Frank, M. et al. Hormone autotrophic growth and differentiation identifies mutant lines of Arabidopsis with altered cytokinin and auxin content or signaling. Plant Physiol. 122, 721–729 (2000).
Mahonen, A. P. et al. A novel two-component hybrid molecule regulates vascular morphogenesis of the Arabidopsis root. Genes Dev. 14, 2938–2943 (2000).
Ueguchi, C., Koizumi, H., Suzuki, T. & Mizuno, T. Novel family of sensor histidine kinase genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. 42, 231–235 (2001).
Elbein, A. D. Inhibitors of the biosynthesis and processing of N-linked oligosaccharides. CRC Crit. Rev. Biochem. 16, 21–49 (1984).
Suzuki, T., Imamura, A., Ueguchi, C. & Mizuno, T. Histidine-containing phosphotransfer (HPt) signal transducers implicated in His-to-Asp phosphorelay in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol. 39, 1258–1268 (1998).
Suzuki, T. et al. Compilation and characterization of histidine-containing phosphotransmitters implicated in His-to-Asp phosphorelay in plants: AHP signal transducers of Arabidopsis thaliana. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 64, 2486–2489 (2000).
Imamura, A. et al. Compilation and characterization of Arabidopsis thaliana response regulators implicated in His-Asp phosphorelay signal transduction. Plant Cell Physiol. 40, 733–742 (1999).
Urao, T., Miyata, S., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. & Shinozaki, K. Possible His to Asp phosphorelay signaling in an Arabidopsis two-component system. FEBS Lett. 478, 227–232 (2000).
Suzuki, T., Sakurai, K., Ueguchi, C. & Mizuno, T. Two types of putative nuclear factors that physically interact with histidine-containing phosphotransfer (Hpt) domains, signaling mediators in His-to-Asp phosphorelay, in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. 42, 37–45 (2001).
Lohrmann, J. et al. The response regulator ARR2: a pollen-specific transcription factor involved in the expression of nuclear genes for components of mitochondrial complex I in Arabidopsis. Mol. Genet. Genomics 265, 2–13 (2001).
Sakai, H., Aoyama, T. & Oka, A. Arabidopsis ARR1 and ARR2 response regulators operate as transcriptional activators. Plant J. 24, 703–711 (2000).
Xiang, C., Han, P., Lutziger, I., Wang, K. & Oliver, D. J. A mini binary vector series for plant transformation. Plant Mol. Biol. 40, 711–717 (1999).
Sussman, M. R., Amasino, R. M., Young, J. C., Krysan, P. J. & Austin-Phillips, S. The Arabidopsis knockout facility at the University of Wisconsin-Madison. Plant Physiol. 124, 1465–1467 (2000).
Nakamura, A. et al. Biochemical characterization of a putative cytokinin-responsive His-kinase, CKI1, from Arabidopsis thaliana. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 63, 1627–1630 (1999).
Urao, T., Yakubov, B., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. & Shinozaki, K. Stress-responsive expression of genes for two-component response regulator-like proteins in Arabidopsis thaliana. FEBS Lett. 427, 175–178 (1998).
Sakai, H., Aoyama, T., Bono, H. & Oka, A. Two-component response regulators from Arabidopsis thaliana contain a putative DNA-binding motif. Plant Cell Physiol. 39, 1232–1239 (1998).
Riou-Khamlichi, C., Huntley, R., Jacqmard, A. & Murray, J. A. Cytokinin activation of Arabidopsis cell division through a D-type cyclin. Science 283, 1541–1544 (1999).
Meijer, M. & Murray, J. A. Cell cycle controls and the development of plant form. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 4, 44–49 (2001).
Gan, S. & Amasino, R. M. Inhibition of leaf senescence by autoregulated production of cytokinin. Science 270, 1986–1988 (1995).
Ori, N. et al. Leaf senescence is delayed in tobacco plants expressing the maize homeobox gene knotted1 under the control of a senescence-activated promoter. Plant Cell 11, 1073–1080 (1999).
Quirino, B. F., Noh, Y. S., Himelblau, E. & Amasino, R. M. Molecular aspects of leaf senescence. Trends Plant Sci. 5, 278–282 (2000).
Tsiantis, M. Control of shoot cell fate. Beyond homeoboxes. Plant Cell 13, 733–738 (2001).
Sheen, J. Ca2+-dependent protein kinases and stress signal transduction in plants. Science 274, 1900–1902 (1996).
Kovtun, Y., Chiu, W. L., Tena, G. & Sheen, J. Functional analysis of oxidative stress-activated mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade in plants. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 97, 2940–2945 (2000).
Clough, S. J. & Bent, A. F. Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 16, 735–743 (1998).
Haseloff, J., Siemering, K. R., Prasher, D. C. & Hodge, S. Removal of a cryptic intron and subcellular localization of green fluorescent protein are required to mark transgenic Arabidopsis plants brightly. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 94, 2122–2127 (1997).
Yanagisawa, S. & Sheen, J. Involvement of maize Dof zinc finger proteins in tissue-specific and light-regulated gene expression. Plant Cell 10, 75–89 (1998).
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank T. Kakimoto for the CKI1 cDNA clone and communicating unpublished results; C. Xiang, K. Wang and D. J. Oliver for the mini-binary vectors; J. Callis for the UBQ10–GUS plasmid; E. Schaller for the ER–GFP construct; J. Elhai, W.-L. Chiu and H. Sze for helpful discussions on the manuscript; B. Moore for help with confocal microscopy; and G. Tena for Arabidopsis plants. This work is supported by NSF and NIH grants to J.S.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hwang, I., Sheen, J. Two-component circuitry in Arabidopsis cytokinin signal transduction. Nature 413, 383–389 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/35096500
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/35096500
This article is cited by
-
Pseudomonas fluorescens imparts cadmium stress tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana via induction of AtPCR2 gene expression
Journal of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (2023)
-
The mutation of CaCKI1 causes seedless fruits in chili pepper (Capsicum annuum)
Theoretical and Applied Genetics (2023)
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of Response Regulators Family Genes in Chinese Hickory (Carya cathayensis) Suggests Their Potential Roles during Grafting
Journal of Plant Growth Regulation (2023)
-
Type-B response regulator OsRR22 forms a transcriptional activation complex with OsSLR1 to modulate OsHKT2;1 expression in rice
Science China Life Sciences (2023)
-
Systematic analysis of Histidine photosphoto transfer gene family in cotton and functional characterization in response to salt and around tolerance
BMC Plant Biology (2022)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.