Abstract
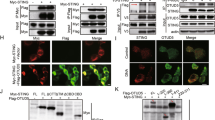
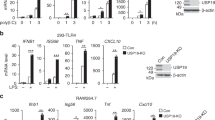
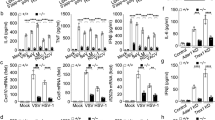
An antiviral innate immune response involves induction of type I interferons (IFNs) and their subsequent autocrine and paracrine actions, but the underlying regulatory mechanisms are incompletely understood. Here we report that CYLD, a deubiquitinase that specifically digests lysine 63-linked ubiquitin chains, is required for antiviral host defense. Loss of CYLD renders mice considerably more susceptible to infection by vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV). Consistently, CYLD-deficient dendritic cells are more sensitive to VSV infection. This functional defect was not due to lack of type I IFN production but rather because of attenuated IFN receptor signaling. In the absence of CYLD, IFN-β is ineffective in the induction of antiviral genes and protection of cells from viral infection. These findings establish CYLD as a novel regulator of antiviral innate immunity and suggest a role for CYLD in regulating IFN receptor signaling.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kumar H, Kawai T, Akira S . Pathogen recognition by the innate immune system. Int Rev Immunol 2011; 30: 16–34.
Theofilopoulos AN, Baccala R, Beutler B, Kono DH . Type I interferons (alpha/beta) in immunity and autoimmunity. Annu Rev Immunol 2005; 23: 307–336.
Nakhaei P, Genin P, Civas A, Hiscott J . RIG-I-like receptors: sensing and responding to RNA virus infection. Semin Immunol 2009; 21: 215–222.
Gack MU, Shin YC, Joo CH, Urano T, Liang C, Sun L et al. TRIM25 RING-finger E3 ubiquitin ligase is essential for RIG-I-mediated antiviral activity. Nature 2007; 446: 916–920.
Zeng W, Sun L, Jiang X, Chen X, Hou F, Adhikari A et al. Reconstitution of the RIG-I pathway reveals a signaling role of unanchored polyubiquitin chains in innate immunity. Cell 2010; 141: 315–330.
Friedman CS, O'Donnell MA, Legarda-Addison D, Ng A, Cárdenas WB, Yount JS et al. The tumour suppressor CYLD is a negative regulator of RIG-I-mediated antiviral response. EMBO Rep 2008; 9: 930–936.
Zhang M, Wu X, Lee AJ, Jin W, Chang M, Wright A et al. Regulation of IkappaB kinase-related kinases and antiviral responses by tumor suppressor CYLD. J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 18621–18626.
Sun SC . CYLD: a tumor suppressor deubiquitinase regulating NF-kappaB activation. Cell Death Differ 2010; 17: 25–34.
Reiley WW, Zhang M, Jin W, Losiewicz M, Donohue KB, Norbury CC et al. Regulation of T cell development by the deubiquitinating enzyme CYLD. Nat Immunol 2006; 7: 411–417.
Reiley WW, Jin W, Lee AJ, Wright A, Wu X, Tewalt EF et al. Deubiquitinating enzyme CYLD negatively regulates the ubiquitin-dependent kinase Tak1 and prevents abnormal T cell responses. J Exp Med 2007; 204: 1475–1485.
Reiley W, Zhang M, Sun SC . Tumor suppressor negatively regulates JNK signaling pathway downstream of TNFR members. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 55161–55167.
Fernandez M, Porosnicu M, Markovic D, Barber GN . Genetically engineered vesicular stomatitis virus in gene therapy: application for treatment of malignant disease. J Virol 2002; 76: 895–904.
Uhlik M, Good L, Xiao G, Harhaj EW, Zandi E, Karin M et al. NF-kappaB-inducing kinase and IkappaB kinase participate in human T-cell leukemia virus I Tax-mediated NF-kappaB activation. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 21132–21136.
Balachandran S, Roberts PC, Brown LE, Truong H, Pattnaik AK, Archer DR et al. Essential role for the dsRNA-dependent protein kinase PKR in innate immunity to viral infection. Immunity 2000; 13: 129–141.
Stojdl DF, Abraham N, Knowles S, Marius R, Brasey A, Lichty BD et al. The murine double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase PKR is required for resistance to vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol 2000; 74: 9580–9585. .
Tenoever BR, Ng SL, Chua MA, McWhirter SM, García-Sastre A, Maniatis T . Multiple functions of the IKK-related kinase IKKepsilon in interferon-mediated antiviral immunity. Science 2007; 315: 1274–1278.
Tsichritzis T, Gaentzsch PC, Kosmidis S, Brown AE, Skoulakis EM, Ligoxygakis P et al. A Drosophila ortholog of the human cylindromatosis tumor suppressor gene regulates triglyceride content and antibacterial defense. Development 2007; 134: 2605–2614.
Kumar KG, Barriere H, Carbone CJ, Liu J, Swaminathan G, Xu P et al. Site-specific ubiquitination exposes a linear motif to promote interferon-alpha receptor endocytosis. J Cell BIol 2007; 179: 935–950.
Acknowledgements
We thank Glen Barber for VSV strain. This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health grant AI064639.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, M., Lee, A., Wu, X. et al. Regulation of antiviral innate immunity by deubiquitinase CYLD. Cell Mol Immunol 8, 502–504 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2011.42
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2011.42
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Modulation of long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) and messenger RNA (mRNA) expression in the liver of Beagle dogs by Toxocara canis infection
Parasites & Vectors (2023)
-
Stabilization of p18 by deubiquitylase CYLD is pivotal for cell cycle progression and viral replication
npj Precision Oncology (2021)
-
The role of ubiquitylation in immune defence and pathogen evasion
Nature Reviews Immunology (2012)