Abstract
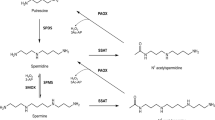
Serum polyamine oxidase (EC 1.4.3.4) is known to react in vitro with radio-labelled spermine4+ to produce di-oxidized spermine which must incorporate the label. Di-oxidized spermine was compatible with a radio-labelled compound2+ separated from the reaction mixture by ion-exchange chromatography. The compound was measured and had a half-life of about 2.3 h in tissue culture medium. It also rapidly and tightly bound to an unidentified serum component (gel-filtration chromatography indicated a complex of mol. wt 70,000) so that dissociation required treatment with strong acid (10N HCl). Findings suggest that the di-oxidized spermine, in either its free cationic or bound form, potently arrested cell proliferation. This arrest was non-cytotoxic and was confined to the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Products of di-oxidized spermine autodegradation, including trace amounts of stable and cytotoxic acrolein (arrested S phase), were unlikely to have contributed significantly to the arrest.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gaugas, J., Dewey, D. Evidence for serum binding of oxidized spermine and its potent G1-phase inhibition of cell proliferation. Br J Cancer 39, 548–557 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1979.100
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1979.100
This article is cited by
-
Functional roles of polyamines and their metabolite acrolein in eukaryotic cells
Amino Acids (2021)
-
Assessing acrolein for determination of the severity of brain stroke, dementia, renal failure, and Sjögren's syndrome
Amino Acids (2020)
-
Polyamines in renal failure
Amino Acids (2006)
-
Inhibition of maize primary root elongation by spermidine: Effect on cell shape and mitotic index
Journal of Plant Growth Regulation (1995)
-
Spermidine cytotoxicity in vitro: Effect of serum and oxygen tension
In Vitro (1984)