Abstract
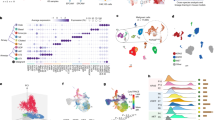
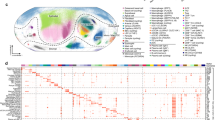
Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyp (CRSwNP) is a refractory inflammatory disease with epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) as one of the key features. Since ubiquitin modification has been shown to regulate the EMT process in other diseases, targeting ubiquitin ligases may be a potential strategy for the treatment of CRSwNP. In this study we investigated whether certain E3 ubiquitin ligases could regulate the EMT process in CRSwNP, and whether these regulations could be the potential drug targets as well as the underlying mechanisms. After screening the potential drug target by bioinformatic analyses, the expression levels of three potential E3 ubiquitin ligases were compared among the control, eosinophilic nasal polyp (ENP) and non-eosinophilic nasal polyp (NENP) group in clinical samples, and the significant decrement of the expression level of NEDD4L was found. Then, IP-MS, bioinformatics and immunohistochemistry studies suggested that low NEDD4L expression may be associated with the EMT process. In human nasal epithelial cells (hNECs) and human nasal epithelial cell line RPMI 2650, knockdown of NEDD4L promoted EMT, while upregulating NEDD4L reversed this effect, suggesting that NEDD4L inhibited EMT in nasal epithelial cells. IP-MS and Co-IP studies revealed that NEDD4L mediated the degradation of DDR1. We demonstrated that NEDD4L inhibited the β-catenin/HIF-1α positive feedback loop either directly (degrading β-catenin and HIF-1α) or indirectly (mediating DDR1 degradation). These results were confirmed in a murine NP model in vivo. This study for the first time reveals the regulatory role of ubiquitin in the EMT process of nasal epithelial cells, and identifies a novel drug target NEDD4L, which has promising efficacy against both ENP and NENP by suppressing β-catenin/HIF-1α positive feedback loop.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stevens W, Lee RJ, Schleimer R, Cohen N. Chronic rhinosinusitis pathogenesis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015;136:1442–53.
Stevens WW, Schleimer RP, Kern RC. Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016;4:565–72.
Ren L, Zhang N, Zhang L, Bachert C. Biologics for the treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps - state of the art. World Allergy Organ J. 2019;12:100050.
Xu X, Reitsma S, Wang DY, Fokkens WJ. Highlights in the advances of chronic rhinosinusitis. Allergy. 2021;76:3349–58.
Small CB, Stryszak P, Danzig M, Damiano A. Onset of symptomatic effect of mometasone furoate nasal spray in the treatment of nasal polyposis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008;121:928–32.
Van Bruaene N, Pérez-Novo CA, Basinski TM, Van Zele T, Holtappels G, De Ruyck N, et al. T-cell regulation in chronic paranasal sinus disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008;121:1435–41. 41.e1-3
Zhang N, Van Zele T, Perez-Novo C, Van Bruaene N, Holtappels G, DeRuyck N, et al. Different types of T-effector cells orchestrate mucosal inflammation in chronic sinus disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008;122:961–8.
Cao PP, Li HB, Wang BF, Wang SB, You XJ, Cui YH, et al. Distinct immunopathologic characteristics of various types of chronic rhinosinusitis in adult Chinese. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009;124:478–84.e2.
Savagner P. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) phenomenon. Ann Oncol. 2010;21:vii89–92.
Yilmaz M, Christofori G. EMT, the cytoskeleton, and cancer cell invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2009;28:15–33.
Liu X. Inflammatory cytokines augments TGF-beta1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in A549 cells by up-regulating TbetaR-I. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2008;65:935–44.
Soyka MB, Wawrzyniak P, Eiwegger T, Holzmann D, Treis A, Wanke K, et al. Defective epithelial barrier in chronic rhinosinusitis: the regulation of tight junctions by IFN-γ and IL-4. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;130:1087–96.e10.
Liu P, Qin D, Deng Z, Tong X, Liu K, Fan W, et al. TET2 deficiency exacerbates nasal polypogenesis by inducing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Allergy. 2022;77:3452–5.
Lee M, Kim DW, Yoon H, So D, Khalmuratova R, Rhee CS, et al. Sirtuin 1 attenuates nasal polypogenesis by suppressing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016;137:87–98.e7.
Rieser E, Cordier SM, Walczak H. Linear ubiquitination: a newly discovered regulator of cell signalling. Trends Biochem Sci. 2013;38:94–102.
Li H, Xu L, Li C, Zhao L, Ma Y, Zheng H, et al. Ubiquitin ligase Cbl-b represses IGF-I-induced epithelial mesenchymal transition via ZEB2 and microRNA-200c regulation in gastric cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 2014;13:136.
Novellasdemunt L, Kucharska A, Jamieson C, Prange-Barczynska M, Baulies A, Antas P, et al. NEDD4 and NEDD4L regulate Wnt signalling and intestinal stem cell priming by degrading LGR5 receptor. EMBO J. 2020;39:e102771.
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW, Shi W, et al. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43:e47.
Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Hopkins C, Hellings PW, Kern R, Reitsma S, et al. European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 2020. Rhinology. 2020;58:1–464.
Choi MR, Xu J, Lee S, Yeon SH, Park SK, Rha KS, et al. Chloroquine treatment suppresses mucosal inflammation in a mouse model of eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis. Allergy, Asthma Immunol Res. 2020;12:994–1011.
Medvar B, Raghuram V, Pisitkun T, Sarkar A, Knepper MA. Comprehensive database of human E3 ubiquitin ligases: application to aquaporin-2 regulation. Physiol Genom. 2016;48:502–12.
Lin Y, Jin H, Wu X, Jian Z, Zou X, Huang J, et al. The cross-talk between DDR1 and STAT3 promotes the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Aging. 2020;12:14391–405.
Zhao Z, Zhao S, Luo L, Xiang Q, Zhu Z, Wang J, et al. miR-199b-5p-DDR1-ERK signalling axis suppresses prostate cancer metastasis via inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Br J Cancer. 2021;124:982–94.
Lamouille S, Xu J, Derynck R. Molecular mechanisms of epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15:178–96.
Bae JS, Ryu G, Kim JH, Kim EH, Rhee YH, Chung YJ, et al. Effects of Wnt signaling on epithelial to mesenchymal transition in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyp. Thorax. 2020;75:982–93.
Chen L, Yang Y, Yan H, Peng X, Zou J. NEDD4L-induced β-catenin ubiquitination suppresses the formation and progression of interstitial pulmonary fibrosis via inhibiting the CTHRC1/HIF-1α axis. Int J Biol Sci. 2021;17:3320–30.
Zhu Y, Tan J, Xie H, Wang J, Meng X, Wang R. HIF-1α regulates EMT via the Snail and β-catenin pathways in paraquat poisoning-induced early pulmonary fibrosis. J Cell Mol Med. 2016;20:688–97.
Dong S, Liang S, Cheng Z, Zhang X, Luo L, Li L, et al. HIF-β-cat 相关性ROS/PI3K/Akt and Wnt/β-catenin signalings activate HIF-1α-induced metabolic reprogramming to impart 5-fluorouracil resistance in colorectal cancer. J Exp Clin cancer Res CR. 2022;41:15.
Tang K, Toyozumi T, Murakami K, Sakata H, Kano M, Endo S, et al. HIF-1α stimulates the progression of oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway. Br J Cancer. 2022;127:474–87.
He G, Nie JJ, Liu X, Ding Z, Luo P, Liu Y, et al. Zinc oxide nanoparticles inhibit osteosarcoma metastasis by downregulating β-catenin via HIF-1α/BNIP3/LC3B-mediated mitophagy pathway. Bioact Mater. 2023;19:690–702.
Korbecki J, Barczak K, Gutowska I, Chlubek D, Baranowska-Bosiacka I. CXCL1: gene, promoter, regulation of expression, mRNA stability, regulation of activity in the intercellular space. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:792.
Rothenberg ME. Eotaxin. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1999;21:291–5.
Yin S, Zhou S, Ren D, Zhang J, Xin H, He X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes attenuate epithelial-mesenchymal transition of HK-2 cells. Tissue Eng Part A. 2022;28:651–9.
Manning JA, Shah SS, Nikolic A, Henshall TL, Khew-Goodall Y, Kumar S. The ubiquitin ligase NEDD4-2/NEDD4L regulates both sodium homeostasis and fibrotic signaling to prevent end-stage renal disease. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12:1–16.
Ling H, Song C, Fang Y, Yin Y, Wu Z, Wang Y, et al. TH5487, a small molecule inhibitor of OGG1, attenuates pulmonary fibrosis by NEDD4L-mediated OGG1 degradation. Chem Biol Interact. 2022;362:109999.
Qu MH, Han C, Srivastava AK, Cui T, Zou N, Gao ZQ, et al. miR-93 promotes TGF-β-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition through downregulation of NEDD4L in lung cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 2016;37:5645–51.
Gao C, Pang L, Ren C, Ma T. Decreased expression of Nedd4L correlates with poor prognosis in gastric cancer patient. Med Oncol. 2012;29:1733–8.
Hu XY, Xu YM, Fu Q, Yu JJ, Huang J. Nedd4L expression is downregulated in prostate cancer compared to benign prostatic hyperplasia. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2009;35:527–31.
He S, Deng J, Li G, Wang B, Cao Y, Tu Y. Down-regulation of Nedd4L is associated with the aggressive progression and worse prognosis of malignant glioma. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2012;42:196–201.
Moll S, Desmoulière A, Moeller MJ, Pache JC, Badi L, Arcadu F, et al. DDR1 role in fibrosis and its pharmacological targeting. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2019;1866:118474.
Molet SM, Hamid QA, Hamilos DL. IL-11 and IL-17 expression in nasal polyps: relationship to collagen deposition and suppression by intranasal fluticasone propionate. Laryngoscope. 2003;113:1803–12.
Borza CM, Bolas G, Bock F, Zhang X, Akabogu FC, Zhang M-Z, et al. DDR1 contributes to kidney inflammation and fibrosis by promoting the phosphorylation of BCR and STAT3. JCI Insight. 2022;7:e150887.
Lee M, Kim DW, Khalmuratova R, Shin SH, Kim YM, Han DH, et al. The IFN-γ–p38, ERK kinase axis exacerbates neutrophilic chronic rhinosinusitis by inducing the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Mucosal Immunol. 2019;12:601–11.
Gao P, Ma X, Yuan M, Yi Y, Liu G, Wen M, et al. E3 ligase Nedd4l promotes antiviral innate immunity by catalyzing K29-linked cysteine ubiquitination of TRAF3. Nat Commun. 2021;12:1194.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82071017, and No. 82271134).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SYC conceived and designed the study, conducted the experiments and analyzed the data, prepared the figures and drafted the paper. PQL, DXQ, HL, and HQZ provided crucial assistance during the animal experiments. YX edited and revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This work was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of Renmin Hospital, Wuhan University (No. WDRY2021-K084). The detailed aims of the study and the planned procedures were explained to all patients, who then signed the informed consent documentation. The Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University approved our animal experiments which were conducted in accordance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals published by the National Institutes of Health (License No. WDRM 20211005).
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Sy., Liu, Pq., Qin, Dx. et al. E3 ubiquitin ligase NEDD4L inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition by suppressing the β-catenin/HIF-1α positive feedback loop in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Acta Pharmacol Sin 45, 831–843 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-023-01190-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-023-01190-8