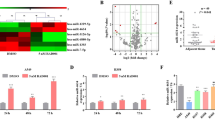
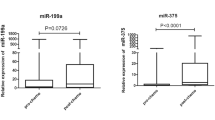
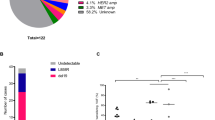
Abstract
Platinum-based chemotherapy is commonly used to treat non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, its efficacy is limited and no molecular biomarkers that predict response are available. In this review, we summarize current knowledge concerning potential epigenetic predictive markers for platinum-based chemotherapy response in NSCLC. A systematic search of PubMed and ClinicalTrials.gov using keywords “non-small cell lung cancer” combined with “chemotherapy predictive biomarkers”, “chemotherapy epigenetics biomarkers”, “chemotherapy microRNA biomarkers”, “chemotherapy DNA methylation” and “chemotherapy miRNA biomarkers” revealed 1740 articles from PubMed and 36 clinical trials. Finally, 22 papers and no trials fulfilled the review criteria. Among miRNA, combination of miR-1290, miR-196b and miR-135a in tumor tissue, and miR-21, miR-25, miR27b, and miR-326 in plasma were predictive for response to platinum-based chemotherapy in advanced NSCLC. RASSF1A methylation measured in tumor or blood was predictive for response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. These biomarkers remain experimental and none have been tested in a prospective trial.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pignon J-P,Tribodet H,Scagliotti GV,Douillard J-Y,Shepherd F,Stephens RJ, et al. Lung adjuvant cisplatin evaluation: a pooled analysis by the LACE Collaborative Group. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:3552–9.
Burdett S, Jp P, Tierney J, Tribodet H, Stewart L, Le Pechoux C, et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy for resected early-stage non-small cell lung cancer (review). Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;2:CD011430.
Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Collaborative Group. Chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis using updated data on individual patients from 52 randomised clinical trials. Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Collaborative Group. BMJ. 1995;311:899–909.
Schiller JH, Harrington D, Belani CP, Langer C, Sandler A, Krook J, et al. Comparison of four chemotherapy regimens for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:92–8.
Scagliotti GV, De Marinis F, Rinaldi M, Crinò L, Gridelli C, Ricci S, et al. Phase III randomized trial comparing three platinum-based doublets in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2002;20:4285–91.
Butts CA, Ding K, Seymour L, Twumasi-Ankrah P, Graham B, Gandara D, et al. Randomized phase III trial of vinorelbine plus cisplatin compared with observation in completely resected stage IB and II non-small-cell lung cancer: Updated survival analysis of JBR-10. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:29–34.
Wallerek S, Sørensen JB. Biomarkers for efficacy of adjuvant chemotherapy following complete resection in NSCLC stages I–IIIA. Eur Respir Rev. 2015;24:340–55.
Felip E, Martinez P. Can sensitivity to cytotoxic chemotherapy be predicted by biomarkers? Ann Oncol. 2012;23:1–4.
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75:843–54.
Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:857–66.
Shen H, Wang L, Ge X, Jiang C, Shi Z. MicroRNA-137 inhibits tumor growth and sensitizes chemosensitivity to paclitaxel and cisplatin in lung cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7:1–15.
Gao W, Lu X, Liu L, Xu J, Feng D, Shu Y. MiRNA-21. A biomarker predictive for platinum-based adjuvant chemotherapy response in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 2012;13:330–40.
Robertson KD. DNA methylation, methyltransferases, and cancer. Oncogene. 2001;20:3139–55.
Hervouet E, Cheray M, Vallette F, Cartron P-F. DNA methylation and apoptosis resistance in cancer cells. Cells. 2013;2:545–73.
Brueckner B, Stresemann C, Kuner R, Mund C, Musch T, Meister M, et al. The human let-7a-3 locus contains an epigenetically regulated microRNA gene with oncogenic function. Cancer Res. 2007;67:1419–23.
Fabbri M, Garzon R, Cimmino A, Liu Z, Zanesi N, Callegari E, et al. MicroRNA-29 family reverts aberrant methylation in lung cancer by targeting DNA methyltransferases 3A and 3B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:15805–10.
Saito M, Shiraishi K, Matsumoto K, Schetter AJ, Ogata-Kawata H, Tsuchiya N, et al. A three-microRNA signature predicts responses to platinum-based doublet chemotherapy in patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20:4784–93.
Eisenhauer Ea, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 2009;45:228–47.
Voortman J, Goto A, Mendiboure J, Sohn JJ, Aaron J, Saito M, et al. MicroRNA expression and clinical outcomes in patients treated with adjuvant chemotherapy after complete resection of non- small cell lung carcinoma. Cancer. 2011;70:8288–98.
Berghmans T, Ameye L, Willems L, Paesmans M, Mascaux C, Lafitte JJ, et al. Identification of microRNA-based signatures for response and survival for non-small cell lung cancer treated with cisplatin-vinorelbine A ELCWP prospective study. Lung Cancer. 2013;82:340–5.
Berghmans T, Ameye L, Lafitte J-J, Colinet B, Cortot A, CsToth I, et al. Prospective validation obtained in a similar group of patients and with similar high throughput biological tests failed to confirm signatures for prediction of response to chemotherapy and survival in advanced NSCLC: a prospective study from the European. Front Oncol. 2015;4:386.
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Ser B. 1995;289–300.
Hou L-K, Ma Y-S, Han Y, Lu G-X, Luo P, Chang Z-Y, et al. Association of microRNA-33a molecular signature with non-small cell lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis after chemotherapy. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0170431.
Dietrich D, Hasinger O, Liebenberg V, Field JK, Kristiansen G, Soltermann A. Methylation of the homeobox genes PITX2 and SHOX2 predicts outcome in non-small-cell lung cancer patients. Diagn Mol Pathol. 2012;21:93–104.
Wu F, Lu M, Qu L, Li D-Q, Hu C-H. DNA methylation of hMLH1 correlates with the clinical response to cisplatin after a surgical resection in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8:5457–63.
De Fraipont F, Levallet G, Creveuil C, Bergot E, Beau-Faller M, Mounawar M, et al. An apoptosis methylation prognostic signature for early lung cancer in the IFCT-0002 trial. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18:2976–86.
Brodie SA, Lombardo C, Li G, Kowalski J, Gandhi K, You S, et al. Aberrant promoter methylation of Caveolin-1 is associated with favorable response to taxane-platinum combination chemotherapy in advanced NSCLC. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e107124.
Wei J, Gao W, Zhu CJ, Liu YQ, Mei Z, Cheng T, et al. Identification of plasma microRNA-21 as a biomarker for early detection and chemosensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer. Chin J Cancer. 2011;30:407–14.
Wei J, Liu LK, Gao W, Zhu CJ, Liu YQ, Cheng T, et al. Reduction of plasma MicroRNA-21 is associated with chemotherapeutic response in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Chin J Cancer Res. 2011;23:123–8.
Li Z-H, Zhang H, Yang Z-G, Wen G-Q, Cui Y-B, Shao G-G. Prognostic significance of serum microRNA-210 levels in nonsmall-cell lung cancer. J Int Med Res. 2013;41:1437–44.
Cui E, Li H, Hua F, Wang B, Mao W, Feng X, et al. Serum microRNA 125b as a diagnostic or prognostic biomarker for advanced NSCLC patients receiving cisplatin-based chemotherapy. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012;34:309–13.
Wu C, Cao Y, He Z, He J, Hu C, Duan H, et al. Serum levels of miR-19b and miR-146a as prognostic biomarkers for non-small cell lung cancer. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2014;232:85–95.
Zhu J, Qi Y, Wu J, Shi M, Feng J. Evaluation of plasma microRNA levels to predict insensitivity of patients with advanced lung adenocarcinomas to pemetrexed and platinum. Oncol Lett. 2016;12:4829–37.
Wang F, Lou JF, Cao Y, Shi XH, Wang P, Xu J, Xie EF, Xu T, Sun RH, Rao JY, Huang PW, Pan SYWH. miR-638 is a new biomarker for outcome prediction of non-small cell lung cancer patients receiving chemotherapy. Exp Mol Med. 2015;47:e162.
Ponomaryova AA, Morozkin ES, Rykova EY, Zaporozhchenko IA, Skvortsova TE, Dobrodeev Y, et al. Dynamic changes in circulating miRNA levels in response to antitumor therapy of lung cancer. Exp Lung Res. 2016;42:1–8.
Lissa D, Robles AI. Methylation analyses in liquid biopsy. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2016;5:492–504.
Ramirez JL, Rosell R, Taron M, Sanchez-Ronco M, Alberola V, de las Peñas R, et al. 14-3-3σ Methylation in pretreatment serum circulating DNA of cisplatin-plus-gemcitabine-treated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients predicts survival: The Spanish Lung Cancer Group. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:9105–12.
Zhai X, Li S-J. Methylation of RASSF1A and CDH13 genes in individualized chemotherapy for patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15:4925–8.
Ponomaryova AA, Rykova EY, Cherdyntseva NV, Skvortsova TE, Dobrodeev AY, Zav’yalov AA, et al. Potentialities of aberrantly methylated circulating DNA for diagnostics and post-treatment follow-up of lung cancer patients. Lung Cancer. 2013;81:397–403.
Schmidt B, Beyer J, Dietrich D, Bork I, Liebenberg V, Fleischhacker M. Quantification of cell-free mSHOX2 plasma DNA for therapy monitoring in advanced stage non-small cell (NSCLC) and small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) patients. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:1–10.
Wang H, Zhang B, Chen D, Xia W, Zhang J, Wang F, et al. Real-time monitoring efficiency and toxicity of chemotherapy in patients with advanced lung cancer. Clin Epigenetics Clin Epigenetics. 2015;7:119.
Liu Z-L, Wang H, Liu J, Wang Z-X. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) expression promotes growth, metastasis, and chemo- or radioresistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting PTEN. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013;372:35–45.
Xu L, Huang Y, Chen D, He J, Zhu W, Zhang Y, et al. Downregulation of miR-21 increases cisplatin sensitivity of non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Genet. 2014;207:214–20.
Dong Z, Ren L, Lin L, Li J, Huang Y, Li J. Effect of microRNA-21 on multidrug resistance reversal in A549/DDP human lung cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 2015;11:682–90.
Saito M, Schetter AJ, Mollerup S, Kohno T, Skaug V, Bowman ED, et al. The association of microRNA expression with prognosis and progression in early-stage, non-small cell lung adenocarcinoma: a retrospective analysis of three cohorts. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:1875–82.
Markou A, Tsaroucha EG, Kaklamanis L, Fotinou M, Georgoulias V, Lianidou ES. Prognostic value of mature MicroRNA-21 and MicroRNA-205 overexpression in non-small cell lung cancer by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. Clin Chem. 2008;54:1696–704.
Robles AI, Arai E, Mathé EA, Okayama H, Schetter AJ, Brown D, et al. An integrated prognostic classifier for stage I lung adenocarcinoma based on mRNA, microRNA, and DNA methylation biomarkers. J Thorac Oncol Int Assoc Study Lung Cancer. 2015;10:1037–48.
Zhu W, Xu B. MicroRNA-21 identified as predictor of cancer outcome: a meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e103373.
Seike M, Goto A, Okano T, Bowman ED, Schetter AJ, Horikawa I, et al. MiR-21 is an EGFR-regulated anti-apoptotic factor in lung cancer in never-smokers. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2009;106:12085–90.
Svoboda M, Sana J, Fabian P, Kocakova I, Gombosova J, Nekvindova J, et al. MicroRNA expression profile associated with response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancer patients. Radiat Oncol Radiat Oncol. 2012;7:195.
Ye L, Jiang T, Shao H, Zhong L, Wang Z, Liu Y, et al. miR-1290 is a novel biomarker in DNA mismatch repair–deficient colon cancer and promotes resistance to 5-fluorouracil by directly targeting hMSH2. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2017;7:453–64.
Zhou L, Qiu T, Xu J, Wang T, Wang J, Zhou X, et al. miR-135a/b modulate cisplatin resistance of human lung cancer cell line by targeting MCL1. Pathol Oncol Res. 2013;19:677–83.
Kjersem JB, Ikdahl T, Lingjaerde OC, Guren T, Tveit KM, Kure EH. Plasma microRNAs predicting clinical outcome in metastatic colorectal cancer patients receiving first-line oxaliplatin-based treatment. Mol Oncol. 2014;8:59–67.
Yang T, Chen T, Li Y, Gao L, Zhang S, Wang T, et al. Downregulation of miR-25 modulates non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting CDC42. Tumor Biol. 2015;36:1903–11.
Song J, Li Y. miR-25-3p reverses epithelial-mesenchymal transition via targeting Sema4C in cisplatin-resistance cervical cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2017;108:23–31.
Rasmussen MH, Jensen NF, Tarpgaard LS, Qvortrup C, Rømer MU, Stenvang J, et al. High expression of microRNA-625-3p is associated with poor response to first-line oxaliplatin based treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. Mol Oncol. 2013;7:1–10.
Jiang J, Lv X, Fan L, Huang G, Zhan Y, Wang M, et al. MicroRNA-27b suppresses growth and invasion of NSCLC cells by targeting Sp1. Tumor Biol. 2014;35:10019–23.
Radhakrishnan VM, Jensen TJ, Cui H, Futscher BW, Martinez JD. Hypomethylation of the 14-3-3σ promoter leads to increased expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Genes Chromosom Cancer. 2011;50:830–6.
Donninger H, Vos MD, Clark GJ. The RASSF1A tumor suppressor. J Cell Sci. 2007 ;120:3163 LP–3172.
Donninger H, Clark J, Rinaldo F, Nelson N, Barnoud T, Schmidt ML, et al. The RASSF1A tumor suppressor regulates XPA-mediated DNA repair. Mol Cell Biol. 2015;35:277–87.
Grawenda AM, O’Neill E. Clinical utility of RASSF1A methylation in human malignancies. Br J Cancer. 2015;113:372–81.
Dubois F, Keller M, Calvayrac O, Soncin F, Hoa L, Hergovich A, et al. RASSF1A suppresses the invasion and metastatic potential of human non-small cell lung cancer cells by inhibiting YAP activation through the GEF-H1/RhoB pathway. Cancer Res. 2016;76:1627–40.
Fischer JR, Ohnmacht U, Rieger N, Zemaitis M, Stoffregen C, Kostrzewa M, et al. Promoter methylation of RASSF1A, RARβ and DAPK predict poor prognosis of patients with malignant mesothelioma. Lung Cancer. 2006;54:109–16.
Vetterkind S, Poythress RH, Lin QQ, Morgan KG. Hierarchical scaffolding of an ERK1/2 activation pathway. Cell Commun Signal. 2013;11:1.
Bertino EM, Williams TM, Nana-Sinkam SP, Shilo K, Chatterjee M, Mo X, et al. Stromal caveolin-1 is associated with response and survival in a phase II trial of nab-Paclitaxel with carboplatin for advanced NSCLC patients. Clin Lung Cancer. 2015;16:466–74.
Li J, Feng Q, Wei X, Yu Y. MicroRNA-490 regulates lung cancer metastasis by targeting poly r(C)-binding protein 1. Tumor Biol. 2016;37:15221–8.
Blower PE, Chung JH, Verducci JS, Lin S, Park JK, Dai Z, et al. MicroRNAs modulate the chemosensitivity of tumor cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008;7:1–9.
Galluzzi L, Morselli E, Vitale I, Kepp O, Senovilla L, Criollo A, et al. miR-181a and miR-630 regulate cisplatin-induced cancer cell death. Cancer Res. 2010;70:1793–803.
Ceppi P, Mudduluru G, Kumarswamy R, Rapa I, Scagliotti GV, Papotti M, et al. Loss of miR-200c expression induces an aggressive, invasive, and chemoresistant phenotype in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 2010;8:1207–16.
Kwon Y, Kim Y, Eom S, Kim M, Park D, Kim H, et al. MicroRNA-26a/-26b-COX-2-MIP-2 loop regulates allergic inflammation and allergic inflammation-promoted enhanced tumorigenic and metastatic potential of cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2015;290:14245–66.
Pérez-Ramírez C, Cañadas-Garre M, Robles AI, Molina MÁ, Faus-Dáder MJ, Calleja-Hernández MÁ. Liquid biopsy in early stage lung cancer. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2016;5:517–24.
Igaz I, Igaz P. Tumor surveillance by circulating microRNAs: a hypothesis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014;71:4081–7.
Chevillet JR, Lee I, Briggs HA, He Y, Wang K. Issues and prospects of microRNA-based biomarkers in blood and other body fluids. Molecules. 2014;19:6080–105.
Tiberio P, Callari M, Angeloni V, Daidone MG, Appierto V Challenges in using circulating miRNAs as cancer biomarkers. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:731479. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/731479
Van Pottelberge GR,Mestdagh P,Bracke KR,Thas O,Van Durme YMTA, Joos GF, et al. Van Durme YMTA, Joos GF, et al. MicroRNA expression in induced sputum of smokers and patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011;183:898–906.
Takahashi K, Yokota S, Tatsumi N, Fukami T, Yokoi T, Nakajima M. Cigarette smoking substantially alters plasma microRNA profiles in healthy subjects. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2013;272:154–60.
Author contributions
Conception and design: WMS, ODR, AIR, TM, UGIF. Administrative support: WMS. Provision of study materials or patients: WMS. Collection and assembly of data: WMS. Data analysis and interpretation: WMS, ODR, AIR, TM, UGIF. Manuscript writing: All authors. Final approval of manuscript: All authors.
Funding
AIR is supported by the Intramural Research Program of the National Cancer Institute, NIH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Szejniuk, W.M., Robles, A.I., McCulloch, T. et al. Epigenetic predictive biomarkers for response or outcome to platinum-based chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer, current state-of-art. Pharmacogenomics J 19, 5–14 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41397-018-0029-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41397-018-0029-1
This article is cited by
-
Association of CCND1 rs9344 polymorphism with lung cancer susceptibility and clinical outcomes: a case-control study
BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2024)
-
Identification of DNA methylation characteristics associated with metastasis and prognosis in colorectal cancer
BMC Medical Genomics (2024)
-
Downregulation of circ-YES1 suppresses NSCLC migration and proliferation through the miR-142-3p–HMGB1 axis
Respiratory Research (2023)
-
Genome-wide DNA methylation signature predict clinical benefit of bevacizumab in non-small cell lung cancer
BMC Cancer (2022)
-
Genome-wide methylation patterns predict clinical benefit of immunotherapy in lung cancer
Clinical Epigenetics (2020)