Abstract
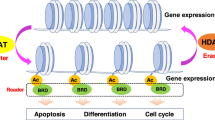
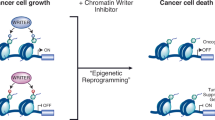
The class-I histone deacetylases (HDACs) HDAC1 and HDAC2 belong to a family of 11 zinc-dependent human HDACs and are overexpressed in many cancers. Inhibitors of these HDACs now in clinical trials show activity against several types of cancers. This review is focused on recent advances in both clinical and preclinical efforts to understand the basis for the actions of HDACis, with emphasis on implications for rational combinations with conventional or other targeted agents. We will address new perspectives on the molecular mechanisms by which HDACs act and how these actions relate to cancer. We will also review new evidence showing that HDACs are direct intracellular targets of the potent sphingolipid mediator S1P, the first identified endogenous nuclear regulator of these enzymes, linking sphingolipid metabolism in the nucleus to remodeling of chromatin and epigenetic regulation of gene expression. Understanding how endogenous molecules regulate HDAC activity in vivo may facilitate the search for safer and more effective anticancer drugs capable of interfering with HDAC functions in a highly specific manner.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albi E, Lazzarini R, Viola Magni M . (2008). Phosphatidylcholine/sphingomyelin metabolism crosstalk inside the nucleus. Biochem J 410: 381–389.
Almenara J, Rosato R, Grant S . (2002). Synergistic induction of mitochondrial damage and apoptosis in human leukemia cells by flavopiridol and the histone deacetylase inhibitor suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA). Leukemia 16: 1331–1343.
Badros A, Burger AM, Philip S, Niesvizky R, Kolla SS, Goloubeva O et al. (2009). Phase I study of vorinostat in combination with bortezomib for relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma. Clin Cancer Res 15: 5250–5257.
Bali P, George P, Cohen P, Tao J, Guo F, Sigua C et al. (2004). Superior activity of the combination of histone deacetylase inhibitor LAQ824 and the FLT-3 kinase inhibitor PKC412 against human acute myelogenous leukemia cells with mutant FLT-3. Clin Cancer Res 10: 4991–4997.
Bali P, Pranpat M, Bradner J, Balasis M, Fiskus W, Guo F et al. (2005). Inhibition of histone deacetylase 6 acetylates and disrupts the chaperone function of heat shock protein 90: a novel basis for antileukemia activity of histone deacetylase inhibitors. J Biol Chem 280: 26729–26734.
Bantscheff M, Hopf C, Savitski MM, Dittmann A, Grandi P, Michon AM et al. (2011). Chemoproteomics profiling of HDAC inhibitors reveals selective targeting of HDAC complexes. Nat Biotechnol 29: 255–265.
Bhaskara S, Chyla BJ, Amann JM, Knutson SK, Cortez D, Sun ZW et al. (2008). Deletion of histone deacetylase 3 reveals critical roles in S phase progression and DNA damage control. Mol Cell 30: 61–72.
Bolden JE, Peart MJ, Johnstone RW . (2006). Anticancer activities of histone deacetylase inhibitors. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5: 769–784.
Boyault C, Sadoul K, Pabion M, Khochbin S . (2007). HDAC6, at the crossroads between cytoskeleton and cell signaling by acetylation and ubiquitination. Oncogene 26: 5468–5476.
Buchwald M, Kramer OH, Heinzel T . (2009). HDACi—targets beyond chromatin. Cancer Lett 280: 160–167.
Calao M, Burny A, Quivy V, Dekoninck A, Van Lint C . (2008). A pervasive role of histone acetyltransferases and deacetylases in an NF-kappaB-signaling code. Trends Biochem Sci 33: 339–439.
Cameron EE, Bachman KE, Myohanen S, Herman JG, Baylin SB . (1999). Synergy of demethylation and histone deacetylase inhibition in the re-expression of genes silenced in cancer. Nat Genet 21: 103–107.
Candido EP, Reeves R, Davie JR . (1978). Sodium butyrate inhibits histone deacetylation in cultured cells. Cell 14: 105–113.
Cerchietti LC, Hatzi K, Caldas-Lopes E, Yang SN, Figueroa ME, Morin RD et al. (2011). BCL6 repression of EP300 in human diffuse large B cell lymphoma cells provides a basis for rational combinatorial therapy. J Clin Invest (in press).
Chang HH, Chiang CP, Hung HC, Lin CY, Deng YT, Kuo MY . (2009). Histone deacetylase 2 expression predicts poorer prognosis in oral cancer patients. Oral Oncol 45: 610–614.
Chen L, Fischle W, Verdin E, Greene WC . (2001). Duration of nuclear NF-kappaB action regulated by reversible acetylation. Science 293: 1653–1657.
Chen LF, Greene WC . (2004). Shaping the nuclear action of NF-kappaB. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5: 392–401.
Chen LF, Mu Y, Greene WC . (2002). Acetylation of RelA at discrete sites regulates distinct nuclear functions of NF-kappaB. EMBO J 21: 6539–6548.
Chen LF, Williams SA, Mu Y, Nakano H, Duerr JM, Buckbinder L et al. (2005). NF-kappaB RelA phosphorylation regulates RelA acetylation. Mol Cell Biol 25: 7966–7975.
Chen S, Dai Y, Harada H, Dent P, Grant S . (2007). Mcl-1 downregulation potentiates ABT-737 lethality by cooperatively inducing Bak activation and Bax translocation. Cancer Res 67: 782–791.
Chen S, Dai Y, Pei XY, Grant S . (2009). Bim upregulation by histone deacetylase inhibitors mediates interactions with the Bcl-2 antagonist ABT-737: evidence for distinct roles for Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, and Mcl-1. Mol Cell Biol 29: 6149–6169.
Choi JH, Kwon HJ, Yoon BI, Kim JH, Han SU, Joo HJ et al. (2001). Expression profile of histone deacetylase 1 in gastric cancer tissues. Jpn J Cancer Res 92: 1300–1304.
Clayton AL, Hazzalin CA, Mahadevan LC . (2006). Enhanced histone acetylation and transcription: a dynamic perspective. Mol Cell 23: 289–296.
Cocco L, Maraldi NM, Manzoli FA, Gilmour RS, Lang A . (1980). Phospholipid interactions in rat liver nuclear matrix. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 96: 890–898.
Cohen HY, Lavu S, Bitterman KJ, Hekking B, Imahiyerobo TA, Miller C et al. (2004). Acetylation of the C terminus of Ku70 by CBP and PCAF controls Bax-mediated apoptosis. Mol Cell 13: 627–638.
Dai CL, Tiwari AK, Wu CP, Su XD, Wang SR, Liu DG et al. (2008a). Lapatinib (Tykerb, GW572016) reverses multidrug resistance in cancer cells by inhibiting the activity of ATP-binding cassette subfamily B member 1 and G member 2. Cancer Res 68: 7905–7914.
Dai Y, Chen S, Kramer LB, Funk VL, Dent P, Grant S . (2008b). Interactions between bortezomib and romidepsin and belinostat in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Clin Cancer Res 14: 549–558.
Dai Y, Guzman ML, Chen S, Wang L, Yeung SK, Pei XY et al. (2010). The NF (nuclear factor)-kappaB inhibitor parthenolide interacts with histone deacetylase inhibitors to induce MKK7/JNK1-dependent apoptosis in human acute myeloid leukaemia cells. Br J Haematol 151: 70–83.
Dai Y, Rahmani M, Dent P, Grant S . (2005). Blockade of histone deacetylase inhibitor-induced RelA/p65 acetylation and NF-kappaB activation potentiates apoptosis in leukemia cells through a process mediated by oxidative damage, XIAP downregulation, and c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 activation. Mol Cell Biol 25: 5429–5444.
Ding G, Sonoda H, Yu H, Kajimoto T, Goparaju SK, Jahangeer S et al. (2007). Protein kinase D-mediated phosphorylation and nuclear export of sphingosine kinase 2. J Biol Chem 282: 27493–27502.
Finnin MS, Donigian JR, Cohen A, Richon VM, Rifkind RA, Marks PA et al. (1999). Structures of a histone deacetylase homologue bound to the TSA and SAHA inhibitors. Nature 401: 188–193.
Fiskus W, Pranpat M, Balasis M, Bali P, Estrella V, Kumaraswamy S et al. (2006). Cotreatment with vorinostat (suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid) enhances activity of dasatinib (BMS-354825) against imatinib mesylate-sensitive or imatinib mesylate-resistant chronic myelogenous leukemia cells. Clin Cancer Res 12: 5869–5878.
Fotheringham S, Epping MT, Stimson L, Khan O, Wood V, Pezzella F et al. (2009). Genome-wide loss-of-function screen reveals an important role for the proteasome in HDAC inhibitor-induced apoptosis. Cancer Cell 15: 57–66.
Fritzsche FR, Weichert W, Roske A, Gekeler V, Beckers T, Stephan C et al. (2008). Class I histone deacetylases 1, 2 and 3 are highly expressed in renal cell cancer. BMC Cancer 8: 381.
Gaymes TJ, Padua RA, Pla M, Orr S, Omidvar N, Chomienne C et al. (2006). Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDI) cause DNA damage in leukemia cells: a mechanism for leukemia-specific HDI-dependent apoptosis? Mol Cancer Res 4: 563–573.
Gillespie S, Borrow J, Zhang XD, Hersey P . (2006). Bim plays a crucial role in synergistic induction of apoptosis by the histone deacetylase inhibitor SBHA and TRAIL in melanoma cells. Apoptosis 11: 2251–2265.
Gloghini A, Buglio D, Khaskhely NM, Georgakis G, Orlowski RZ, Neelapu SS et al. (2009). Expression of histone deacetylases in lymphoma: implication for the development of selective inhibitors. Br J Haematol 147: 515–525.
Glozak MA, Seto E . (2007). Histone deacetylases and cancer. Oncogene 26: 5420–5432.
Gore SD, Baylin S, Sugar E, Carraway H, Miller CB, Carducci M et al. (2006). Combined DNA methyltransferase and histone deacetylase inhibition in the treatment of myeloid neoplasms. Cancer Res 66: 6361–6369.
Grant S, Easley C, Kirkpatrick P . (2007). Vorinostat. Nat Rev Drug Discov 6: 21–22.
Haberland M, Montgomery RL, Olson EN . (2009). The many roles of histone deacetylases in development and physiology: implications for disease and therapy. Nat Rev Genet 10: 32–42.
Hait NC, Allegood J, Maceyka M, Strub GM, Harikumar KB, Singh SK et al. (2009). Regulation of histone acetylation in the nucleus by sphingosine-1-phosphate. Science 325: 1254–1257.
Hait NC, Bellamy A, Milstien S, Kordula T, Spiegel S . (2007). Sphingosine kinase type 2 activation by ERK-mediated phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 282: 12058–12065.
Hideshima T, Bradner JE, Wong J, Chauhan D, Richardson P, Schreiber SL et al. (2005). Small-molecule inhibition of proteasome and aggresome function induces synergistic antitumor activity in multiple myeloma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 8567–8572.
Hinz M, Stilmann M, Arslan SC, Khanna KK, Dittmar G, Scheidereit C . (2010). A cytoplasmic ATM–TRAF6–cIAP1 module links nuclear DNA damage signaling to ubiquitin-mediated NF-kappaB activation. Mol Cell 40: 63–74.
Hodawadekar SC, Marmorstein R . (2007). Chemistry of acetyl transfer by histone modifying enzymes: structure, mechanism and implications for effector design. Oncogene 26: 5528–5540.
Hu Y, Lu W, Chen G, Zhang H, Jia Y, Wei Y et al. (2010). Overcoming resistance to histone deacetylase inhibitors in human leukemia with the redox modulating compound beta-phenylethyl isothiocyanate. Blood 116: 2732–2741.
Huang BH, Laban M, Leung CH, Lee L, Lee CK, Salto-Tellez M et al. (2005). Inhibition of histone deacetylase 2 increases apoptosis and p21Cip1/WAF1 expression, independent of histone deacetylase 1. Cell Death Differ 12: 395–404.
Hubbert C, Guardiola A, Shao R, Kawaguchi Y, Ito A, Nixon A et al. (2002). HDAC6 is a microtubule-associated deacetylase. Nature 417: 455–458.
Igarashi N, Okada T, Hayashi S, Fujita T, Jahangeer S, Nakamura SI . (2003). Sphingosine kinase 2 is a nuclear protein and inhibits DNA synthesis. J Biol Chem 278: 46832–46839.
Insinga A, Monestiroli S, Ronzoni S, Gelmetti V, Marchesi F, Viale A et al. (2005). Inhibitors of histone deacetylases induce tumor-selective apoptosis through activation of the death receptor pathway. Nat Med 11: 71–76.
Kachhap SK, Rosmus N, Collis SJ, Kortenhorst MS, Wissing MD, Hedayati M et al. (2010). Downregulation of homologous recombination DNA repair genes by HDAC inhibition in prostate cancer is mediated through the E2F1 transcription factor. PLoS One 5: e11208.
Kastan MB, Bartek J . (2004). Cell-cycle checkpoints and cancer. Nature 432: 316–323.
Kawada J, Zou P, Mazitschek R, Bradner JE, Cohen JI . (2009). Tubacin kills Epstein–Barr virus (EBV)–Burkitt lymphoma cells by inducing reactive oxygen species and EBV lymphoblastoid cells by inducing apoptosis. J Biol Chem 284: 17102–17109.
Khan O, Fotheringham S, Wood V, Stimson L, Zhang C, Pezzella F et al. (2010). HR23B is a biomarker for tumor sensitivity to HDAC inhibitor-based therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107: 6532–6537.
Krusche CA, Wulfing P, Kersting C, Vloet A, Bocker W, Kiesel L et al. (2005). Histone deacetylase-1 and -3 protein expression in human breast cancer: a tissue microarray analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat 90: 15–23.
Lagger G, O'Carroll D, Rembold M, Khier H, Tischler J, Weitzer G et al. (2002). Essential function of histone deacetylase 1 in proliferation control and CDK inhibitor repression. EMBO J 21: 2672–2681.
Lagger S, Meunier D, Mikula M, Brunmeir R, Schlederer M, Artaker M et al. (2010). Crucial function of histone deacetylase 1 for differentiation of teratomas in mice and humans. EMBO J 29: 3992–4007.
Lahm A, Paolini C, Pallaoro M, Nardi MC, Jones P, Neddermann P et al. (2007). Unraveling the hidden catalytic activity of vertebrate class IIa histone deacetylases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104: 17335–17340.
Lee JH, Choy ML, Ngo L, Foster SS, Marks PA . (2010a). Histone deacetylase inhibitor induces DNA damage, which normal but not transformed cells can repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107: 14639–14644.
Lee JS, Smith E, Shilatifard A . (2010b). The language of histone crosstalk. Cell 142: 682–685.
Luszczek W, Cheriyath V, Mekhail TM, Borden EC . (2010). Combinations of DNA methyltransferase and histone deacetylase inhibitors induce DNA damage in small cell lung cancer cells: correlation of resistance with IFN-stimulated gene expression. Mol Cancer Ther 9: 2309–2321.
Mandawat A, Fiskus W, Buckley KM, Robbins K, Rao R, Balusu R et al. (2010). Pan-histone deacetylase inhibitor panobinostat depletes CXCR4 levels and signaling and exerts synergistic antimyeloid activity in combination with CXCR4 antagonists. Blood 116: 5306–5315.
Marchion DC, Bicaku E, Daud AI, Richon V, Sullivan DM, Munster PN . (2004). Sequence-specific potentiation of topoisomerase II inhibitors by the histone deacetylase inhibitor suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid. J Cell Biochem 92: 223–237.
Marks PA . (2010). The clinical development of histone deacetylase inhibitors as targeted anticancer drugs. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 19: 1049–1066.
Miller KM, Tjeertes JV, Coates J, Legube G, Polo SE, Britton S et al. (2010). Human HDAC1 and HDAC2 function in the DNA-damage response to promote DNA nonhomologous end-joining. Nat Struct Mol Biol 17: 1144–1151.
Minucci S, Pelicci PG . (2006). Histone deacetylase inhibitors and the promise of epigenetic (and more) treatments for cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6: 38–51.
Mitsiades CS, Mitsiades NS, McMullan CJ, Poulaki V, Shringarpure R, Hideshima T et al. (2004). Transcriptional signature of histone deacetylase inhibition in multiple myeloma: biological and clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 540–545.
Miyake K, Yoshizumi T, Imura S, Sugimoto K, Batmunkh E, Kanemura H et al. (2008). Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha, histone deacetylase 1, and metastasis-associated protein 1 in pancreatic carcinoma: correlation with poor prognosis with possible regulation. Pancreas 36: e1–e9.
Moreno DA, Scrideli CA, Cortez MA, de Paula Queiroz R, Valera ET, da Silva Silveira V et al. (2010). Differential expression of HDAC3, HDAC7 and HDAC9 is associated with prognosis and survival in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Br J Haematol 150: 665–673.
Nebbioso A, Clarke N, Voltz E, Germain E, Ambrosino C, Bontempo P et al. (2005). Tumor-selective action of HDAC inhibitors involves TRAIL induction in acute myeloid leukemia cells. Nat Med 11: 77–84.
Neckers L, Ivy SP . (2003). Heat shock protein 90. Curr Opin Oncol 15: 419–424.
Nusinzon I, Horvath CM . (2003). Interferon-stimulated transcription and innate antiviral immunity require deacetylase activity and histone deacetylase 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 14742–14747.
Ocker M, Schneider-Stock R . (2007). Histone deacetylase inhibitors: signalling towards p21cip1/waf1. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 39: 1367–1374.
Oehme I, Deubzer HE, Lodrini M, Milde T, Witt O . (2009). Targeting of HDAC8 and investigational inhibitors in neuroblastoma. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 18: 1605–1617.
Osada H, Tatematsu Y, Saito H, Yatabe Y, Mitsudomi T, Takahashi T . (2004). Reduced expression of class II histone deacetylase genes is associated with poor prognosis in lung cancer patients. Int J Cancer 112: 26–32.
Ozdag H, Teschendorff AE, Ahmed AA, Hyland SJ, Blenkiron C, Bobrow L et al. (2006). Differential expression of selected histone modifier genes in human solid cancers. BMC Genomics 7: 90.
Park MA, Mitchell C, Zhang G, Yacoub A, Allegood J, Haussinger D et al. (2010). Vorinostat and sorafenib increase CD95 activation in gastrointestinal tumor cells through a Ca(2+)–de novo ceramide–PP2A–reactive oxygen species-dependent signaling pathway. Cancer Res 70: 6313–6324.
Park MA, Zhang G, Martin AP, Hamed H, Mitchell C, Hylemon PB et al. (2008). Vorinostat and sorafenib increase ER stress, autophagy and apoptosis via ceramide-dependent CD95 and PERK activation. Cancer Biol Ther 7: 1648–1662.
Qian DZ, Wang X, Kachhap SK, Kato Y, Wei Y, Zhang L et al. (2004). The histone deacetylase inhibitor NVP-LAQ824 inhibits angiogenesis and has a greater antitumor effect in combination with the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor PTK787/ZK222584. Cancer Res 64: 6626–6634.
Rahmani M, Reese E, Dai Y, Bauer C, Payne SG, Dent P et al. (2005). Coadministration of histone deacetylase inhibitors and perifosine synergistically induces apoptosis in human leukemia cells through Akt and ERK1/2 inactivation and the generation of ceramide and reactive oxygen species. Cancer Res 65: 2422–2432.
Rahmani M, Yu C, Dai Y, Reese E, Ahmed W, Dent P et al. (2003). Coadministration of the heat shock protein 90 antagonist 17-allylamino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin with suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid or sodium butyrate synergistically induces apoptosis in human leukemia cells. Cancer Res 63: 8420–8427.
Ray S, Lee C, Hou T, Boldogh I, Brasier AR . (2008). Requirement of histone deacetylase1 (HDAC1) in signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) nucleocytoplasmic distribution. Nucleic Acids Res 36: 4510–4520.
Rikimaru T, Taketomi A, Yamashita Y, Shirabe K, Hamatsu T, Shimada M et al. (2007). Clinical significance of histone deacetylase 1 expression in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology 72: 69–74.
Ropero S, Fraga MF, Ballestar E, Hamelin R, Yamamoto H, Boix-Chornet M et al. (2006). A truncating mutation of HDAC2 in human cancers confers resistance to histone deacetylase inhibition. Nat Genet 38: 566–569.
Rosato RR, Almenara JA, Dai Y, Grant S . (2003a). Simultaneous activation of the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways by histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors and tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) synergistically induces mitochondrial damage and apoptosis in human leukemia cells. Mol Cancer Ther 2: 1273–1284.
Rosato RR, Almenara JA, Grant S . (2003b). The histone deacetylase inhibitor MS-275 promotes differentiation or apoptosis in human leukemia cells through a process regulated by generation of reactive oxygen species and induction of p21CIP1/WAF1 1. Cancer Res 63: 3637–3645.
Rosato RR, Almenara JA, Maggio SC, Coe S, Atadja P, Dent P et al. (2008). Role of histone deacetylase inhibitor-induced reactive oxygen species and DNA damage in LAQ-824/fludarabine antileukemic interactions. Mol Cancer Ther 7: 3285–3297.
Rosato RR, Kolla SS, Hock SK, Almenara JA, Patel A, Amin S et al. (2010). Histone deacetylase inhibitors activate NF-kappaB in human leukemia cells through an ATM/NEMO-related pathway. J Biol Chem 285: 10064–10077.
Ruefli AA, Ausserlechner MJ, Bernhard D, Sutton VR, Tainton KM, Kofler R et al. (2001). The histone deacetylase inhibitor and chemotherapeutic agent suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) induces a cell-death pathway characterized by cleavage of Bid and production of reactive oxygen species. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 10833–10838.
Sakuma T, Uzawa K, Onda T, Shiiba M, Yokoe H, Shibahara T et al. (2006). Aberrant expression of histone deacetylase 6 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol 29: 117–124.
Sankala HM, Hait NC, Paugh SW, Shida D, Lepine S, Elmore LW et al. (2007). Involvement of sphingosine kinase 2 in p53-independent induction of p21 by the chemotherapeutic drug doxorubicin. Cancer Res 67: 10466–10474.
Schuler S, Fritsche P, Diersch S, Arlt A, Schmid RM, Saur D et al. (2010). HDAC2 attenuates TRAIL-induced apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells. Mol Cancer 9: 80.
Sharma SV, Lee DY, Li B, Quinlan MP, Takahashi F, Maheswaran S et al. (2010). A chromatin-mediated reversible drug-tolerant state in cancer cell subpopulations. Cell 141: 69–80.
Shida D, Takabe K, Kapitonov D, Milstien S, Spiegel S . (2008). Targeting SphK1 as a new strategy against cancer. Curr Drug Targets 9: 662–673.
Simboeck E, Sawicka A, Zupkovitz G, Senese S, Winter S, Dequiedt F et al. (2010). A phosphorylation switch regulates the transcriptional activation of cell cycle regulator p21 by histone deacetylase inhibitors. J Biol Chem 285: 41062–41073.
Soane J, Le HV, Massague J . (2002). Myc suppression of the p21 (Cip) cdk inhibitor influences the outcome of the p53 response to DNA damage. Nature 419: 729–734.
Spiegel S, Milstien S . (2003). Sphingosine-1-phosphate: an enigmatic signalling lipid. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4: 397–407.
Spiegel S, Milstien S . (2007). Functions of the multifaceted family of sphingosine kinases and some close relatives. J Biol Chem 282: 2125–2129.
Subramanian C, Opipari Jr AW, Bian X, Castle VP, Kwok RP . (2005). Ku70 acetylation mediates neuroblastoma cell death induced by histone deacetylase inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 4842–4847.
Takabe K, Kim RH, Allegood JC, Mitra P, Ramachandran S, Nagahashi M et al. (2010). Estradiol induces export of sphingosine 1-phosphate from breast cancer cells via ABCC1 and ABCG2. J Biol Chem 285: 10477–10486.
Takabe K, Paugh SW, Milstien S, Spiegel S . (2008). ‘Inside-out’ signaling of sphingosine-1-phosphate: therapeutic targets. Pharmacol Rev 60: 181–195.
Thangaraju M, Gopal E, Martin PM, Ananth S, Smith SB, Prasad PD et al. (2006). SLC5A8 triggers tumor cell apoptosis through pyruvate-dependent inhibition of histone deacetylases. Cancer Res 66: 11560–11564.
Ungerstedt JS, Sowa Y, Xu WS, Shao Y, Dokmanovic M, Perez G et al. (2005). Role of thioredoxin in the response of normal and transformed cells to histone deacetylase inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 673–678.
Valenzuela-Fernandez A, Cabrero JR, Serrador JM, Sanchez-Madrid F . (2008). HDAC6: a key regulator of cytoskeleton, cell migration and cell–cell interactions. Trends Cell Biol 18: 291–297.
Walker T, Mitchell C, Park MA, Yacoub A, Graf M, Rahmani M et al. (2009). Sorafenib and vorinostat kill colon cancer cells by CD95-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Mol Pharmacol 76: 342–355.
Walkinshaw DR, Tahmasebi S, Bertos NR, Yang XJ . (2008). Histone deacetylases as transducers and targets of nuclear signaling. J Cell Biochem 104: 1541–1552.
Wang Z, Zang C, Cui K, Schones DE, Barski A, Peng W et al. (2009). Genome-wide mapping of HATs and HDACs reveals distinct functions in active and inactive genes. Cell 138: 1019–1031.
Warburg O . (1956). On the origin of cancer cells. Science 123: 309–314.
Warrener R, Beamish H, Burgess A, Waterhouse NJ, Giles N, Fairlie D et al. (2003). Tumor cell-selective cytotoxicity by targeting cell cycle checkpoints. FASEB J 17: 1550–1552.
Weichert W, Roske A, Gekeler V, Beckers T, Stephan C, Jung K et al. (2008). Histone deacetylases 1, 2 and 3 are highly expressed in prostate cancer and HDAC2 expression is associated with shorter PSA relapse time after radical prostatectomy. Br J Cancer 98: 604–610.
Whitesell L, Lindquist SL . (2005). HSP90 and the chaperoning of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 5: 761–772.
Witta SE, Gemmill RM, Hirsch FR, Coldren CD, Hedman K, Ravdel L et al. (2006). Restoring E-cadherin expression increases sensitivity to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors in lung cancer cell lines. Cancer Res 66: 944–950.
Wooten-Blanks LG, Song P, Senkal CE, Ogretmen B . (2007). Mechanisms of ceramide-mediated repression of the human telomerase reverse transcriptase promoter via deacetylation of Sp3 by histone deacetylase 1. FASEB J 21: 3386–3397.
Workman P, Burrows F, Neckers L, Rosen N . (2007). Drugging the cancer chaperone HSP90: combinatorial therapeutic exploitation of oncogene addiction and tumor stress. Ann NY Acad Sci 1113: 202–216.
Wu CJ, Conze DB, Li T, Srinivasula SM, Ashwell JD . (2006). Sensing of Lys 63-linked polyubiquitination by NEMO is a key event in NF-kappaB activation [corrected]. Nat Cell Biol 8: 398–406.
Wu ZH, Wong ET, Shi Y, Niu J, Chen Z, Miyamoto S et al. (2010). ATM- and NEMO-dependent ELKS ubiquitination coordinates TAK1-mediated IKK activation in response to genotoxic stress. Mol Cell 40: 75–86.
Yang XJ, Seto E . (2008). The Rpd3/Hda1 family of lysine deacetylases: from bacteria and yeast to mice and men. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9: 206–218.
Yu C, Rahmani M, Almenara J, Subler M, Krystal G, Conrad D et al. (2003). Histone deacetylase inhibitors promote STI571-mediated apoptosis in STI571-sensitive and -resistant Bcr/Abl+ human myeloid leukemia cells. Cancer Res 63: 2118–2126.
Yuan ZL, Guan YJ, Chatterjee D, Chin YE . (2005). Stat3 dimerization regulated by reversible acetylation of a single lysine residue. Science 307: 269–273.
Zhang Z, Yamashita H, Toyama T, Sugiura H, Ando Y, Mita K et al. (2005). Quantitation of HDAC1 mRNA expression in invasive carcinoma of the breast*. Breast Cancer Res Treat 94: 11–16.
Zhao Y, Tan J, Zhuang L, Jiang X, Liu ET, Yu Q . (2005). Inhibitors of histone deacetylases target the Rb–E2F1 pathway for apoptosis induction through activation of proapoptotic protein Bim. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 16090–16095.
Zupkovitz G, Grausenburger R, Brunmeir R, Senese S, Tischler J, Jurkin J et al. (2010). The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 is a crucial target for histone deacetylase 1 as a regulator of cellular proliferation. Mol Cell Biol 30: 1171–1181.
Acknowledgements
We apologize to authors whose work has not been cited here owing to space limitations. This work was supported by R01CA61774 (SS) R37GM043880 (SS), R01AI50094 (SS), 1U19AI077435 (SS),), R01AI50094 (SS), 1U19AI077435 (SS), RO1CA93738-05 (SG), CA100866 (SG), 1P50CA142509 (SG), RC2CA148431 (SG), 1P50CA130805 (SG), 1R21CA137823, the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society of America 6181-10 (SG), the V Foundation and the Multiple Myeloma Research Foundation (SG).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spiegel, S., Milstien, S. & Grant, S. Endogenous modulators and pharmacological inhibitors of histone deacetylases in cancer therapy. Oncogene 31, 537–551 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.267
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.267
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Investigation of in vitro HDAC 1 inhibitory activity of Curcuma longa L. extracts, isolated fractions and curcumin
European Food Research and Technology (2024)
-
Targeting Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Signaling in Immune-Mediated Diseases: Beyond Multiple Sclerosis
Drugs (2021)
-
Therapeutic potential of CKD-506, a novel selective histone deacetylase 6 inhibitor, in a murine model of rheumatoid arthritis
Arthritis Research & Therapy (2020)
-
EGFR‐vIII downregulated H2AZK4/7AC though the PI3K/AKT‐HDAC2 axis to regulate cell cycle progression
Clinical and Translational Medicine (2020)
-
Maternal exposure to perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) causes liver toxicity through PPAR-α pathway and lowered histone acetylation in female offspring mice
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2019)