Abstract
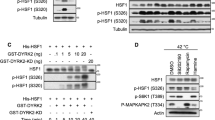
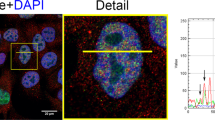
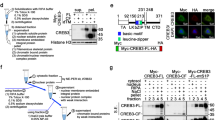
Y-box-binding protein 1 (YB-1) is an oncogenic transcription factor whose overexpression and nuclear localization is associated with tumor progression and drug resistance. Transcriptional activation of YB-1 in response to genotoxic stress is believed to occur in the cytoplasm through sequence-specific endoproteolytic cleavage by the 20S Proteasome, followed by nuclear translocation of cleaved YB-1. To study the proteolysis model, we developed a two-step affinity purification of endogenous YB-1 protein species and characterized the products using mass spectrometry. Whereas full-length YB-1 was readily identified, the smaller protein band thought to be activated YB-1 was identified as hnRNP A1. An antibody specific for YB-1 was generated, which revealed only one YB-1 species, even after genotoxic stress-induced nuclear YB-1 translocation. These findings warrant re-evaluation of the mechanism of YB-1 nuclear translocation and transcriptional activation. The relationship between nuclear YB-1 and tumor progression may also have to re-evaluated in some cases.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asakuno K, Kohno K, Uchiumi T, Kubo T, Sato S, Isono M et al. (1994). Involvement of a DNA binding protein, MDR-NF1/YB-1, in human MDR1 gene expression by Actinomycin D. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 199: 1428–1435.
Bargou RC, Jurchott K, Wagener C, Bergmann S, Metzner S, Bommert K et al. (1997). Nuclear localization and increased levels of transcription factor YB-1 in primary human breast cancers are associated with intrinsic MDR1 gene expression. Nat Med 3: 447–450.
Berquin IM, Pang B, Dziubinski ML, Scott LM, Chen YQ, Nolan GP et al. (2005). Y-box-binding protein 1 confers EGF independence to human mammary epithelial cells. Oncogene 24: 3177–3186.
Chatterjee M, Rancso C, Stuhmer T, Eckstein N, Andrulis M, Gerecke C et al. (2008). The Y-box binding protein YB-1 is associated with progressive disease and mediates survival and drug resistance in multiple myeloma. Blood 111: 3714–3722.
Fujita T, Ito K, Izumi H, Kimura M, Sano M, Nakagomi H et al. (2005). Increased nuclear localization of transcription factor Y-box binding protein 1 accompanied by up-regulation of P-glycoprotein in breast cancer pretreated with paclitaxel. Clin Cancer Res 11: 8837–8844.
Gimenez-Bonafe P, Fedoruk MN, Whitmore TG, Akbari M, Ralph JL, Ettinger S et al. (2004). YB-1 is upregulated during prostate cancer tumor progression and increases P-glycoprotein activity. Prostate 59: 337–349.
Guay D, Evoy A, Paquet E, Garand C, Bachvarova M, Bachvarov D et al. (2008). The strand separation and nuclease activities associated with YB-1 are dispensable for cisplatin resistance but overexpression of YB-1 in MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 breast tumor cells generates several chemoresistance signatures. Intl J Biochem Cell Biol 40: 2492–2507.
Horwitz EM, Maloney KA, Ley TJ . (1994). A human protein containing a ‘cold shock’ domain binds specifically to H-DNA upstream from the human γ-globin genes. J Biol Chem 269: 14130–14139.
Ito Y, Yoshida H, Shibahara K, Uruno T, Nakano K, Takamura Y et al. (2003). Y-box binding protein expression in thyroid neoplasms: its linkage with anaplastic transformation. Pathol Intl 53: 429–433.
Kohno K, Izumi H, Uchiumi T, Ashizuka M, Kuwano M . (2003). The pleiotropic functions of the Y-box-binding protein, YB-1. BioEssays 25: 691–698.
Lee SM, Dunnavant FD, Jang H, Zunt J, Levin MC . (2006). Autoantibodies that recognize functional domains of hnRNP A1 implicate molecular mimicry in the pathogenesis of neurological disease. Neurosci Lett 401: 188–193.
Oda Y, Sakamoto A, Shinohara N, Ohga T, Uchiumi T, Kohno K et al. (1998). Nuclear expression of YB-1 protein correlates with P-glycoprotein expression in human osteosarcoma. Clin Cancer Res 4: 2273–2277.
Oda Y, Ohishi Y, Saito T, Hinoshita E, Uchiumi T, Kinukawa N et al. (2003). Nuclear expression of Y-box binding protein-1 correlates with P-glycoprotein and topoisomerase II alpha expression, and with poor prognosis in synovial sarcoma. J Pathol 199: 251–258.
Ohga T, Koike K, Ono M, Makino Y, Itagaki Y, Tanimoto M et al. (1996). Role of the human Y box-binding protein YB-1 in cellular sensitivity to the DNA-damaging agents cisplatin, mitomycin C, and ultraviolet light. Cancer Res 56: 4224–4228.
Raffetseder U, Frye B, Rauen T, Jurchott K, Royer HD, Jansen PL et al. (2003). Splicing factor SRp30c interaction with Y-box protein-1 confers nuclear YB-1 shuttling and alternative splice site selection. J Biol Chem 278: 18241–18248.
Shibahara K, Sugio K, Osak T, Uchiumi T, Maehara Y, Kohno K et al. (2001). Nuclear expression of the Y-box binding protein, YB-1, as a novel marker of disease progression in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 7: 3151–3155.
Sorokin AV, Selyutina AA, Skabkin MA, Guryanov SG, Nazimov IV, Richard C et al. (2005). Proteasome-mediated cleavage of the Y-box-binding protein 1 is linked to DNA-damage stress response. EMBO J 24: 3602–3612.
Stenina OI, Poptic EJ, DiCorleto PE . (2000). Thrombin activates a Y box-binding protein (DNA-binding protein B) in endothelial cells. J Clin Invest 106: 579–587.
Sutherland BW, Kucab J, Wu J, Lee C, Cheang M, Yorida E et al. (2005). Akt phosphorylates the Y-box binding protein 1 at Ser102 located in the cold shock domain and affects the anchorage-independent growth of breast cancer cells. Oncogene 24: 4281–4292.
Wolffe AP . (1994). Structural and functional properties of the evolutionarily ancient Y-box family of nucleic acid binding proteins. BioEssays 16: 245–251.
Acknowledgements
We thank Professor H-D Royer (CASEAR, Bonn, Germany) for a generous gift of the C-terminal YB-1 antibody. This research was supported by the National Health & Medical Research Council of Australia (SBC, 423405; PJP, 477100), the Cancer Institute NSW (AWB, WM, 05/RLP/1-01), the Health Research Council of New Zealand (AWB, AMW, RH, MA 07/284A) and the Children's Medical Research Institute Jeans-for-Genes Campaign (VAV).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cohen, S., Ma, W., Valova, V. et al. Genotoxic stress-induced nuclear localization of oncoprotein YB-1 in the absence of proteolytic processing. Oncogene 29, 403–410 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.321
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.321
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Holistic anti-tumor resistance mechanism of YBX1 and its potential as a chemoresistance target in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Holistic Integrative Oncology (2023)
-
Uncoupling of EGFR–RAS signaling and nuclear localization of YBX1 in colorectal cancer
Oncogenesis (2016)
-
New paradigms in the repair of oxidative damage in human genome: mechanisms ensuring repair of mutagenic base lesions during replication and involvement of accessory proteins
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2015)
-
The role of cold shock domain proteins in inflammatory diseases
Journal of Molecular Medicine (2014)
-
Cold shock Y-box protein-1 proteolysis autoregulates its transcriptional activities
Cell Communication and Signaling (2013)