Abstract
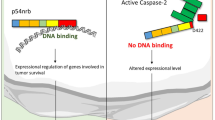
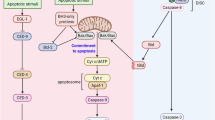
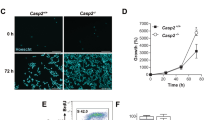
Despite the early discovery of caspase-2, its physiological function has long remained an enigma. A number of recent publications now suggest not just one, but multiple functions, including roles in apoptosis, DNA repair and tumor suppression. How can one enzyme have so many talents? Considering the diversity of interaction partners and the specific mode of pro-apoptotic action proposed in these studies, caspase-2 might in fact represent a primordial protease serving numerous pathways, established before the advent of a more elaborate functionally diversified caspases system.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arama E, Agapite J, Steller H . (2003). Caspase activity and a specific cytochrome C are required for sperm differentiation in Drosophila. Dev Cell 4: 687–697.
Bergeron L, Perez GI, Macdonald G, Shi L, Sun Y, Jurisicova A et al (1998). Defects in regulation of apoptosis in caspase-2-deficient mice. Genes Dev 12: 1304–1314.
Braga M, Sinha Hikim AP, Datta S, Ferrini MG, Brown D, Kovacheva EL et al. (2008). Involvement of oxidative stress and caspase 2-mediated intrinsic pathway signaling in age-related increase in muscle cell apoptosis in mice. Apoptosis 13: 822–832.
De Botton S, Sabri S, Daugas E, Zermati Y, Guidotti JE, Hermine O et al. (2002). Platelet formation is the consequence of caspase activation within megakaryocytes. Blood 100: 1310–1317.
Ditzel M, Broemer M, Tenev T, Bolduc C, Lee TV, Rigbolt KT et al. (2008). Inactivation of effector caspases through nondegradative polyubiquitylation. Mol Cell 32: 540–553.
Duan H, Dixit VM . (1997). RAIDD is a new ‘death’ adaptor molecule. Nature 385: 86–89.
Gonzalvez F, Schug ZT, Houtkooper RH, MacKenzie ED, Brooks DG, Wanders RJ et al. (2008). Cardiolipin provides an essential activating platform for caspase-8 on mitochondria. J Cell Biol 183: 681–696.
Ho LH, Taylor R, Dorstyn L, Cakouros D, Bouillet P, Kumar S . (2009). A tumor suppressor function for caspase-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106: 5336–5341.
Krumschnabel G, Sohm B, Bock F, Manzl C, Villunger A . (2009). The enigma of caspase-2: the laymen's view. Cell Death Differ 16: 195–207.
Kumar S, Tomooka Y, Noda M . (1992). Identification of a set of genes with developmentally down-regulated expression in the mouse brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 185: 1155–1161.
Lamkanfi M, Festjens N, Declercq W, Vanden Berghe T, Vandenabeele P . (2007). Caspases in cell survival, proliferation and differentiation. Cell Death Differ 14: 44–55.
Lavrik IN, Golks A, Baumann S, Krammer PH . (2006). Caspase-2 is activated at the CD95 death-inducing signaling complex in the course of CD95-induced apoptosis. Blood 108: 559–565.
Li J, Yuan J . (2008). Caspases in apoptosis and beyond. Oncogene 27: 6194–6206.
Mancini M, Machamer CE, Roy S, Nicholson DW, Thornberry NA, Casciola-Rosen LA et al. (2000). Caspase-2 is localized at the Golgi complex and cleaves golgin-160 during apoptosis. J Cell Biol 149: 603–612.
Nutt LK, Margolis SS, Jensen M, Herman CE, Dunphy WG, Rathmell JC et al. (2005). Metabolic regulation of oocyte cell death through the CaMKII-mediated phosphorylation of caspase-2. Cell 123: 89–103.
Olsson M, Vakifahmetoglu H, Abruzzo PM, Hogstrand K, Grandien A, Zhivotovsky B . (2009). DISC-mediated activation of caspase-2 in DNA damage-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 28: 1949–1959.
Samraj AK, Sohn D, Schulze-Osthoff K, Schmitz I . (2007). Loss of caspase-9 reveals its essential role for caspase-2 activation and mitochondrial membrane depolarization. Mol Biol Cell 18: 84–93.
Scott CL, Schuler M, Marsden VS, Egle A, Pellegrini M, Nesic D et al. (2004). Apaf-1 and caspase-9 do not act as tumor suppressors in myc-induced lymphomagenesis or mouse embryo fibroblast transformation. J Cell Biol 164: 89–96.
Shi M, Vivian CJ, Lee KJ, Ge C, Morotomi-Yano K, Manzl C et al. (2009). DNA-PKcs-PIDDosome: a nuclear caspase-2-activating complex with role in G2/M checkpoint maintenance. Cell 136: 508–520.
Sidi S, Sanda T, Kennedy RD, Hagen AT, Jette CA, Hoffmans R et al. (2008). Chk1 suppresses a caspase-2 apoptotic response to DNA damage that bypasses p53, Bcl-2, and caspase-3. Cell 133: 864–877.
Tinel A, Tschopp J . (2004). The PIDDosome, a protein complex implicated in activation of caspase-2 in response to genotoxic stress. Science 304: 843–846.
Yi CH, Yuan J . (2009). The Jekyll and Hyde functions of caspases. Dev Cell 16: 21–34.
Zhang Y, Padalecki SS, Chaudhuri AR, De Waal E, Goins BA, Grubbs B et al. (2007). Caspase-2 deficiency enhances aging-related traits in mice. Mech Ageing Dev 128: 213–221.
Zhivotovsky B, Orrenius S . (2006). Carcinogenesis and apoptosis: paradigms and paradoxes. Carcinogenesis 27: 1939–1945.
Acknowledgements
The work in our laboratory is supported by fellowships and grants from the Austrian Science Fund (Y212-B13, SFB021, MCBO), EU-FP6 (ApopTrain) and the Tyrolean Science Fund (TWF). We apologize to the many scientists in this field whose excellent research was not cited but was only referred to indirectly through reviews.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krumschnabel, G., Manzl, C. & Villunger, A. Caspase-2: killer, savior and safeguard—emerging versatile roles for an ill-defined caspase. Oncogene 28, 3093–3096 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.173
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.173
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Bacterial Pore-Forming Toxins Promote the Activation of Caspases in Parallel to Necroptosis to Enhance Alarmin Release and Inflammation During Pneumonia
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
The tumor-modulatory effects of Caspase-2 and Pidd1 do not require the scaffold protein Raidd
Cell Death & Differentiation (2015)
-
Efficient in vivo microRNA targeting of liver metastasis
Oncogene (2011)
-
Caspase 2 in apoptosis, the DNA damage response and tumour suppression: enigma no more?
Nature Reviews Cancer (2010)
-
The engine driving the ship: metabolic steering of cell proliferation and death
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2010)