Abstract
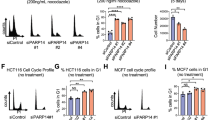
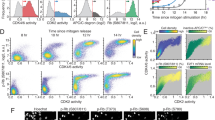
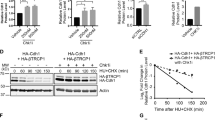
Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) are important in regulating cell cycle transitions, particularly in coordinating DNA replication. Although the role of CDK2 activity on the replication apparatus has been extensively studied, the role of CDK4/6 in DNA replication control is less understood. Through targeted inhibition of CDK4/6 activity, we demonstrate that CDK4/6 kinase activity promotes cdc6 and cdt1 expression, and pre-replication complex (pre-RC) assembly in cycling cells. Conversely, CDK2 inhibition had no effect on the pre-RC assembly. The inhibition of pre-RC assembly is dependent on a functional retinoblastoma (RB) protein, which mediates downstream effects. As such, CDK4/6 inhibition has minimal effect on the replication apparatus in the absence of RB. The requirement of CDK4/6 was further interrogated using cells lacking D-type cyclins, in which replication complexes form normally, and correspondingly CDK4/6 inhibition had no effect on cell cycle or replication control. However, in the absence of D-type cyclins, CDK2 inhibition resulted in the attenuation of cdc6 and cdt1 levels, suggesting overlapping roles for CDK4/6 and CDK2 in regulating replication protein activity. Finally, CDK4/6 inhibition prevented the accumulation of cdc6 and cdt1 as cells progressed from mitosis through the subsequent G1. Combined, these studies indicate that CDK4/6 activity is important in regulating the expression of these critical mediators of DNA replication.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
22 March 2023
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-023-02663-0
References
Aggarwal P, Lessie MD, Lin DI, Pontano L, Gladden AB, Nuskey B et al. (2007). Nuclear accumulation of cyclin D1 during S phase inhibits Cu14-dependent Cdt1 proteolysis and triggers p53-dependent DNA rereplication. Genes Dev 21: 2908–2922.
Angus SP, Mayhew CN, Solomon DA, Braden WA, Markey MP, Okuno Y et al. (2004). RB reversibly inhibits DNA replication via two temporally distinct mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol 24: 5404–5420.
Bartek J, Bartkova J, Lukas J . (1997). The retinoblastoma protein pathway in cell cycle control and cancer. Exp Cell Res 237: 1–6.
Bartkova J, Lukas J, Bartek J . (1997). Aberrations of the G1- and G1/S-regulating genes in human cancer. Prog Cell Cycle Res 3: 211–220.
Bell SP, Dutta A . (2002). DNA replication in eukaryotic cells. Annu Rev Biochem 71: 333–374.
Blow JJ, Hodgson B . (2002). Replication licensing—defining the proliferative state? Trends Cell Biol 12: 72–78.
Braden WA, Lenihan JM, Lan Z, Luce KS, Zagorski W, Bosco E et al. (2006). Distinct action of the retinoblastoma pathway on the DNA replication machinery defines specific roles for cyclin-dependent kinase complexes in prereplication complex assembly and S-phase progression. Mol Cell Biol 26: 7667–7681.
Broceno C, Wilkie S, Mittnacht S . (2002). RB activation defect in tumor cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99: 14200–14205.
Coverley D, Laman H, Laskey RA . (2002). Distinct roles for cyclins E and A during DNA replication complex assembly and activation. Nat Cell Biol 4: 523–528.
Dahmann C, Diffley JF, Nasmyth KA . (1995). S-phase-promoting cyclin-dependent kinases prevent re-replication by inhibiting the transition of replication origins to a pre-replicative state. Curr Biol 5: 1257–1269.
Diehl JA . (2002). Cycling to cancer with cyclin D1. Cancer Biol Ther 1: 226–231.
Diffley JF . (1994). Eukaryotic DNA replication. Curr Opin Cell Biol 6: 368–372.
Diffley JF . (2004). Regulation of early events in chromosome replication. Curr Biol 14: R778–R786.
Diffley JF, Labib K . (2002). The chromosome replication cycle. J Cell Sci 115: 869–872.
Dimitrova DS, Prokhorova TA, Blow JJ, Todorov IT, Gilbert DM . (2002). Mammalian nuclei become licensed for DNA replication during late telophase. J Cell Sci 115: 51–59.
Dimitrova DS, Todorov IT, Melendy T, Gilbert DM . (1999). Mcm2, but not RPA, is a component of the mammalian early G1-phase prereplication complex. J Cell Biol 146: 709–722.
Dutta A, Bell SP . (1997). Initiation of DNA replication in eukaryotic cells. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 13: 293–332.
Dyson N . (1998). The regulation of E2F by pRB-family proteins. Genes Dev 12: 2245–2262.
Ekholm-Reed S, Mendez J, Tedesco D, Zetterberg A, Stillman B, Reed SI . (2004). Deregulation of cyclin E in human cells interferes with prereplication complex assembly. J Cell Biol 165: 789–800.
Fry DW, Harvey PJ, Keller PR, Elliott WL, Meade M, Trachet E et al. (2004). Specific inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 by PD 0332991 and associated antitumor activity in human tumor xenografts. Mol Cancer Ther 3: 1427–1438.
Fujita M, Kiyono T, Hayashi Y, Ishibashi M . (1996). hCDC47, a human member of the MCM family. Dissociation of the nucleus-bound form during S phase. J Biol Chem 271: 4349–4354.
Geng Y, Lee YM, Welcker M, Swanger J, Zagozdzon A, Winer JD et al. (2007). Kinase-independent function of cyclin E. Mol Cell 25: 127–139.
Guo Y, Stacey DW, Hitomi M . (2002). Post-transcriptional regulation of cyclin D1 expression during G2 phase. Oncogene 21: 7545–7556.
Hateboer G, Wobst A, Petersen BO, Le Cam L, Vigo E, Sardet C et al. (1998). Cell cycle-regulated expression of mammalian CDC6 is dependent on E2F. Mol Cell Biol 18: 6679–6697.
Hua XH, Yan H, Newport J . (1997). A role for Cdk2 kinase in negatively regulating DNA replication during S phase of the cell cycle. J Cell Biol 137: 183–192.
Hwang HC, Clurman BE . (2005). Cyclin E in normal and neoplastic cell cycles. Oncogene 24: 2776–2786.
Knudsen KE, Diehl JA, Haiman CA, Knudsen ES . (2006). Cyclin D1: polymorphism, aberrant splicing and cancer risk. Oncogene 25: 1620–1628.
Koff A, Cross F, Fisher A, Schumacher J, Leguellec K, Philippe M et al. (1991). Human cyclin E, a new cyclin that interacts with two members of the CDC2 gene family. Cell 66: 1217–1228.
Koff A, Giordano A, Desai D, Yamashita K, Harper JW, Elledge S et al. (1992). Formation and activation of a cyclin E-cdk2 complex during the G1 phase of the human cell cycle. Science 257: 1689–1694.
Kozar K, Ciemerych MA, Rebel VI, Shigematsu H, Zagozdzon A, Sicinska E et al. (2004). Mouse development and cell proliferation in the absence of D-cyclins. Cell 118: 477–491.
Labib K, Kearsey SE, Diffley JF . (2001). MCM2-7 proteins are essential components of prereplicative complexes that accumulate cooperatively in the nucleus during G1-phase and are required to establish, but not maintain, the S-phase checkpoint. Mol Biol Cell 12: 3658–3667.
Labib K, Tercero JA, Diffley JF . (2000). Uninterrupted MCM2-7 function required for DNA replication fork progression. Science 288: 1643–1647.
Lei M, Kawasaki Y, Young MR, Kihara M, Sugino A, Tye BK . (1997). Mcm2 is a target of regulation by Cdc7-Dbf4 during the initiation of DNA synthesis. Genes Dev 11: 3365–3374.
Liu E, Li X, Yan F, Zhao Q, Wu X . (2004). Cyclin-dependent kinases phosphorylate human Cdt1 and induce its degradation. J Biol Chem 279: 17283–17288.
Mailand N, Diffley JF . (2005). CDKs promote DNA replication origin licensing in human cells by protecting Cdc6 from APC/C-dependent proteolysis. Cell 122: 915–926.
Malumbres M, Sotillo R, Santamaria D, Galan J, Cerezo A, Ortega S et al. (2004). Mammalian cells cycle without the D-type cyclin-dependent kinases Cdk4 and Cdk6. Cell 118: 493–504.
Markey MP, Angus SP, Strobeck MW, Williams SL, Gunawardena RW, Aronow BJ et al. (2002). Unbiased analysis of RB-mediated transcriptional repression identifies novel targets and distinctions from E2F action. Cancer Res 62: 6587–6597.
Mendez J, Stillman B . (2000). Chromatin association of human origin recognition complex, cdc6, and minichromosome maintenance proteins during the cell cycle: assembly of prereplication complexes in late mitosis. Mol Cell Biol 20: 8602–8612.
Mimura S, Seki T, Tanaka S, Diffley JF . (2004). Phosphorylation-dependent binding of mitotic cyclins to Cdc6 contributes to DNA replication control. Nature 431: 1118–1123.
Nguyen VQ, Co C, Li JJ . (2001). Cyclin-dependent kinases prevent DNA re-replication through multiple mechanisms. Nature 411: 1068–1073.
Noton E, Diffley JF . (2000). CDK inactivation is the only essential function of the APC/C and the mitotic exit network proteins for origin resetting during mitosis. Mol Cell 5: 85–95.
Okuno Y, McNairn AJ, den Elzen N, Pines J, Gilbert DM . (2001). Stability, chromatin association and functional activity of mammalian pre-replication complex proteins during the cell cycle. EMBO J 20: 4263–4277.
Palmero I, Peters G . (1996). Perturbation of cell cycle regulators in human cancer. Cancer Surv 27: 351–367.
Savio M, Cerri M, Cazzalini O, Perucca P, Stivala LA, Pichierri P et al. (2006). Replication-dependent DNA damage response triggered by roscovitine induces an uncoupling of DNA replication proteins. Cell Cycle 5: 2153–2159.
Senga T, Sivaprasad U, Zhu W, Park JH, Arias EE, Walter JC et al. (2006). PCNA is a cofactor for Cdt1 degradation by CUL4/DDB1-mediated N-terminal ubiquitination. J Biol Chem 281: 6246–6252.
Sever-Chroneos Z, Angus SP, Fribourg AF, Wan H, Todorov I, Knudsen KE et al. (2001). Retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein signals through inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 2 activity to disrupt PCNA function in S phase. Mol Cell Biol 21: 4032–4045.
Sherr CJ . (1996). Cancer cell cycles. Science 274: 1672–1677.
Sherr CJ . (2000). Cell cycle control and cancer. Harvey Lect 96: 73–92.
Sherr CJ . (2001). The INK4a/ARF network in tumour suppression. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2: 731–737.
Sherr CJ, McCormick F . (2002). The RB and p53 pathways in cancer. Cancer Cell 2: 103–112.
Sherr CJ, Roberts JM . (1999). CDK inhibitors: positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression. Genes Dev 13: 1501–1512.
Stillman B . (2005). Origin recognition and the chromosome cycle. FEBS Lett 579: 877–884.
Sullivan M, Morgan DO . (2007). Finishing mitosis, one step at a time. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8: 894–903.
Tanaka S, Diffley JF . (2002). Deregulated G1-cyclin expression induces genomic instability by preventing efficient pre-RC formation. Genes Dev 16: 2639–2649.
Vaziri C, Saxena S, Jeon Y, Lee C, Murata K, Machida Y et al. (2003). A p53-dependent checkpoint pathway prevents rereplication. Mol Cell 11: 997–1008.
Woo RA, Poon RY . (2003). Cyclin-dependent kinases and S phase control in mammalian cells. Cell Cycle 2: 316–324.
Yan Z, DeGregori J, Shohet R, Leone G, Stillman B, Nevins JR et al. (1998). Cdc6 is regulated by E2F and is essential for DNA replication in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 3603–3608.
Yang K, Hitomi M, Stacey DW . (2006). Variations in cyclin D1 levels through the cell cycle determine the proliferative fate of a cell. Cell Div 1: 32.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Karen Knudsen and members of both Knudsen laboratories for critical review of the paper. Critical reagents were provided by Dr Piotr Sicinski and Pfizer Corp. This study was funded by a grant to ESK from the NCI CA106471. WAB and AKM are supported by NIEHS training grant T32 ES07250-16.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Braden, W., McClendon, A. & Knudsen, E. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 activity is a critical determinant of pre-replication complex assembly. Oncogene 27, 7083–7093 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.319
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.319
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Therapeutic potential of CDK4/6 inhibitors in renal cell carcinoma
Nature Reviews Urology (2022)
-
The E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIP12 participates in cell cycle progression and chromosome stability
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Berberine downregulates CDC6 and inhibits proliferation via targeting JAK-STAT3 signaling in keratinocytes
Cell Death & Disease (2019)
-
Non-canonical roles of PFKFB3 in regulation of cell cycle through binding to CDK4
Oncogene (2018)
-
KMTase Set7/9 is a critical regulator of E2F1 activity upon genotoxic stress
Cell Death & Differentiation (2014)