Abstract
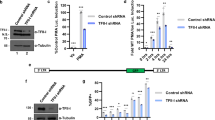
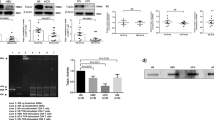
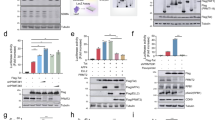
Human T-cell leukemia virus type I (HTLV-I) can infect a variety of cell types, so the cause of T-cell-specific oncogenesis remains to be elucidated. The trans-activator protein Tax of HTLV-I can promote cell-cycle progression in resting T cells along with induction of cyclin D2 and cyclin-dependent kinase (cdk6) gene expression. Here, we found that Tax cannot induce cell-cycle progression in resting fibroblasts and analysed the molecular basis of the cell-type specificity. Tax activated cyclin D2 and cdk6 promoters in T cells, but not in fibroblasts, depending on its ability to activate the transcription factor nuclear factor (NF)-κB. Expression of cyclin D2 and CDK6 activated the transcription factor E2F, which is essential for cell-cycle progression, in both T cells and fibroblasts. Short-hairpin RNA (shRNA)-mediated inhibition of cyclin D2 and CDK6 induction suppressed Tax-induced activation of E2F in T cells. Finally, shRNA-mediated downregulation of NF-κB p65 or p100 expression reduced Tax-induced activation of cyclin D2 and/or cdk6 promoters and cell-cycle progression in T cells. These results indicate that Tax-induced cell-cycle progression in T cells is mediated, at least in part, through cell-type-specific activation of the cyclin D2 and cdk6 genes through NF-κB and may be important for the cell-type-specific oncogenesis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huang Y, Ohtani K, Iwanaga R, Matsumura Y, Nakamura M . (2001). Direct trans-activation of the human cyclin D2 gene by the oncogene product Tax of human T-cell leukemia virus type I. Oncogene 20: 1094–1102.
Inoue J, Gohda J, Akiyama T, Semba K . (2007). NF-κB activation in development and progression of cancer. Cancer Sci 98: 268–274.
Iwanaga R, Ohtani K, Hayashi T, Nakamura M . (2001). Molecular mechanism of cell cycle progression induced by the oncogene product Tax of human T-cell leukemia virus type I. Oncogene 20: 2055–2067.
Lee B, Tanaka Y, Tozawa H . (1989). Monoclonal antibody defining tax protein of human T-cell leukemia virus type I. Tohoku J Exp Med 157: 1–11.
Manel N, Kim FJ, Kinet S, Taylor N, Sitbon M, Battini JL . (2003). The ubiquitous glucose transporter GLUT-1 is a receptor for HTLV. Cell 115: 449–459.
Nakamura M, Niki M, Nagata K, Ohtani K, Saito S, Hinuma Y et al. (1989). Cell line-dependent response of the enhancer element of simian virus 40 to transactivator p40tax encoded by human T-cell leukemia virus type I. J Biol Chem 264: 20189–20192.
Neuveut C, Low KG, Maldarelli F, Schmitt I, Majone F, Grassmann R et al. (1998). Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax and cell cycle progression: role of cyclin D-cdk and p110Rb. Mol Cell Biol 18: 3620–3632.
Ohtani K, Iwanaga R, Arai M, Huang Y, Matsumura Y, Nakamura M . (2000). Cell type-specific E2F activation and cell cycle progression induced by the oncogene product Tax of human T-cell leukemia virus type I. J Biol Chem 275: 11154–11163.
Ohtani K, Nakamura M, Saito S, Noda T, Ito Y, Sugamura K et al. (1987). Identification of two distinct elements in the long terminal repeat of HTLV-I responsible for maximum gene expression. EMBO J 6: 389–395.
Ohtani K, Tsujimoto A, Tsukahara T, Numata N, Miura S, Sugamura K et al. (1998). Molecular mechanisms of promoter regulation of the gp34 gene that is trans-activated by an oncoprotein Tax of human T cell leukemia virus type I. J Biol Chem 273: 14119–14129.
Schmitt I, Rosin O, Rohwer P, Gossen M, Grassmann R . (1998). Stimulation of cyclin-dependent kinase activity and G1- to S-phase transition in human lymphocytes by the human T-cell leukemia/lymphotropic virus type 1 Tax protein. J Virol 72: 633–640.
Sun SC, Yamaoka S . (2005). Activation of NF-κB by HTLV-I and implications for cell transformation. Oncogene 24: 5952–5964.
Yamaoka S, Inoue H, Sakurai M, Sugiyama T, Hazama M, Yamada T et al. (1996). Constitutive activation of NF-κB is essential for transformation of rat fibroblasts by the human T-cell leukemia virus type I Tax protein. EMBO J 15: 873–887.
Yoshida M . (2005). Discovery of HTLV-1, the first human retrovirus, its unique regulatory mechanisms, and insights into pathogenesis. Oncogene 24: 5931–5937.
Acknowledgements
We thank S Yamaoka for critical comments on western blot analysis of p100. This work was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iwanaga, R., Ozono, E., Fujisawa, J. et al. Activation of the cyclin D2 and cdk6 genes through NF-κB is critical for cell-cycle progression induced by HTLV-I Tax. Oncogene 27, 5635–5642 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.174
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.174
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
FKBP4 integrates FKBP4/Hsp90/IKK with FKBP4/Hsp70/RelA complex to promote lung adenocarcinoma progression via IKK/NF-κB signaling
Cell Death & Disease (2021)
-
Importin β1 regulates cell growth and survival during adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma therapy
Investigational New Drugs (2021)
-
PKC-ѳ is dispensable for OX40L-induced TCR-independent Treg proliferation but contributes by enabling IL-2 production from effector T-cells
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Acetylation at lysine 346 controls the transforming activity of the HTLV-1 Tax oncoprotein in the Rat-1 fibroblast model
Retrovirology (2013)
-
Visualizing spatiotemporal dynamics of apoptosis after G1 arrest by human T cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax and insights into gene expression changes using microarray-based gene expression analysis
BMC Genomics (2012)