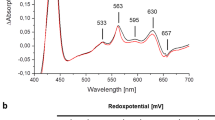
Abstract
Fumarate respiration is one of the most widespread types of anaerobic respiration. The soluble fumarate reductase of Shewanella putrefaciens MR-1 is a periplasmic tetraheme flavocytochrome c. The crystal structures of the enzyme were solved to 2.9 Å for the uncomplexed form and to 2.8 Å and 2.5 Å for the fumarate and the succinate-bound protein, respectively. The structures reveal a flexible capping domain linked to the FAD-binding domain. A catalytic mechanism for fumarate reduction based on the structure of the complexed protein is proposed. The mechanism for the reverse reaction is a model for the homologous succinate dehydrogenase (complex II) of the respiratory chain. In flavocytochrome c fumarate reductase, all redox centers are in van der Waals contact with one another, thus providing an efficient conduit of electrons from the hemes via the FAD to fumarate.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kroger, A., Geisler, V., Lemma, E. Theis, F. & Lenger, R. Arch. Microbiol. 158, 311–314 (1992).
Van Hellemond, J.J. & Tielens, A.G. Biochem. J. 304, 321–331 (1994).
Arikawa, Y., Enomoto, K., Muratsubaki, H. & Okazaki, M. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 165,111–116 (1998).
Mracek, J., Snyder, S.J., Chavez, U.B. & Turrens, J.F. J. Protozool. 38, 554–558 (1991).
Pealing, S.L. et al. Biochemistry 48, 12132–12140 (1992).
Myers, C.R. & Myers, J.M. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 98, 13–20 (1992).
Maklashina, E., Berthold, D.A. & Cecchini, G. J. Bacteriol. 180, 5989–5996 (1998).
Pealing, S.L. et al. Biochemistry 34,6153–6158 (1995).
Turner, K.L. et al. Biochemistry 38, 3302–3309 (1999).
Myers, C.R. & Nealson, K.H. J. Bacteriol. 172, 6232–6238 (1990).
Myers, C.R. & Myers, J.M. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 25, 162–168 (1997).
Reid, G.A. et al. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 26, 418–421 (1998).
Gordon, E.H., Pealing, S.L., Chapman, S.K., Ward, F.B. & Reid, G.A. Microbiology 144, 937–945 (1998).
Matias, P.M. et al. Protein Sci. 5,1342–1354 (1996).
Iverson, T.M., Luna-Chavez, C., Cecchini, G. & Rees, D.C. Science 284, 1961–1966 (1999).
Mattevi, A. et al. Structure 15, 745–756 (1999).
Karplus, P.A. & Schulz, G.E. J. Mol. Biol. 195, 701–29 (1987).
Chen, Z.W. et al. Science 266, 430–432 (1994).
Vik, S.B. & Hatefi, Y. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 78, 6749–6753 (1987).
Schroder, I., Gunsalus, R.P., Ackrell, B.A., Cochran, B. & Cecchini, G. J. Biol. Chem. 266, 13572–13579 (1991).
Iverson, T.M. et al. Nature Struct. Biol. 11, 1005–1012 (1998).
Xia, Z.X. & Mathews, F.S. J. Mol. Biol. 212, 837–863 (1990).
Mathews, F.S., Chen, Z.W., Bellamy, H.D. & McIntire, W.S. Biochemistry 30, 238–247 (1991).
Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. Methods Enzymol. 276, 307–326 (1997).
Otwinowski, Z. Isomorphous replacement and anomalous scattering 80 (SERC Daresbury Laboratory, Warrington, England; 1991).
Collaborative Computational Project, Number 4. Acta Crystallogr. D 50, 760–763 (1994).
Navaza., J. Acta. Crystallogr. A. 50, 157–163 (1994).
Roussel, A. & Cambillau, C. TURBO-FRODO, Biographics (AFMB, Marseille, France; 1992).
Murshudov, G.N., Vagin, A.A. & Dodson, E.J. Acta Crystallogr. D 53, 240–255 (1997).
Kraulis, P.J. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 24, 946–950 (1991).
Merrit, E.A. & Murphy, M.E.P. Acta Crystallogr. D 50, 869–873 (1994).
Brunger, A.T. Nature 355, 472–475 (1992).
Acknowledgements
D.L. is a research assistant at the Fund for Scientific Research-Flanders. J.J.V.B. is indebted to the same institution for a research project and to the Bijzonder Onderzoeksfonds of the University of Ghent for a Concerted Research Action. Part of this work was supported by a grant from NIH. We thank S. Chapman and G. Reid for helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leys, D., Tsapin, A., Nealson, K. et al. Structure and mechanism of the flavocytochrome c fumarate reductase of Shewanella putrefaciens MR-1. Nat Struct Mol Biol 6, 1113–1117 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/70051
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/70051
This article is cited by
-
Microbial synthesis of Prussian blue for potentiating checkpoint blockade immunotherapy
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Structural characterization of the microbial enzyme urocanate reductase mediating imidazole propionate production
Nature Communications (2021)
-
Molecular basis of maintaining an oxidizing environment under anaerobiosis by soluble fumarate reductase
Nature Communications (2018)
-
Structure and function of the divalent anion/Na+ symporter from Vibrio cholerae and a humanized variant
Nature Communications (2017)
-
Extracellular electron transfer mechanisms between microorganisms and minerals
Nature Reviews Microbiology (2016)