Abstract
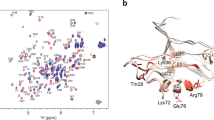
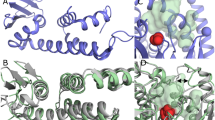
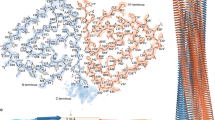
The phox homology (PX) domain is a novel protein module containing a conserved proline-rich motif. We have shown that the PX domain isolated from the human p47phox protein, a soluble subunit of phagocyte NADPH oxidase, binds specifically to the C-terminal SH3 domain derived from the same protein. The solution structure of p47 PX has an α + β structure with a novel folding motif topology and reveals that the proline-rich motif is presented on the molecular surface for easy recognition by the SH3 domain. The proline-rich motif of p47 PX in the free state adopts a distorted left-handed polyproline type II helix conformation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Ponting, C.P. Protein Sci. 5, 2353–2357 (1996).
Schultz, J., Copley, R.R., Doerks, T., Ponting, C.P. & Bork, P. Nucleic Acids Res. 28, 231–234 (2000).
SMART Simple Modular Architecture Research Tool (V3.1) http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/
Kay, B.K., Williamson, M.P. & Sudol, M. FASEB J. 14, 231–241 (2000).
DeLeo, F.R. & Quinn, M.T. J. Leukocyte Biol. 60, 677–691 (1996).
Ago, T., Nunoi, H., Ito, T. & Sumimoto, H. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 33644–33653 (1999).
Lim, W.A., Richards, F.M. & Fox, R.O. Nature 372, 375–379 (1994).
Feng, S., Chen, J.K., Yu, H., Simon, J.A. & Schreiber, S.L. Science 266, 1241–1247 (1994).
Terasawa, H. et al. Nature Struct. Biol. 1, 891–897 (1994).
Musacchio, A., Gibson, T., Lehto, V.-P. & Saraste, M. FEBS Lett. 307, 55–61 (1992).
Yu, H., Chen, J.K., Feng, S., Dalgarno, D.C., Brauer, A.W. & Schreiber, S.L. Cell 76, 933–945 (1994).
Liu, X., Marengere, L.E., Koch, C.A. & Pawson, T. Mol. Cell Biol. 13, 5225–5232 (1993).
Tanaka, S. et al. Mol. Cell Biol. 13, 4409–4415 (1993).
Sumimoto, H. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 5345–5349 (1994).
Leto, T. L., Adams, A. G. & de Mendez, I. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 10650–10654 (1994).
Güntert, P., Mumenthaler, C. & Wüthrich, K. J. Mol. Biol. 273, 283–298 (1997).
Nakai, T., Kidera, H. & Nakamura, H. J. Biomol. NMR 3, 19–40 (1993).
Holm, L. & Sander, C. J. Mol. Biol. 233, 123–138 (1993).
The Dali server, http://www2.ebi.ac.uk/dali
Lim, W.A. Structure 4, 657–659 (1996).
Gorina, S. & Pavletich, N.P. Science 274, 1001–1005 (1996).
Sicheri, F. & Kuriyan, J. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 7, 777–785 (1997).
Delaglio, F., Grzesiek, S., Vuister, G.W., Zhu G., Pfeifer, J. & Bax, A. J. Biomol. NMR 6, 277–293 (1995).
Bartels, C., Xia, T.-H., Billeter, M., Güntert, P. & Wüthrich, K. J. Biomol. NMR 5, 1–10 (1995).
Abe, Y. et al. Cell 100, 551–560 (2000).
Koradi, R., Billeter, M. & Wüthrich, K. J. Mol. Graph. 14, 52–55 (1996).
Thompson, J.D., Gibson, T.J., Plewniak, F., Jeanmougin, F. & Higgins, D.G. Nucleic Acids Res. 25, 4876–4882 (1997).
Yu, H. et al. Science 258, 1665–1668 (1992).
Acknowledgements
We thank H. Nakamura for the program EMBOSS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hiroaki, H., Ago, T., Ito, T. et al. Solution structure of the PX domain, a target of the SH3 domain. Nat Struct Mol Biol 8, 526–530 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/88591
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/88591
This article is cited by
-
Genomic analysis of phospholipase D family and characterization of GmPLDαs in soybean (Glycine max)
Journal of Plant Research (2012)
-
Combating oxidative stress in vascular disease: NADPH oxidases as therapeutic targets
Nature Reviews Drug Discovery (2011)
-
A simplified recipe for assigning amide NMR signals using combinatorial 14N amino acid inverse-labeling
Journal of Structural and Functional Genomics (2011)
-
Translation of the phosphoinositide code by PI effectors
Nature Chemical Biology (2010)
-
Nox enzymes in immune cells
Seminars in Immunopathology (2008)