Abstract
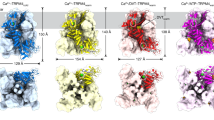
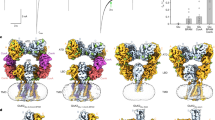
We report here the first three-dimensional structure of α-latrotoxin, a black widow spider neurotoxin, which forms membrane pores and stimulates secretion in the presence of divalent cations. We discovered that α-latrotoxin exists in two oligomeric forms: it is dimeric in EDTA but forms tetramers in the presence of Ca2+ or Mg2+. The dimer and tetramer structures were determined independently at 18 Å and 14 Å resolution, respectively, using cryo-electron microscopy and angular reconstitution. The α-latrotoxin monomer consists of three domains. The N- and C-terminal domains have been identified using antibodies and atomic fitting. The C4-symmetric tetramers represent the active form of α-latrotoxin; they have an axial channel and can insert into lipid bilayers with their hydrophobic base, providing the first model of α-latrotoxin pore formation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gorio, A., Rubin, L.L. & Mauro, A. J. Neurocytol. 7, 193– 202 (1978).
Lang, J., Ushkaryov, Y., Grasso, A. & Wollheim, C.B. EMBO J. 17, 648–657 ( 1998).
Liu, J. & Misler, S. J. Neurosci. 18, 6113–6125 (1998).
Rosenthal, L. & Meldolesi, J. Pharmacol. Ther. 42 , 115–134 (1989).
Grasso, A., Alema, S., Rufini, S. & Senni, M.I. Nature 283, 774–776 (1980).
Deri, Z., Bors, P. & Adam-Vizi, V. J. Neurochem. 60, 1065– 1072 (1993).
Davletov, B.A. et al. EMBO J. 17, 3909–3920 (1998).
Finkelstein, A., Rubin, L.L. & Tzeng, M.C. Science 193, 1009– 1011 (1976).
Mironov, S.L., Sokolov, Y.V., Chanturiya, A.N. & Lishko, V.K. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 862, 185–198 (1986).
Dulubova, I.E. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 7535– 7543 (1996).
Frontali, N. et al. J. Cell Biol. 68, 462– 479 (1976).
Kiyatkin, N.I., Dulubova, I.E., Chekhovskaya, I.A. & Grishin, E.V. FEBS Lett. 270, 127–131 (1990).
Ushkarev, Iu.A. & Grishin, E.V. Bioorg. Khim. 12, 71–80 ( 1986).
Gouaux, E. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 7, 566–573 (1997).
van Heel, M. Ultramicroscopy 21, 111–124 (1987).
Dubochet, J. et al. Quat. Rev. Biophys. 21, 129– 228 (1988).
Meldolesi, J., Madeddu, L., Torda, M., Gatti, G. & Niutta, E. Neuroscience 10, 997– 1009 (1983).
Misler, S. & Hurlbut, W.P. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 76, 991–995 ( 1979).
Scheer, H. et al. J. Physiol. (Paris) 79, 216– 221 (1984).
Dube, P., Tavares, P., Lurz, R. & van Heel, M. EMBO J. 12, 1303–1309 (1993).
Volynski, K.E., Nosyreva, E.D., Ushkaryov, Y.A. & Grishin, E.V. FEBS Lett. 442, 25–28 ( 1999).
Batchelor, A.H., Piper, D.E., de la Brousse, F.C., McKnight, S.L. & Wolberger, C. Science 279, 1037– 1041 (1998).
Jacobs, M.D. & Harrison, S.C. Cell 95, 749–758 (1998).
Bork, P. Proteins 17, 363–374 ( 1993).
Madeddu, L. et al. J. Neurochem. 45, 1708– 1718 (1985).
Gilbert, R.J. et al. Cell 97, 647–655 (1999).
Ichtchenko, K. et al. EMBO J. 17, 6188–6199 (1998).
van Heel, M., Harauz, G. & Orlova, E.V. J. Struct. Biol. 116, 17– 24 (1996).
van Heel, M. Optik 82, 114–126 ( 1989).
Schatz, M., Orlova, E.V., Dube, P., Jager, J. & van Heel, M. J. Struct. Biol. 114 , 28–40 (1995).
Harauz, G. & van Heel, M. Optik 73, 146–156 (1986).
Radermacher, M. J. Elect. Microsc. Tech. 9, 359–394 (1988).
van Heel, M. & Harauz, G. Optik 73 , 119–122 (1986).
Jones, T.A., Zou, J.Y., Cowan, S.W. & Kjeldgaard, M. Acta Crystallogr. A. 47, 110–119 ( 1991).
Acknowledgements
We thank R. Weinzierl for the use of the DLS spectrometer. The work was funded by a Wellcome Trust Senior European Research Fellowship (to Y.A.U.) and BBSRC and EC grants (to M.v.H.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orlova, E., Rahman, M., Gowen, B. et al. Structure of α-latrotoxin oligomers reveals that divalent cation-dependent tetramers form membrane pores. Nat Struct Mol Biol 7, 48–53 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/71247
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/71247
This article is cited by
-
Acute Myocarditis After Black Widow Spider Bite: A Case Report
Cardiology and Therapy (2020)
-
House spider genome uncovers evolutionary shifts in the diversity and expression of black widow venom proteins associated with extreme toxicity
BMC Genomics (2017)
-
Activation of α-Latrotoxin Receptors in Neuromuscular Synapses Leads to a Prolonged Splash Acetylcholine Release
Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine (2009)