Key Points
-
The vascular endothelium synthesizes and releases a range of vasodilators and vasoconstrictors that have key roles in the local regulation of vascular tone.
-
Endothelin (ET) — a highly potent peptidic vasoconstrictor — regulates blood pressure through effects on blood vessels, heart and kidneys.
-
The ET system can be overactive in disorders such as hypertension, heart failure and renal disease, and considerable efforts have been made to develop antagonists of its actions in the hope that they would have therapeutic potential.
-
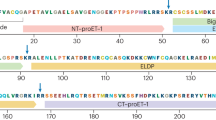
ET-1 is the predominant isoform of the ET peptide family, which also includes ET-2 and ET-3. The biological activity of ET-1 is regulated by a complex process of synthesis and breakdown.
-
The effects of ET are mediated by binding to G-protein-coupled receptors. So far, two types of ET receptor have been identified in humans. The ET type-A receptor (ETA) has higher binding affinity for ET-1 and ET-2 than for ET-3, whereas the type-B receptor (ETB) binds the three isopeptides with comparable affinity.
-
Once ETs and the ET receptors had been identified, many companies set up screens for antagonists, which are classified as either ETA - or ETB -receptor selective, or mixed antagonists. Most are either ETA -receptor selective or mixed antagonists. Non-peptide antagonists of each type have been developed, and many are orally bioavailable.
-
any antagonists showed promising results in animal models of renal disease, hypertension, heart failure and more recently, several types of cancer.
-
However, results in human trials have generally been less exciting than hoped. Trial results in several areas are described, including arterial hypertension, congestive heart failure and chronic renal failure, and possible approaches to maximizing the potential of ET antagonism in these and other novel indications, such as secondary hyperparathyroidism, are discussed.
Abstract
The discovery of endothelin — a highly potent endogenous vasoconstrictor — in 1988 has led to considerable efforts to develop antagonists of endothelin receptors that could have therapeutic potential in disorders including hypertension, heart failure and renal diseases. However, in general, the results of trials in humans have not mirrored the highly promising effects in animal disease models. Here, we discuss preclinical and clinical results with endothelin antagonists, and consider possible approaches to fully realizing the potential of endothelin antagonism.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yanagisawa, M. et al. A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature 332, 411–415 (1988). This seminal article describes the discovery of ET-1, and represents the starting point for more than 14,000 subsequent studies elucidating pathophysiological roles of the peptide in normal and disease conditions.
Rubanyi, G. M. & Vanhoutte, P. M. Hypoxia releases a vasoconstrictor substance from the canine vascular endothelium. J. Physiol. 364, 45–56 (1985).
Levin, E. R. Endothelins. N. Engl. J. Med. 333, 356–363 (1995).
Inoue, A. et al. The human endothelin family: three structurally and pharmacologically distinct isopeptides predicted by three separate genes. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 86, 2863–2867 (1989). The authors report a pivotal observation of the existence of three components of the ET family discovered by screening a genomic DNA library with synthetic oligonucleotides encoding a portion of the ET sequence.
Saida, K., Mitsui, Y. & Ishida, I. A novel peptide, vasoactive intestinal contractor, of a new (endothelin) peptide family. Molecular cloning, expression and biological activity. J. Biol. Chem. 264, 14613–14616 (1989).
Bloch, K. D., Hong, C. C., Eddy, R. L., Shows, T. B. & Quertermous, T. cDNA cloning and chromosomal assignment of the endothelin-2 gene: vasoactive intestinal contractor peptide is rat endothelin-2. Genomics 10, 236–242 (1991).
Alberts, G. F., Peifley, K. A., Johns, A., Kleha, J. F. & Winkles, J. A. Constitutive endothelin-1 overexpression promotes smooth muscle cell proliferation via an external autocrine loop. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 10112–10118 (1994).
Fujisaki, H. et al. Natriuretic peptides inhibit angiotensin II-induced proliferation of rat cardiac fibroblasts by blocking endothelin-1 gene expression. J. Clin. Invest. 96, 1059–1065 (1995).
Iwasaki, S., Homma, T., Matsuda, Y. & Kon, V. Endothelin receptor subtype B mediates autoinduction of endothelin-1 in rat mesangial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 6997–7003 (1995).
Malek, A. & Izumo, S. Physiological fluid shear stress causes downregulation of endothelin-1 mRNA in bovine aortic endothelium. Am. J. Physiol. 263, C389–C396 (1992).
Barton, M., Shaw, S., d'Uscio, L. V., Moreau, P. & Luscher, T. F. Angiotensin II increases vascular and renal endothelin-1 and functional endothelin converting enzyme activity in vivo: role of ETA receptors for endothelin regulation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 238, 861–865 (1997).
Ito, H. et al. Endothelin-1 is an autocrine/paracrine factor in the mechanism of angiotensin II-induced hypertrophy in cultured rat cardiomyocytes. J. Clin. Invest. 92, 398–403 (1993).
Matsumura, A., Yamochi, W., Hirata, K., Kawashima, S. & Yokoama, M. Stimulatory interaction between vascular endothelial growth factor and endothelin-1 on each gene expression. Hypertension 32, 89–95 (1998).
Corder, R., Carrier, M., Khan, N., Klemm, P. & Vane, J. R. Cytokine regulation of endothelin-1 release from bovine aortic endothelial cells. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 26 (Suppl. 3), S56–S58 (1995).
Schwarting, A. et al. Endothelin-1 modulates the expression of adhesion molecules on fibroblast-like synovial cells (FLS). Scand. J. Rheumatol. 25, 246–256 (1996).
Boulanger, C. & Luscher, T. F. Release of endothelin from the porcine aorta. Inhibition by endothelium-derived nitric oxide. J. Clin. Invest. 85, 587–590 (1990).
Stewart, D. et al. Role of cyclic nucleotides in the regulation of endothelin-1 production by human endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. 266, H944–H951 (1994).
Wada, A. et al. Endogenous atrial natriuretic peptide inhibits endothelin-1 secretion in dogs with severe congestive heart failure. Am. J. Physiol. 270, H1819–H1824 (1996).
Yu, J. C. & Davenport, A. P. Secretion of endothelin-1 and endothelin-3 by human cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 114, 551–557 (1995).
Benigni, A. Endothelin antagonists in renal disease. Kidney Int. 57, 1778–1794 (2000).
Kitamura, K. & Tomita, K. Endothelin receptor antagonists prevent parathyroid cell proliferation caused by hypocalcemia in rats. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 11, 411–415 (2002). A comprehensive review that deals with ET-receptor antagonism as an important therapeutic strategy to treat secondary hyperparathyroidism in chronic renal failure.
Russell, F. D., Skepper, J. N. & Davenport, A. P. Human endothelial cell storage granules: a novel intracellular site for isoforms of the endothelin-converting enzyme. Circ. Res. 83, 314–321 (1998).
Russell, F. D., Skepper, J. N. & Davenport, A. P. Evidence using immunoelectron microscopy for regulated and constitutive pathways in the transport and release of endothelin. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 31, 424–430 (1998).
Benigni, A. & Remuzzi, G. Endothelin antagonists. Lancet 353, 133–138 (1999).
Valdenaire, O., Rohrbacher, E. & Mattei, M. G. Organization of the gene encoding the human endothelin-converting enzyme (ECE-1). J. Biol. Chem. 270, 29794–29798 (1995).
Schweizer, A. et al. Human endothelin-converting enzyme (ECE-1): three isoforms with distinct subcellular localizations. Biochem. J. 328, 871–878 (1997).
Xu, D. et al. ECE-1: a membrane-bound metalloprotease that catalyzes the proteolytic activation of big endothelin-1. Cell 78, 473–485 (1994).
Valdenaire, O. et al. A fourth isoform of endothelin-converting enzyme (ECE-1) is generated from an additional promoter. Molecular cloning and characterization. Eur. J. Biochem. 264, 341–349 (1999).
Abassi, Z. A., Klein, H., Golomb, E. & Keiser, H. R. Urinary endothelin: a possible biological marker of renal damage. Am. J. Hypertens. 6, 1046–1054 (1993).
Deng, Y., Martin, L. L., DelGrande, D. & Jeng, A. Y. A soluble protease identified from rat kidney degrades endothelin-1 but not proendothelin-1. J. Biochem. 112, 168–172 (1992).
Yamaguchi, T., Fukase, M., Arao, M., Sugimoto, T. & Chichara, K. Endothelin-1 hydrolysis by rat kidney membranes. FEBS Lett. 309, 303–306 (1992).
Makinen, P. L. & Makinen, K. K. The Enterococcus faecalis extracellular metalloendopeptidase (EC 3.4.24.30; coccolysin) inactivates human endothelin at bonds involving hydrophobic amino acid residues. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 200, 981–985 (1994).
Lee, M.-E., Bloch, K. D., Clifford, J. A. & Quatermous, T. Functional analysis of the endothelin-1 gene promoter. Evidence for an endothelial cell-specific cis-acting sequence. J. Biol. Chem. 265, 10446–10450 (1990).
Hu, R. M. et al. High density lipoproteins stimulate the production and secretion of endothelin-1 from cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells. J. Clin. Invest. 93, 1056–1062 (1994).
Hu, R. M., Levin, E. R., Pedram, A. & Frank, H. J. L. Atrial natriuretic peptide inhibits the production and secretion of endothelin from cultured endothelial cells: mediation through the C receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 17384–17389 (1992).
Arai, H., Hori, S., Aramori, I., Ohkubo, H. & Nakanishi, S. Cloning and expression of a cDNA encoding an endothelin receptor. Nature 348, 730–732 (1990). A seminal article that describes the cloning, selectivity and distribution of the ET A -receptor subtype.
Sakurai, T. et al. Cloning of a cDNA encoding a non-isopeptide-selective subtype of the endothelin receptor. Nature 348, 732–737 (1990). A key finding on the cloning and characterization of the cDNA that encodes the ET B -receptor subtype.
Clouthier, D. E. et al. Cranial and cardiac neural crest defects in endothelin-A receptor-deficient mice. Development 125, 813–824 (1998).
Davenport, A. P. International Union of Pharmacology. XXIX. Update on endothelin receptor nomenclature. Pharmacol. Rev. 54, 219–226 (2002). A comprehensive and updated overview on ET receptors and their physiology, with a brief summary of the general characteristics of receptor antagonists.
Kumart, C. et al. Cloning and characterization of a novel endothelin receptor from Xenopus heart. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 13414–13420 (1994).
Haynes, W. G. & Webb, D. Y. Contribution of endogenous generation of endothelin-1 to basal vascular tone. Lancet 344, 852–854 (1994).
Verhaar, M. C. et al. Endothelin-A receptor antagonist-mediated vasodilatation is attenuated by inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis by endothelin-B receptor blockade. Circulation 97, 752–756 (1998).
Moreland, S., McMullen, D. M., Delaney, C. L., Lee, V. G. & Hunt, J. T. Venous smooth muscle contains vasoconstrictor ETB-like receptors. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 184, 100–106 (1992).
Fukuroda, T. et al. Clearance of circulating endothelin-1 by ETB receptors in rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 199, 1461–1465 (1994).
Saijonmaa, O., Nyman, T. & Fyhrquist, F. Endothelin-1 stimulates its own synthesis on human endothelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 188, 286–291 (1992).
Buchan, K. W. et al. Characterization of three non-peptide endothelin receptor ligands using human cloned ETA and ETB receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 112, 1251–1257 (1994).
Masaki, T. The endothelin family: an overview. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 35 (Suppl. 2), S3–S5 (2000).
McGiff, J. C. & Quilley, J. 20-HETE and the kidney: resolution of old problems and new beginnings. Am. J. Physiol. 277, R607–R623 (1999).
Doherty, A. M. Design and discovery of nonpeptide endothelin antagonists. Drug Discov. Today 1, 60–69 (1996).
Ihara, M. et al. Biological profiles of highly potent novel endothelin antagonists selective for the ET(A) receptor. Life Sci. 50, 247–255 (1991).
Aramori, I. et al. Subtype selectivity of a novel endothelin antagonist, FR139317, for the two endothelin receptors in transfected chinese hamster ovary cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 43, 127–131 (1993).
Breu, V., Ertel, S. I., Roux, S. & Clozel, M. The pharmacology of bosentan. Exp. Opin. Invest. Drugs 7, 1173–1192 (1998).
Yokokawa, K. et al. Hypertension associated with endothelin-secreting malignant hemangioendothelioma. Ann. Intern. Med. 114, 213–215 (1991).
Burt, V. L. et al. Prevalence of hypertension in the US adult population. Results from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988–1991. Hypertension 25, 305–313 (1995).
Saito, Y., Nakao, K., Mukoyama, M. & Imura, H. Increased plasma endothelin level in patients with essential hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 322, 205 (1990).
Zoccali, C., Leonardis, D., Parlongo, S., Mallamaci, F. & Postorino, M. Urinary and plasma endothelin-1 in essential hypertension and in hypertension secondary to renoparenchymal disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 10, 1320–1323 (1995).
Januszewicz, A. et al. Elevated endothelin-1 plasma concentration in patients with essential hypertension. J. Cardiovasc. Risk 1, 81–85 (1994).
Amoroso, A. et al. Increased plasma levels of endothelin in patients with essential arterial hypertension. Riv. Eur. Sci. Med. Farmacol. 18, 33–37 (1996).
Shichiri, M. et al. Plasma endothelin levels in hypertension and chronic renal failure. Hypertension 15, 493–496 (1990).
Davenport, A. P. et al. A sensitive radioimmunoassay measuring endothelin-like immunoreactivity in human plasma: comparison of levels in patients with essential hypertension and normotensive control subjects. Clin. Sci. 78, 261–264 (1990).
Miyauchi, T. et al. Age- and sex-related variation of plasma endothelin-1 concentration in normal and hypertensive subjects. Am. Heart J. 123, 1092–1093 (1992).
Veglio, F. et al. Plasma endothelin in essential hypertension and diabetes mellitus. J. Human Hypertens. 7, 321–325 (1993).
Schiffrin, E. L. & Thibault, G. Plasma endothelin in human essential hypertension. Am. J. Hypertens. 4, 303–308 (1991).
Sorensen, S. S. et al. Endothelin in renovascular and essential hypertension. Blood Pressure 3, 364–369 (1994).
Fernandez-Cruz, A. et al. Plasma endothelin is increased in young essential hypertensives but not in elderly essential or diabetic hypertensives. J. Hypertens. 11 (Suppl. 5), S146–S147 (1993).
Ergul, S., Parish, D. C., Puette, D. & Ergul, A. Racial differences in plasma endothelin-1 concentrations in individuals with essential hypertension. Hypertension 28, 652–655 (1996).
Widimsky, J. Jr, Horry, K. & Dvorakova, J. Plasma endothelin-1,2 levels in mild and severe hypertension. J. Hypertens. 9, S194–S195 (1991).
Lemne, C. E., Ludenberg, T., Theodorsson, E. & De Faire, U. Increased basal concentrations of plasma endothelin in borderline hypertension. J. Hypertens. 12, 1069–1074 (1994).
Krum, H. et al. The effect of an endothelin-receptor antagonist, Bosentan, on blood pressure in patients with essential hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 338, 784–790 (1998). The first large trial to describe how ET-receptor blockade with a mixed antagonist affects blood pressure in essential hypertension.
Nakov, R., Pfarr, E. & Eberle, S. Darusentan: an effective endothelin A receptor antagonist for treatment of hypertension. Am. J. Hypertens. 15, 583–589 (2002). An important paper that indicates the therapeutic benefit of selective ET A -receptor antagonism in human hypertension.
Allcock, G. H., Venema, R. C. & Pollock, D. M. ETA-receptor blockade attenuates the hypertension but not renal dysfunction in DOCA-salt rats. Am. J. Physiol. 275, R245–R252 (1998).
Matsumura, Y. et al. Different contributions of endothelin-A and endothelin-B receptors in the pathogenesis of deoxycorticosterone acetate-salt-induced hypertension in rats. Hypertension 33, 759–765 (1999).
Pollock, D. M., Allcock, G. H. & Pollock, J. S. Upregulation of endothelin B receptors in kidney of DOCA-salt hypertensive rats. Am. J. Physiol. 278, F279–F286 (2000).
Clozel, M. & Breu, V. The role of ETB receptors in normotensive and hypertensive rats as revealed by the non-peptide selective ETB receptor antagonist Ro 46-8443. FEBS Lett. 383, 42–45 (1996).
Kassab, S. et al. Endothelin-A receptor antagonism attenuates the hypertension and renal injury in Dahl salt-sensitive rats. Hypertension 31, 397–402 (1998).
D'Uscio, L., Barton, M., Shaw, S., Moreau, P. & Luscher, T. F. Structure and function of small arteries in salt-induced hypertension: effects of chronic ETA-receptor blockade. Hypertension 30, 905–911 (1997).
Barton, M. et al. ETA-receptor blockade prevents increased tissue endothelin-1, vascular hypertrophy, and endothelial dysfunction in salt-sensitive hypertension. Hypertension 31, 499–504 (1998).
Evans, R. R., Philips, B. G., Singh, G., Bauman, J. L. & Gulati, A. Racial and gender differences in endothelin-1. Am. J. Cardiol. 78, 486–488 (1996).
Ergul, S. et al. The effect of regulation of high blood pressure on plasma endothelin-1 levels in blacks with hypertension. Am. J. Hypertens. 11, 1381–1385 (1998).
Treiber, F. A. et al. Racial differences in endothelin-1 at rest and in response to acute stress in adolescent males. Hypertension 35, 722–725 (2000).
Safian, R. D. & Textor, S. C. Renal-artery stenosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 344, 431–442 (2001).
Rizzoni, D. et al. Vascular hypertrophy and remodeling in secondary hypertension. Hypertension 28, 785–790 (1996).
Newman, J. H. Treatment of primary pulmonary hypertension — the next generation. N. Engl. J. Med. 346, 933–935 (2002).
Rich, S., Kaufmann, E. & Levy, P. S. The effect of high doses of calcium-channel blockers on survival in primary pulmonary hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 327, 76–81 (1992).
Chen, Y.-F. & Oparil, S. Endothelin and pulmonary hypertension. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 35 (Suppl. 2), S49–S53 (2000).
Williamson, D. J. et al. Hemodynamic effects of bosentan, an endothelin receptor antagonist, in patients with pulmonary hypertension. Circulation 102, 411–418 (2000).
Channick, R. N. et al. Effects of the dual endothelin-receptor antagonist bosentan in patients with pulmonary hypertension: a randomised placebo-controlled study. Lancet 358, 1119–1123 (2001).
Rubin, L. J. et al. Bosentan therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 346, 896–903 (2002). The most recent large trial in pulmonary hypertension, highlighting the efficacy of ET-receptor antagonism with oral bosentan, and also showing some concern about safety.
Barst, R. J. et al. A comparison of continuous intravenous epoprostenol (prostacyclin) with conventional therapy for primary pulmonary hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 334, 296–301 (1996).
McLaughlin, V. V., Shillington, A. & Rich, S. Survival in primary pulmonary hypertension. The impact of epoprostenol therapy. Circulation 106, 1477–1482 (2002).
Prasad, S., Wilkinson, J. & Gratzoulis, M. A. Sildenafil in primary pulmonary hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 343, 1342–1345 (2000).
Spieker, L. E., Noll, G., Ruschitzka, F. T. & Luscher, T. F. Endothelin receptor antagonists in congestive heart failure: a new therapeutic principle for the future? J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 37, 1493–1505 (2001). An elegant review that focuses on the role of ET in congestive heart failure. It examines the rationale of using ET-receptor blockers in this condition and provides results on their efficacy in animal models of heart failure. Current clinical trials are discussed.
McMurray, J. J., Ray, S. G., Adbullah, I., Dasgie, H. J. & Mortou, J. J. Plasma endothelin in chronic heart failure. Circulation 85, 1374–1379 (1992).
Rodeheffer, R. J., Lerman, A., Heublein, D. M. & Burnett, J. J. Incrased plasma concentrations of endothelin in congestive heart failure in humans. Mayo Clin. Proc. 67, 719–724 (1992).
Wei, C. M., Lerman, A. & Rodeheffer, R. J. Endothelin in human congestive heart failure. Circulation 89, 1580–1586 (1994).
Tuinenburg, A. E. et al. Comparison of plasma neurohormones in congestive heart failure patients with atrial fibrillation versus patients with sinus rhyhm. Am. J. Cardiol. 81, 1207–1210 (1998).
Pacher, R. et al. Prognostic impact of big endothelin-1 plasma concentrations compared with invasive hemodynamic evaluation in severe heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 27, 633–641 (1996).
McMurray, J. & Pfeffer, M. A. New therapeutic options in congestive heart failure: part I. Circulation 105, 2099–2106 (2002).
Seed, A., Love, M. P. & McMurray, J. Clinical experience with endothelin receptor antagonists in chronic renal failure. Heart Failure Rev. 6, 317–323 (2001). A description of completed and ongoing clinical trials with ET-receptor antagonists as therapeutics for chronic heart failure: acute and chronic haemodynamic effects.
Sütsch, G. et al. Short-term oral endothelin-receptor antagonist therapy in conventionally treated patients with symptomatic severe heart failure. Circulation 98, 2262–2268 (1998).
Packer, M. et al. Multicentre, double-blind, placebo controlled study of long-term endothelin blockade with bosentan in chronic heart failure — results of the REACH-1 trial. Circulation 98, I3 (1998).
Kalra, P. R., Moon, J. C. C. & Coats, A. J. S. Do results of the ENABLE (endothelin antagonist bosentan for lowering cardiac events in heart failure) study spell the end for non-selective endothelin antagonism in heart failure? Int. J. Cardiol. 85, 195–197 (2002). A critical analysis of the ENABLE trial that examines the future of ET-receptor antagonists.
Louis, A. et al. Clinical trials update: CAPRICORN, COPERNICUS, MIRACLE, STAF, RITZ-2, RECOVER, and RENAISSANCE and cachexia and cholesterol in heart failure. Highlights of the scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology, 2001. Eur. J. Heart Failure 3, 381–387 (2001).
Thackray, S. et al. Clinical trial updates: highlights of the scientific sessions of the American Heart Association Year 2000: ValHeFT, COPERNICUS, MERIT, CIBIS-II, BEST, AMIOVIRT, V-MAC, BREATHE, HEAT, MIRACL, FLORIDA, VIVA and the first human cardiac skeletal muscle myoblast transfer for heart failure. Eur. J. Heart Failure 3, 117–124 (2001).
Benigni, A. & Remuzzi, G. The renoprotective potential of endothelin receptor antagonist. Exp. Opin. Ther. Patents 7, 139–149 (1997).
Kohan, D. E. Endothelins in the kidney: physiology and pathophysiology. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 22, 493–510 (1993).
Benigni, A., Perico, N. & Remuzzi, G. Research on renal endothelin in proteinuric nephropathies dictates novel strategies to prevent progression. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 10, 1–6 (2001).
Benigni, A. et al. A specific endothelin subtype A receptor antagonist protects against injury in renal disease progression. Kidney Int. 44, 440–444 (1993).
Benigni, A. et al. Blocking both type A and B endothelin receptors in the kidney attenuates renal injury and prolongs survival in rats with remnant kidney. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 27, 416–423 (1996).
Nabokov, A. et al. Influence of specific and non-specific endothelin receptor antagonists on renal morphology in rats with surgical renal ablation. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 11, 514–520 (1996).
Benigni, A. et al. Renoprotective effect of contemporary blocking of angiotensin II and endothelin-1 in rats with membranous nephropathy. Kidney Int. 54, 353–359 (1998).
Nakamura, T., Ebihara, I., Tomino, Y. & Koide, H. Effect of a specific endothelin A receptor antagonist on mRNA levels for extracellular matrix components and growth factors in diabetic glomeruli. Diabetes 44, 895–899 (1995).
Benigni, A. et al. Unselective inhibition of endothelin receptors reduces renal dysfunction in experimental diabetes. Diabetes 47, 450–456 (1998).
Nakamura, T., Ebihara, I., Tomino, Y. & Koide, H. Effect of a specific endothelin A receptor antagonist on murine lupus nephritis. Kidney Int. 47, 481–489 (1995).
Lopez-Farre, A., Gomez-Garre, D., Barnabeu, F. & Lopez-Novoa, J. M. A role for endothelin in the maintenance of post ischemic renal failure on rats. J. Physiol. 444, 513–522 (1991).
Roubert, P. et al. Upregulation of renal endothelin receptor in glycerol-induced acute renal failure in the rat. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 22, S303–S305 (1993).
Nambi, P., Pullen, M., Jugus, M. & Gellai, M. Rat kidney endothelin receptor in ischaemia-induced acute renal failure. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 264, 345–348 (1993).
Mino, A. et al. Protective effect of selective endothelin receptor antagonist, BQ 123, in ischemic acute renal failure in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 221, 77–83 (1992).
Kusumoto, K. et al. Effects of a new endothelin antagonist, TAK 044, on post ischemic acute renal failure in rats. Life Sci. 55, 301–310 (1994).
Lloyd, I. Pharma Project Version 2.1 (PJB Publications, London, 1999).
Perico, N., Dadan, J. & Remuzzi, G. Endothelin mediates the renal vasoconstriction induced by cyclosporine in the rat. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1, 76–83 (1990).
Binet, I., Wallnöfer, A., Weber, C., Jones, R. & Thiel, G. Renal hemodynamics and pharmacokinetics of bosentan with and without cyclosporine A. Kidney Int. 57, 224–231 (2000).
Ruggenenti, P. et al. Calcium channel blockers protect transplant patients from cyclosporine-induced daily renal hypoperfusion. Kidney Int. 43, 706–711 (1993).
Bachmann-Brandt, S., Bittner, I., Neuhaus, P., Frei, U. & Schindler, R. Plasma levels of endothelin-1 in patients with the hepatorenal syndrome after successful liver transplantation. Transpl. Int. 13, 357–362 (2000).
Epstein, M. & Goligorsky, M. S. Endothelin and nitric oxide in hepatorenal syndrome: a balance reset. J. Nephrol. 10, 120–135 (1997).
Moore, K. et al. Plasma endothelin immunoreactivity in liver disease and the hepatorenal syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 327, 1774–1778 (1992).
Anand, R. et al. Endothelin is an important determinant of renal function in a rat model of acute liver and renal failure. Gut 50, 111–117 (2002).
Soper, C. P. R., Latif, A. B. & Bending, M. R. Amelioration of hepatorenal syndrome with selective endothelin-A antagonist. Lancet 347, 1842–1843 (1996).
Lerman, A. et al. Circulating and tissue endothelin immunoreactivity in advanced atherosclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 325, 997–1001 (1991).
d'Uscio, L. V., Barton, M., Shaw, S. & Luscher, T. F. Endothelin in atherosclerosis: importance of risk factors and therapeutic implications. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 35 (Suppl. 2), S55–S59 (2000).
Moreau, P. et al. Angiotensin II increases tissue endothelin and induces vascular hypertrophy: reversal by ETA receptor antagonist. Circulation 96, 1593–1597 (1997).
Barton, M. et al. Endothelin ETA receptor blockade restores NO-mediated endothelin dysfunction and inhibits atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 14367–14372 (1998).
Hsu, J. Y. & Pfahl, M. ET-1 expression and growth inhibition of prostate cancer cells: a retinoid target with novel specifity. Cancer Res. 58, 4817–4822 (1998).
Nelson, J. B. et al. Endothelin-1 production and decreased endothelin B receptor expression in advanced prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 56, 663–668 (1996). An interesting study on the role of ET and its receptors in the pathophysiology of metastatic prostate cancer. It opens an uncharted therapeutic area for ET-receptor antagonists.
Llach, F. & Bover, J. in The Kidney 5th edn (ed. Brenner, B. M.) 2187–2273 (Saunders, Philadelphia, 1996).
Kanesaka, Y. et al. Endothelin receptor antagonist prevents parathyroid cell proliferation of low calcium diet-induced hyperparathyroidism in rats. Endocrinol. 142, 407–413 (2000).
Ray, A., Hedge, L. G., Chugh, A. & Gupta, J. B. Endothelin-receptor antagonists: current and future perspectives. Drug Discov. Today 5, 455–464 (2000).
Honing, M. L. H., Yang, F., Padley, R., Morrison, P. J. & Rabelink, T. J. ABT-627, a selective ETA-receptor antagonist, reduces albuminuria in patients with diabetes mellitus. Proc. 6th Int. Conf. Endothelin Abstract 46 (1999).
Ohuchi, T. et al. Elevation of blood pressure by genetic and pharmacological disruption of ETB receptor in mice. Am. J. Physiol. 276, R1071–R1077 (1999).
Strachan, F. E. et al. Systemic blockade of the endothelin-B receptor increases peripheral vascular resistance in healthy men. Hypertension 33, 581–585 (1999).
Lipa, J. E. et al. Vasoconstrictor effect of endothelin-1 in human skin: role of ETA-receptors. Am. J. Physiol. 276, H359–H367 (1999).
Nangaku, M. et al. ETB receptor protects the tubulointerstitium in experimental thrombotic microangiopathy. Kidney Int. 62, 922–928 (2002).
Gariepy, C., Ohuchi, T., Williams, S. C., Richardson, J. A. & Yanagisawa, M. Salt-sensitive hypertension in endothelin-B receptor-deficient rats. J. Clin. Invest. 105, 925–933 (2000). A sophisticated experimental study, both for the methodology of targeted disruption of ET B receptors in the kidney and the demonstration of the role of ET B receptors in the regulation of fluid volume in the rat.
Cowburn, P. J. et al. Endothelin B receptors are functionally important in mediating vasoconstriction in the systemic circulation in patients with left ventricular systolic dysfunction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 33, 932–938 (1999). An accurate study underlining the functional relevance of ET B receptors in systemic vasoconstriction, at least in patients with chronic left- ventricular systolic dysfunction. Implications for therapeutic interventions with ET A - and ET B -receptor antagonists.
Rabelink, T. J., Stroes, E. S. G., Banten, K. P. & Morrison, P. Endothelin blockers and renal protection: a new strategy to prevent end-organ damage in CV diseases? Cardiovasc. Res. 39, 543–549 (1998).
Tzanidis, A. et al. Combined angiotensin and endothelin receptor blockade attenuates adverse cardiac remodeling post-myocardial infarction in the rat: possible role of transforming growth factor β1. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 33, 969–981 (2001).
Fraccarollo, D., Bauersachs, J., Kellner, M., Galuppo, P. & Ertl, G. Cardioprotection by long-term ETA-receptor blockade and ACE inhibition in rats with congestive heart failure: mono- versus combination therapy. Cardiovasc. Res. 54, 85–94 (2002).
Mulder, P. et al. Long-term survival and hemodynamics after endothelin-A receptor antagonism and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition in rats with chronic heart failure. Monotherapy versus combination therapy. Circulation 106, 1159–1164 (2002).
Ikeda, T. et al. Antihypertensive effects of a mixed endothelin-A- and -B-receptor antagonist, J-104132, were augmented in the presence of an AT1-receptor antagonist, MK-954. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 36 (Suppl.1), S337–S341 (2000).
Remuzzi, G., Ruggenenti, P. & Perico, N. Chronic renal diseases: renoprotective benefits of renin–angiotensin system inhibition. Ann. Intern. Med. 136, 604–615 (2002).
Ruggenenti, P., Schieppati, A. & Remuzzi, G. Progression, remission, regression of chronic renal diseases. Lancet 357, 1601–1608 (2001).
Murugesan, N. et al. Discovery of N-isoxazolyl biphenylsufonamides as potent dual angiotensin II and endothelin A receptor antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 45, 3829–3835 (2002).
Clozel, M. et al. Pathophysiological role of endothelin revealed by the first orally active endothelin receptor antagonist. Nature 365, 759–766 (1993).
Rossi, G. P., Seccia, T. M. & Nussdorfer, G. G. Reciprocal regulation of endothelin-1 and nitric oxide: relevance in the physiology and pathology of the cardiovascular system. Int. Rev. Cytol. 209, 241–272 (2001).
De Nucci, G. et al. Pressor effects of circulating endothelin are limited by its removal in the pulmonary circulation and by the release of prostacyclin and endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 85, 9797–9800 (1988).
Miller, W. L., Redfield, M. M. & Burnett, J. C. Jr. Integrated cardiac, renal and endocrine actions of endothelin. J. Clin. Invest. 83, 317–320 (1989).
Mortensen, L. H. & Fink, G. D. Hemodynamic effect of human and rat endothelin administration into conscious rats. Am. J. Physiol. 258, H362–H368 (1990).
Ito, H. et al. ET-1 induces hypertrophy with enhanced expression of muscle specific genes in cultured neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. Circ. Res. 69, 209–215 (1991).
Schiebinger, R. J. & Gomez-Sanchez, C. E. Endothelin: a potent stimulus of atrial natriuretic peptide secretion by superfused rat atria and its dependency on calcium. Endocrinology 127, 119–125 (1990).
Pernow, J. et al. Potent selective vasoconstrictor effects of endothelin in the pig kidney in vivo. Acta. Physiol. Scand. 134, 573–574 (1988).
King, A. J., Brenner, B. M. & Anderson, S. Endothelin: a potent renal and systemic vasoconstrictor peptide. Am. J. Physiol. 256, F1051–F1058 (1989).
Badr, K. F. et al. Mesangial cell, glomerular, and renal vascular responses to endothelin in the kidney. Elucidation of signal transduction pathways. J. Clin. Invest. 83, 336–342 (1989).
Edwards, R. M., Trizna, W. T. & Ohlstein, E. H. Renal microvascular effects of endothelin. Am. J. Physiol. 259, F217–F221 (1990).
Ishimura, E., Shouji, S., Nishizawa, Y., Morii, H. & Kashgarian, M. Regulation of mRNA expression for extracellular matrix (ECM) by cultured rat mesangial cells. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2, 546 (1991).
Chou, S.-Y., Dahhan, A. & Porush, J. C. Renal actions of endothelin: interaction with prostacyclin. Am. J. Physiol. 259, F645–F652 (1990).
Perico, N., Dadan, J., Gabanelli, M. & Remuzzi, G. Cyclooxygenase products and atrial natriuretic peptide modulate the renal response to endothelin. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 252, 1213–1220 (1990).
Garvin, J. L. & Sanders, K. Endothelin inhibits fluid and bicarbonate transport in part by reducing the Na+/K+-ATPase activity in the rat proximal straight tubule. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2, 976–982 (1991).
Garcia, N. H. & Garvin, J. L. Endothelin's biphasic effect on fluid absorption in the proximal straight tubule and its inhibitory cascade. J. Clin. Invest. 93, 2572–2577 (1994).
Eiam-Ong, S., Hilden, S. A., King, A. J., Johns, C. A. & Madias, N. E. Endothelin-1 stimulates the Na+/H+ and Na+/HCO3− transporters in rabbit renal cortex. Kidney Int. 42, 18–24 (1992).
Laghmani, K., Preisig, A. & Alpern, R. J. The role of endothelin in proximal tubule proton secretion and the adaptation to a chronic metabolic acidosis. J. Nephrol. 15 (Suppl. 5), S75–S87 (2002). An example of ETs as powerful effector peptides that control several aspects of kidney function, focused on the ET effects on proximal-tubule H+ secretion.
Plato, C. F. & Garvin, J. L. Endothelin inhibits chloride flux in the cortical thick ascending limb (cTALH) via activation of the ETB subtype receptor. FASEB J. 13, A724 (1999).
Zeidel, M. L., Brady, H. R., Kone, B. C., Gullans, S. R. & Brenner, B. M. Endothelin, a peptide inhibitor of Na+/K+-ATPase in intact renal tubular epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. 257, C1101–C1107 (1989).
Oishi, R., Nonoguchi, H., Tomita, K. & Marumo, F. Endothelin-1 inhibits AVP-stimulated osmotic water permeability in rat inner medullary collecting duct. Am. J. Physiol. 261, F951–F956 (1991).
Perico, N. et al. Endothelin induces diuresis and natriuresis in the rat by acting on proximal tubular cells through a mechanism mediated by lipoxygenase. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2, 57–69 (1991).
Schnermann, J., Lorenz, J. N., Briggs, J. P. & Keiser, J. A. Induction of water diuresis by endothelin in rats. Am. J. Physiol. 263, F516–F526 (1992).
Fagan, K. A., McMurtry, I. F. & Rodman, D. M. Role of endothelin-1 in lung disease. Respir. Res. 2, 90–101 (2001).
Goldie, R. G. & Fernandes, L. B. A possible mediator role for endothelin-1 in respiratory disease. Monaldi. Arch. Chest Dis. 55, 162–167 (2000).
Glassberg, M. K., Ergul, A., Wanner, A. & Puett, D. Endothelin-1 promotes mitogenesis in airway smooth muscle cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 10, 316–321 (1994).
Henry, P. J. Endothelin receptor and distribution and function in the airways. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 26, 162–167 (1999). An overview of recent advances in our understanding of the distribution and function of ET receptors within the airway wall and peripheral lung.
Shimura, S., et al. Endothelin regulation of mucous glycoprotein secretion from feline tracheal submucosal glands. Am. J. Physiol. 262, L208–L213 (1992).
Goldie, R. G., Knott, P. G., Carr, M. J., Hay, D. W. & Henry, P. J. The endothelins in the pulmonary system. Pulm. Pharmacol. 9, 69–93 (1996).
Fernandes, L. B., Henry, P. J., Rigby, P. J. & Goldie, R. G. Endothelin B (ETB) receptor-activated potentiation of cholinergic nerve-mediated contration in human bronchus. Br. J. Pharmacol. 118, 1873–1874 (1996).
Encabo, A., Ferrer, M., Marin, J., Villamor, J. & Balfagon, G. Vasoconstriction responses elicited in bovine cerebral arteries. Gen. Pharmacol. 23, 263–267 (1992).
Vigne, P., Lopez Farre, A. & Frelin, C. Na+/K+/Cl− cotransporter of brain capillary endothelial cells: properties and regulation by endothelins, hyperosmolar solutions, calyculin A, and interleukin-1. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 19925–19930 (1994).
Levin, E. R., Frank, H. J. L. & Pedram, A. Endothelin receptors on cultured fetal rat diencephalic glia. J. Neurochem. 58, 659–666 (1992).
Shichiri, M. et al. Effect of endothelin-1 on release of arginine-vasopressin from perifused rat hypothalamus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 163, 1332–1337 (1989).
Yamamoto, T. et al. Central effects of endothelin-1 on vasopressin release, blood pressure, and renal solute excretion. Am. J. Physiol. 262, E856–E862 (1992).
Kanyicksa, B., Burris, T. P. & Freeman, M. E. Endothelin-3 inhibits prolactin and stimulates LH, FSH and TSH secretion from pituitary cell culture. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 174, 338–343 (1991).
Fujii, Y. et al. Endothelin as an autocrine factor in the regulation of parathyroid cells. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 88, 4235–4239 (1991).
Douglas, S. A., Elliott, J. D. & Ohlstein, E. H. Regional vasodilation to endothelin-1 is mediated by a non-ETA receptor subtype in the anaesthetized rats: effect of BQ-123 on systemic haemodynamic responses. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 221, 315–324 (1992).
DiCarlo, V.S. et al. Endothelin-A receptor antagonist prevents and reverses chronic hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension in rat. Am. J. Physiol. 169, L690–L697 (1995).
Sakai, S., Miyauchi, T., Kobayashi, M., Yamaguchi, K. & Yasuro, S. Inhibition of myocardial endothelin pathway improves long-term survival in heart failure. Nature 348, 353–355 (1996).
Grover, G. J., Dzwonczyk, S. & Parham, C. S. The endothelin-1 receptor antagonist BQ-123 reduces infarct size in a canine model of coronary occlusion and reperfusion. Cardiovasc. Res. 27, 1613–1618 (1993).
Mino, N., et al. Protective affect of a selective endothelin receptor antagonist, BQ123, in ischemic acute renal failure in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 221, 77–83 (1992).
Okada, M. et al. Effects of a selective endothelin A-receptor antagonist, BQ-123, in salt-loaded stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 22, 763–768 (1995).
Büyükgebiz, O. et al. BQ-123, a specific endothelin (ETA) receptor antagonist, prevents ischemia–reperfusion injury in kidney transplantation. Transpl. Int. 9, 201–207 (1996).
Wada, A. et al. Comparison of the effects of selective endothelin ETA- and ETB-receptor antagonists in congestive heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 30, 1385–1392 (1997).
Yoshimura, M. et al. Different secretion patterns of atrial natriuretic peptide and brain natriuretic peptide in patients with congestive heart failure. Circulation 87, 464–469 (1993).
Watanabe, T. et al. Pharmacology of a non-selective ETA and ETB receptor antagonist, TAK-044, and the inhibition of myocardial infact size in rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 114, 949–954 (1995).
Kojima, M., Kusumoto, K., Fujiwara, S., Watanabe, T. & Fujino, M. Role of endogenous endothelin in the extension of myocardial infarct size studied with the endothelin receptor antagonist, TAK-044. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 26, 365–368 (1995).
Mitaka, C. et al. Improvement of renal dysfunction in dogs with endotoxemia by a nonselective endothelin receptor antagonist. Crit. Care Med. 27, 146–153 (1999).
d'Uscio, L. V., Shaw, S., Moreau, P., Barton, M. & Luescher, T. F. Blood pressure-independent effects of chronic selective ETA-receptor blockade in L-NAME-induced hypertension. FASEB J. 12, A98 (1998).
Barton, M. & Luscher, T. F. Endothelin antagonist for hypertension and renal disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 8, 549–556 (1999).
Li, J. S., Turgeon, A. & Schiffrin, E. L. Effect of chronic treatment with two different ET(A) selectve endothelin receptor antagonists on blood pressure and small artery structure of deoxycorticosterone acetate (DOCA)-salt hypertensive rats. Am. J. Hypertens. 11, 554–562 (1998).
Munter, K., Hergenroder, S. & Kirchengast, M. Endothelin-A receptor antagonist combined with hydralazine improves survival and renal function in hypertensive rats. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 31 (Suppl. 1), S245–S248 (1998).
Brochu, E. et al. Differential effects of endothelin-1 antagonist in erythropoietin-induced hypertension in renal failure. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 10, 1440–1446 (1999).
Ehmke, H., Faulhaber, J., Munter, K., Kirchengast, M. & Wiesner, R. J. Chronic ETA-receptor blockade attenuates cardiac hypertrophy independently of blood pressure effects in renovascular hypertensive rats. Hypertension 33, 954–996 (1999).
Prie, S., Leung, T. K., Cernacek, P., Ryan, J. W. & Dupuis, J. The orally active ET(A) receptor antagonist (+)-(S)-2-(4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-yloxy)-3-methoxy-3,3-diphenylpropionic acid (LU 135252) prevents the development of pulmonary hypertension and endothelial metabolic dysfunction in monocrotaline-treated rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 282, 1312–1318 (1997).
Dupuis, J. & Prie, S. The ET(A)-receptor antagonist LU 135252 prevents the progression of established pulmonary hypertension induced by monocrotaline in rats. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. Ther. 4, 33–39 (1999).
Birck, R. et al. Improvement of postischemic acute renal failure with the novel orally active endothelin-A-receptor antagonist LU 135252 in the rat. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 32, 80–86 (1998).
Orth, S. R. et al. Nephroprotection of an ET(A)-receptor blocker (LU 135252) in salt-loaded uninephrectomized stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertension 31, 995–1000 (1998).
Orth, S. R. et al. The ET(A) receptor blocker LU 135252 prevents chronic transplant nephropathy in the 'Fisher to Lewis' model. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 10, 387–391 (1999).
Underwood, D. C., Bochnowicz, S., Osborn, R. R., Luttmann, M. A. & Hay, D. W. Nonpeptide endothelin receptor antagonists. X. Inhibition of endothelin-1 and hypoxia-induced pulmonary pressor response in the guinea pig by the endothelin receptor antagonist, S 217242. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 283, 1130–1137 (1997).
Underwood, D. C. et al. Chronic hypoxia-induced cardiopulmonary changes in three rat strains: inhibition by the endothelin receptor antagonist S 217242. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 31, S453–455 (1998).
Pandey, S., Stewart, D., Dawood, F., Wen, W. H. & Liu, P. The endothelin blocker S-217242 preserves myocardial function in a chronic myocarditis model of heart failure. Circulation 92 (Suppl. 8), I61 (1995).
Chandra, S. et al. Application of serial in vivo magnetic resonance imaging to evaluate the efficacy of endothelin receptor antagonist S 217242 in the rat carotid artery model of neointima formation. Circulation 97, 50–58 (1998).
Barone, F. C., White, R. F., Elliott, J. D., Feuerstein, G. Z. & Ohlstein, E. H. The endothelin receptor antagonist S 217242 reduces cerebral focal ischemic brain injury. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 26 (Suppl. 3), S404–S407 (1995).
Hulpke-Wette, M. & Buchhorn, R. BMS-193884 and BMS-207940 Bristol-Myers Squibb. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 3, 1057–1061 (2002).
Miyauchi, T. et al. Endothelin-1 and right-sided heart failure in rats: effects of an endothelin receptor antagonist on the failing right ventricle. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 36 (Suppl. 1), S327–S330 (2000).
Saad, D. et al. The effects of endothelin-A receptor blockade during the progression of pacing-induced congestive heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 32, 1779–1786 (1998).
Clozel, M. et al. Pharmacological characterization of bosentan, a new potent orally active nonpeptide endothelin receptor antagonist. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 270, 228–238 (1994).
Li, J. S., Lariviere, R. & Schffrin, E. L. Effect of nonselective endothelin antagonist on vascular remodeling in deoxycorticosterone acetate-salt hypertensive rats. Evidence for a role of endothelin in vascular hypertrophy. Hypertension 24, 183–188 (1994).
Li, J. S., Schurch, W. & Schiffrin, E. L. Renal and vascular effects of chronic endothelin receptor antagonism in malignant hypertensive rats. Am. J. Hypertens. 9, 803–811 (1996).
Chillon, J. M., Heistad, D. D. & Baumbach, G. L. Effects of endothelin receptor inhibition on cerebral arterioles in hypertensive rats. Hypertension 27, 794–798 (1996).
Chen, S. J. et al. Endothelin receptor antagonist bosentan prevents and reverses hypoxic pulmonary hypertension in rats. J. Appl. Physiol. 79, 2122–2131 (1995).
Teerlink, J. R. et al. Role of endothelin in the maintenance of blood pressure in conscious rats with chronic heart failure. Acute effects of the endothelin receptor antagonist Ro 47-0203 (bosentan). Circulation 90, 2510–2518 (1994).
Mulder, P. et al. Role of endogenous endothelin in chronic heart failure: effect of long-term treatment with an endothelin antagonist in survival, hemodynamics, and cardiac remodeling. Circulation 96, 1976–1982 (1997).
Li, X. S., Wang, Q. D. & Pernow, J. Beneficial effect of the endothelin receptor antagonist bosentan on myocardial and endothelial injury following ischaemia/reperfusion in the rat. Eur. J Pharmacol. 283, 161–168 (1995).
Karam, H. et al. Role of endothelin in acute renal failure due to rhabdomyolysis in rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 274, 481–486 (1995).
Kramer, H. J., Schwarting, K., Backer, A. & Meyer-Lehnert, H. Renal endothelin system in obstructive jaundice: its role in impaired renal function of bile-duct ligated rats. Clin. Sci. 92, 579–585 (1997).
Oldroyd, S. D., Haylor, J. L. & Morcos, S. K. Bosentan, an orally active endothelin antagonist: effect on the renal response to contrast media. Radiology 196, 661–665 (1995).
Gomez-Garre, D. et al. An orally active ETA/ETB receptor antagonist ameliorates proteinuria and glomerular lesions in rats with proliferative nephritis. Kidney Int. 50, 962–972 (1996).
Herrero, I., Torras, J. & Riera, M. Prevention of cold ischemia-reperfusion injury by an endothelin receptor antagonist in experimental renal transplantion. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 8, A657 (1997).
Roux, S. et al. The role of endothelin in experimental cerebral vasospasm. Neurosurgery 37, 78–85 (1995).
Shigeno, T., Clozel, M., Sakai, S., Saito, A. & Goto, K. The effect of bosentan, a new potent endothelin receptor antagonist, on the pathogenesis of cerebral vasospasm. Neurosurgery 37, 87–90 (1995).
Wu, C. et al. Endothelin antagonists: substituted mesitylcarboxamides with high potency and selectivity for ET(A) receptors. J. Med. Chem. 42, 4485–4499 (1999).
Tilton, R. G. et al. Attenuation of pulmonary vascular hypertension and cardiac hypertrophy with sitaxsetan sodium, an orally active ET(A) receptor antagonist. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 13, 87–97 (2000).
Wu-Wong, J. R. Sitaxsentan (ICOS–Texas Biotechnology). Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs. 2, 531–536 (2001).
Clozel, M. et al. Pharmacology of tezosentan, new endothelin receptor antagonist designed for parenteral use. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 290, 840–846 (1999).
Amberg, W. et al. LU208075 and LU302146, two novel ETA-selective endothelin receptor antagonists: SAR of 3,3-diaryl propionoic acid derivatives. 6th Int. Conf. Endothelin P20 (1999).
Wassale, J. L. et al. Pharmacology of endothelin receptor antagonists ABT-627, ABT-546, A-182086 and A-192621: ex vivo and in vivo studies. Clin. Sci. (Lond.) 103 (Suppl. 1), 112S–117S (2002).
Norman, P. Atrasentan Abbott. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 3, 1240–1248 (2002).
Wu-Wong, J. R. S-0139. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 3, 1051–1056 (2002).
Shimizu, T., Kuroda, T., Ikeda, M., Hata, S. & Fujimoto, M. Potential contribution of endothelin to renal abnormalities in glycerol-induced acute renal failure in rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 286, 977–983 (1998).
Shimizu, T., Hata, S., Kuroda, T., Mihara, S. & Fujimoto, M. Different roles of two types of endothelin receptors in partial ablation-induced chronic renal failure in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 381, 39–49 (1999).
Kita, T. et al. Profiles of an intravenously available endothelin A-receptor antagonist, S-0139, for preventing cerebral vasospasm in a canine two-hemorrhage model. Life Sci. 63, 305–315 (1998).
Kon, V., Hunley, T. E. & Fogo, A. Combined antagonism of endothelin A/B receptors links endothelin to vasoconstriction whereas angiotensin II affects fibrosis. Transplantation 60, 89–95 (1995).
Ishikawa, A., Suzuki, K. & Fujita, K. Effect of the endothelin receptor antagonist, SB 209670 on cyclosporine-induced nephrotoxicity. Transplant Proc. 30, 40–42 (1998).
Blezer, E. L. et al. Early-onset but not late-onset endothelin-A-receptor blockade can modulate hypertension, cerebral edema, and proteinuria in stroke-prone hypertensive rats. Hypertension 33, 137–144 (1999).
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the Comitato 30 Ore per la Vita (Rome, Italy) and the Banca Popolare di Bergamo–Credito Varesino (Bergamo, Italy), A. Piccinelli for the invaluable assistance in drawing the figures and M. Passera for the help in preparing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Related links
Related links
DATABASES
Cancer.gov
LocusLink
FURTHER INFORMATION
Glossary
- WEIBEL–PALADE BODIES
-
Storage granules present in endothelial cells.
- MALIGNANT HAEMANGIOENDOTHELIOMA
-
A rare vascular neoplasm of endothelial-cell proliferation.
- AUTOCRINE
-
Describing an agent secreted from a cell that acts on the cell in which it is produced.
- PARACRINE
-
Describing an agent secreted from a cell that acts on other cells in the local environment.
- CARDIAC INDEX
-
The cardiac output divided by body surface area.
- BORG DYSPNOEA INDEX
-
A measure of perceived breathlessness on a scale of 0 to 10, with higher values indicating more severe dyspnoea.
- WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION FUNCTIONAL CLASS
-
A classification of pulmonary hypertension according to a modification of the New York Heart Association (NYHA) class, with higher classes indicating more severe disease.
- PROTEINURIA
-
The excretion rate of total proteins in urine.
- RENIN–ANGIOTENSIN SYSTEM
-
A key regulator of blood pressure. Renin cleaves the protein angiotensinogen to produce the inactive peptide angiotensin I. This is cleaved by the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) to give the peptide angiotensin II, which activates the angiotensin II type 1 (AT1) receptor, leading to various effects, including vasoconstriction.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Remuzzi, G., Perico, N. & Benigni, A. New therapeutics that antagonize endothelin: promises and frustrations. Nat Rev Drug Discov 1, 986–1001 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd962
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd962
This article is cited by
-
X-ray structures of endothelin ETB receptor bound to clinical antagonist bosentan and its analog
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (2017)
-
Activation mechanism of endothelin ETB receptor by endothelin-1
Nature (2016)
-
Drug Treatment of Hypertension: Focus on Vascular Health
Drugs (2016)
-
Endothelin Receptor Antagonists: New Hope for Renal Protection?
Current Hypertension Reports (2015)
-
How were new medicines discovered?
Nature Reviews Drug Discovery (2011)